Abstract
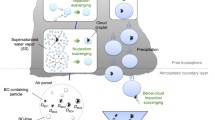
Wet deposition of acid-related substances takes place by two processes: precipitation scavenging and fog water impaction/sedimentation on natural surfaces. The relative importance of each deposition pathway depends on the frequency of occurrence of precipitation or fog, the magnitude of the event and the efficiency of pollutant removal by each mechanism. The latter, in turn, is governed by the type of cloud or fog, complex precipitation formation mechanisms and cloud-surface interactions. These factors are examined in the light of our current knowledge. Particular emphasis is placed on how cloud micro-physical as well as air and precipitation measurements, made aloft by aircraft and at the ground, have been used to further our knowledge of wet deposition mechanisms. Future research is needed to quantify the importance of the fog-water deposition pathway in eastern North America to better understand the interaction of gaseous pollutants with cloud and fog-water and to improve our knowledge of pollutant scavenging processes in mesoscale and synoptic weather systems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barrie, L.A.: 1985, J. Geophys. Res., 90, 5789.
Barrie, L.A. and Sirois, A.: 1986, J. Water Air Soil Poll., submitted.
Chameides, W.L.: 1984, J. Geophys. Res., 89, 4739.
Court, A. and Gerston, R.D.: 1966, Geograph. Rev., 56, 1966.
Daum, P.H., Schwartz, S.E., and Newman, L.: 1984, J. Geophys Res., 89, 1147.
Easter, R.C. and Hales, J.M.: 1983, Interpretations of the OSCAR data for reactive gas scavenging, Precipitation Scavenging, Dry Deposition and Resuspension, eds. Pruppacher, Semonin, Slinn, Elsevier, New York, pp 649–662.
Falconer, R.E. and Falconer, P.D.: 1980, J. Geophys. Res., 85, 7465.
Fuzzi, S., Orsi, G., and Mariotti, M.: 1983, J. Aerosol. Sci., 14, 135.
Galloway, J.N. and Whelpdale, D.M.: 1980, Atmospheric Environment, 14, 409.
Hegg, D.A., Hobbs, P.V., and Radke, L.F.: 1984a, Atmospheric Environment, 18, 1939.
Hegg, D.A., Rutledge, S.A., and Hobbs, P.V.: 1984b, J. Geophys. Res., 89, 7133.
Hidy, G.M. and Countess, R.: 1984, Combined analysis of air quality and precipitation chemistry data, Chapt. 3 in Deposition: Both Wet and Dry, Acid Precipitation Ser., Vol 4, ed. by H.H. Hicks, 37–62, Butterworth, Boston.
Hoffman, M.R.: 1985, American Chemical Society abstracts, 190th national Meeting, AMS Division of Environmental Chemistry, Chicago, Ill., 25, 10–11.
Hudson, J.G.: 1980, J. Atmos. Sci., 37, 1854.
Jensen, J.B. and Charlson, R.J.: 1984, Tellus, 36B, 367.
Jiusto, J.E.: 1981, Fog structure. From, Clouds: Their Formation, Optical Properties, and Effects, Academic Press, edited by P.V. Hobbs and A. Deepak, 187–235.
Joe, P.I.: 1985, private communication.
Lazrus, A.L., Haagensen, P.L., Kok, G.L., Huebert, B.J., Kreitzberg, C.W., Likens, G.E., Mohnen, V.A., Wilson, W.E., and Winchester, J.W.: 1983, Atmospheric Environment, 17, 581.
Leaitch, W.R., Strapp, J.W., Wiebe, H.A., ANauf, K.G., and Isaac, G.A.: 1985, J. Geophys. Res., submitted.
Lovett, G.M.: 1984, Atmospheric Environment, 18, 361.
Lovett, G.M. and Reiners, W.A.: 1986, J. Water Air Soil Poll., 1986.
Martin, J.J., Wang, P.K., and Pruppacher, H.R.: 1980, J. Colloid and Interf. Sci., 78, 44.
Merriam, R.A.: 1973, Water Resour. Res., 9, 1591.
Nagel, J.F.: 1956, Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 82, 452.
Parsons, D.B. and Hobbs, P.V.: 1983, J. Atmos. Sci., 40, 2377.
Pruppacher, H.R. and Klett,J.D.: 1978, Microphysics of clouds and precipitation, Reidel, Dordrecht, Boston, London, 714 pp.
Scott, B.C.: 1981, J. Appl. Met., 20, 619.
Shuttleworth, W.J.: 1977, Bound.-Layer Meteor., 12, 463.
Slinn, W.G.N.: 1984, Precipitation scavenging in Atmospheric Sciences and Power Production, edited by D. Randerson, Chapt. 12, US DOG Tech. Inf. Centre, Oak Ridge, Tennessee, 533–572.
Summers, P.W. and Barrie, L.A.: 1986, J. Water Air Soil Poll., 1986.
Tremblay, A. and Leighton, H.: 1986, J. Climate Appl. Meteor., in press.
Thorp, J.M. and Scott, B.C.: 1982, Atmospheric Environment, 16, 1763.
Wisniewski, J.: 1982, Water, Air, Soil Pollut., 17, 361.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barrie, L.A., Schemenauer, R.S. Pollutant wet deposition mechanisms in precipitation and fog water. Water Air Soil Pollut 30, 91–104 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00305178
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00305178