Abstract
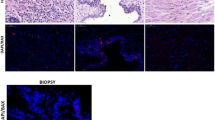
The Bcl-2 protein prolongs cell survival by overriding apoptosis. To explore the role of Bcl-2 in prostate tumorigenesis, immunoreactivity for Bcl-2 was examined in untreated and androgen-deprived tumours and lymph node metastasis. Following the transurethral resection, 150 untreated patients were maintained under surveillance until death or for a minimum of 11 years, and castration was performed at symptomatic progression. The Bcl-2 index (BI) was defined as the percentage of immunoreactive cells in a tumour. The mean BI was 12 in the untreated tumours, and BI was significantly higher in high-grade tumours, mean BI 17, than in low-grade tumours, mean BI 6. There was no correlation between BI and stage or metastatic disease, nor did BI predict cancer-specific survival. In 16 androgen-deprived, but non-relapsed tumours, the mean BI was 54, at a mean time of 22 months after castration, indicating a permanent increase of Bcl-2 protein expression after androgen withdrawal. In six patients, tissues from the prostate tumour and obturator lymph node metastasis were available. Four primary tumours immunostained for Bcl-2, but only one metastasis stained. Foci of high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PIN) were present in 44 of the 150 untreated tumours. All PIN foci were intensely immunoreactive for Bcl-2, and mean BI was 79, suggesting that Bcl-2 protein expression is associated with early prostate tumorigenesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berges RR, Vukanovic J, Epstein JI, CarMichel M, Cisek L, Johnson DE, Veltri RW, Walsh PC, Isaacs JT (1995) Implication of cell kinetic changes during the progression of human prostatic cancer. Clin Cancer Res 1:473
Brawer MK (1992) Prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia: a premalignant lesion. Hum Pathol 23:242
Bronner MP, Culin C, Reed JC, Furth EE (1995) The bcl-2 proto-oncogene and the gastrointestinal epithelial tumor progression model. Am J Pathol 146:20
Cambell MJ, Machin D (1993) Medical Statistics. Wiley, Chichester
Castle VP, Heidelberger KP, Bromberg J, Ou XG, Dole M, Nunez G (1993) Expression of the apoptosis-suppressing protein bcl-2 in neuroblastoma is associated with unfavorable histology and N-myc amplification. Am J Pathol 143:1543
Chiarodo A (ed) (1991) Prostate cancer working group: National Cancer Institute round table on prostate cancer: future research directions. Cancer Res 51:2498
Colombel M, Symmans F, Gil S, Otoole KM, Chopin D, Benson M, Olsson CA, Korsmeyer S, Buttyan R (1993) Detection of the apoptosis-suppressing oncoprotein bcl-2 in hormone-refractory human prostate cancers. Am J Pathol 143:390
Craig RW (1995) The bcl-2 gene family. Semin Cancer Biol 6:35
Ferguson J, Zincke H, Ellison E, Bergstrahl E, Bostwick DG (1994) Decrease of prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia following androgen deprivation therapy in patients with stage T3 carcinoma treated by radical prostatectomy. Urology 44:91
Gompel A, Sabourin JC, Martin A, Yaneva H, Audouin J, Decroix Y, Poitout P (1994) Bcl-2 expression in normal endometrium during the menstrual cycle. Am J Pathol 144:1195
Grönberg H, Bergh A, Damber J-E, Jonnson H, Lenner P, Ångström T (1994) Prostate cancer in northern Sweden. Incidence, survival and mortality in relation to tumour grade. Acta Oncol 33:359
Hockenberry D, Nunez G, Milliman C, Schreiber RD, Korsmeyer SJ (1990) Bcl-2 is an inner mitochondrial membrane protein that blocks programmed cell death. Nature 348:334
Hockenberry DM, Zutter M, Hickey W, Nahm M, Korsmeyer SJ (1991) Bcl-2 protein is topographically restricted in tissues characterized by apoptotic cell death. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:6961
Joensuu H, Pylkkanen L, Toikkanen S (1994) Bcl-2 protein expression and long-term survival in breast cancer. Am J Pathol 145:1191
Krajewski S, Blomqvist C, Franssila K, Krajewska M, Wasenius V-M, Niskanen E, Nordling S, Reed JC (1995) Reduced expression of proapoptotic gene bax is associated with poor response rates to combination chemotherapy and shorter survival in women with metastatic breast adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res 55:4471
