Summary
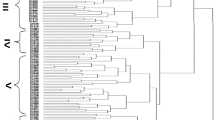
The yield data of 39 cultivars of diverse commercial classes of beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) planted in seven locations in Michigan were subjected to cluster and canonical variate analyses. The essential findings and conclusions can be summarized as follows: (1) Cluster analysis classified the cultivars into sub-sets or clusters almost identically coinciding with their commercial class designation. Canonical variate analysis completely confirmed the sub-groupings. Within class similarities were attributed to a narrow genetic base resulting from a common genetic relationship, or at least sharing of a common gene pool. (2) It was found that two clusters could possess almost identical mean (cluster mean) yields, and deviate in opposite directions over the same range of environments. (3) When total genotype × environmental interaction variance was partitioned into between and within clusters, the cluster × environment portion constituted 80% of the total. (4) These results imply that if the behavior of a given cultivar across a series of environments is known, the behavior of all other members of the class across a similar range of environments would be predictable.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature
Abou-El-Fittouh, H.A.; Rawlings, J.O.; Miller, P.A. (1969): Classification of environments to control genotype by environment interactions with an application to cotton. Crop Sci. 9, 135–140
Adams, M.W. (1977): An estimation of homogeneity in crop plants, with special reference to genetic vulnerability in the dry bean, Phaseolus vulgaris L. Euphytica 26, 665–679
Avley, N.G.; Banfield, C.F.; Baxter, R.I.; Gower, J.C.; Krzanowski, W.J.; Lane, P.W.; Leech, P.K.; Nelder, J.A.; Payne, R.W.; Phelps, K.M.; Rogers, C.E.; Ross, G.V.S.; Simpson, H.R.; Todd, A.D.; Wedderburn, R.M.W.; Wilkinson, G.N. (1977): GENSTAT: A General Statistical Program. Rothamsted, England: Rothamsted Exper. Stn., Stat. Dep.
Blackith, R.E.; Reyment, R.A. (1971): Multivariate Morphometrics. New York: Acad. Press
Byth, D.E.; Eisemann, R.L.; DeLacy, I.H. (1976): Two-way pattern analysis of a large data set to evaluate genotypic adaptation. Heredity 37, 215–230
Eberhart, S.A.; Russell, W.A. (1966): Stability parameters for comparing varieties. Crop Sci. 6, 36–40
Finlay, K.W.; Wilkinson, G.N. (1963): The analysis of adaptation in a plant breeding programme. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 14, 742–754
Freemann, G.H. (1973): Statistical methods for the analysis of genotype — environment interactions. Heredity 31, 339–354
Ghaderi, A.; Everson, E.H.; Cress, C.E. (1980): Classification of environments and genotypes in wheat. Crop Sci. 20, 707–710
Gollob, H.F. (1968): A statistical model which combines features of factor analytic and analysis of variance techniques. Psychometrica 33, 73–116
Klecka, W.R. (1975): Discriminant analysis. In: SPSS, Statistical Package for Social Sciences (eds. Nie, N.H.; Hull, C.H.; Jenkins, J.; Steinbrenner, K.; Bent, D.H.), pp. 434–467. New York: McGraw Hill
Lin, Chuang Sheng; Thompson, B. (1975): An empirical method of grouping genotypes based on linear function of the genotype — environment interaction. Heredity 34, 255–263
Mandel, J. (1961): Non-additivity in two-way analysis of variance. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 56, 878–888
Mandel, J. (1972): Principal components, analysis of variance and data structure. Stat. Neerl. 26, 119–129
Muntgomery, V.E.; Shorter, R.; Byth, D.E. (1974): Genotype × environment interactions and environmental adaptation. I. Pattern analysis-application to soybean populations. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 25, 59–72
Shorter, R.; Byth, D.E.; Muntgomery, V.E. (1977): Genotype × environment interactions and environmental adaptation. II. Assessment of environmental contributions. Austr. J. Agric. Res. 28, 233–235
Verma, M.M.; Chahal, G.S. (1978): Limitations of conventional regression analysis, a proposed modification. Theor. Appl. Genet. 53, 89–91
Wishart, D. (1978): Clustan User Manual. Inter-University/ Research Council Series, Report No. 47. Edinburgh University
Yates, F.; Cochran, W.G. (1938): The analysis of groups of experiments. J. Agric. Sci. 28, 556–580
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by R. W. Allard
Journal Article No. 10329 of the Michigan Agricultural Experiment Station
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghaderi, A., Adams, M.W. & Saettler, A.W. Environmental response patterns in commercial classes of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Theoret. Appl. Genetics 63, 17–22 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00303484
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00303484