Lauwers GY, Scott GV, Hendricks J (1994) Immunohistochemical evidence of aberrant bcl-2 protein expression in gastric epithelial dysplasia. Cancer 73:2900
Leek RD, Kaklamanis L, Pezzella F, Gatter KC, Harris AL (1994) bcl-2 in normal human breast and carcinoma, association with oestrogen receptor-positive, epidermal growth factor receptor-negative tumours and in situ cancer. Br J Cancer 69:135
Lu-Yao GL, Greenberg ER (1994) Changes in prostate cancer incidence and treatment in USA. Lancet 343:251
McDonnell TJ, Nunez G, Platt FM, Hockenberry D, London L, McKearn JP, Korsmeyer SJ (1990) Deregulated Bcl-2-immunoglobulin transgene expands a resting but responsive immunoglobulin M and D expressing B-cell population. Mol Cell Biol 10:1901
McDonnell TJ, Troncoso P, Brisbay SM, Logothetis C, Chung LWK, Hsieh JT, Tu SM, Campbell ML (1992) Expression of the protooncogene bcl-2 in the prostate and its association with emergence of androgen-independent prostate cancer. Cancer Res 52:6940
McNeal JE, Bostwick DG (1986) Intraductal dysplasia: a premalignant lesion of the prostate. Hum Pathol 17:64
Mostofi FK, Sesterhenn IA, Sobin LH (1980) International histological classification of prostate tumours. In: Mostofi FK (ed) International histological classification of prostate tumours. WHO, Geneva
Norusis MJ (1993) SPSS for Windows, SPSS Inc, Chicago
Pilotti S, Collini P, Rilke F, Cattoretti G, Delbo R, Pierotti MA (1994) bcl-2 protein expression in carcinomas originating from the follicular epithelium of the thyroid gland. J Pathol 172:337
Raffo AJ, Perlman H, Chen M-W, Day ML, Streitman JS, Buttyan R (1995) Overexpression of bcl-2 protects prostate cancer cells from apoptosis in vitro and confers resistance to androgen depletion in vivo. Cancer Res 55:4438
Reed JC (1995) Bcl-2: prevention of apoptosis as a mechanism of drug resistance. Hematol/Oncol Clin North Am 9:451
Rinker-Schaeffer CW, Isaacs WB, Isaacs JT (1993) Molecular and cellular markers for metastatic prostate cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev 12:3
Sabourin JC, Martin A, Baruch J, Truc JB, Gompel A, Poitout P (1994) bcl-2 expression in normal breast tissue during the menstrual cycle. Int J Cancer 59:1
Shi SR, Key ME, Kalra KL (1991) Antigen retrieval in formalinfixed paraffin embedded tissues: an enhancement method for immunohistochemical staining based on microwave oven heating of tissue sections. J Histochem Cytochem 39:741
Silvestrini R, Veneroni S, Daidone MG, Benini E, Boracchi P, Mezzetti M, Di Fronzo G, Rilke F, Veronesi U (1994) The Bcl-2 protein: a prognostic indicator strongly related to p53 protein in lymph node-negative breast cancer patients. J Natl Cancer Inst 86:499
Sinicrope FA, Ruan SB, Cleary KR, Stephens LC, Lee JJ,Levin B (1995) bcl-2 and p53 oncoprotein expression during colorectal tumorigenesis. Cancer Res 55:237
Tron VA, Krajewski S, Klein-Parker H, Li G, Ho VC, Reed JC (1995) Immunohistochemical analysis of bcl-2 protein regulation in cutaneous melanoma. Am J Pathol 146:643
UICC (Union Internationale Contre le Cancer) (1978) TNM classification of malignant tumours, 2 edn. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Vaux D, Cory S, Adams J (1988) Bcl-2 gene promotes haematopoetic cell survival and co-operates with c-myc to immortalize B cells. Nature 335:440
Viale G, Roncalilli M, Grimelius L, Graziani D, Wilander E, Johansson H, Bergholm U, Coggi G (1995) Prognostic value of Bcl-2 immunoreactivity in medullary thyroid carcinoma. Hum Pathol 26:945
Westin P, Stattin P, Damber J-E, Bergh A (1995) Castration therapy rapidly induces apoptosis in a minority and decreases cell proliferation in a majority of human prostatic tumors. Am J Pathol 146:1368
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stattin, P., Damber, J.E., Karlberg, L. et al. Bcl-2 immunoreactivity in prostate tumorigenesis in relation to prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia, grade, hormonal status, metastatic growth and survival. Urol. Res. 24, 257–264 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00304774
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00304774