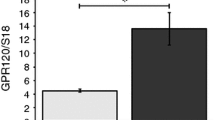
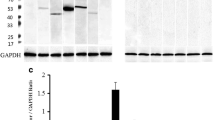
Summary
The localization of luteinizing hormone beta (LHβ)-mRNA was studied by in situ hybridization in the pars tuberalis of sheep using a homologous sheep double-stranded 32P-or 35S-cDNA. The labelled cDNA probe detected one mRNA sequence in the pars tuberalis by Northern blot analysis; this sequence was similar to that detected in the pituitary. In situ, the labelling of LHβ-mRNA in the horizontal and sagittal tissue sections was found throughout the pars tuberalis. This labelling was prevented by adding an excess of cold probe or treating the sections by ribonuclease before in situ hybridization. Controls showed a labelling in the pars distalis, but not in the median eminence, hypothalamus, cerebral cortex and liver sections. Double labelling by using a specific LHβ-antiserum indicated that the labelling of LHβ-mRNA appeared more intense in LH-containing cells that were found only in the ventral part of the pars tuberalis. These results suggest that the entire pars tuberalis is able to produce the LHβ subunit, but that the level of translation greatly varies according to the location of the cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguado LI, Hancke JL (1982) Luteinizing hormone content of the pars tuberalis of the hypophysis of neonatally androgenized female rats. Experientia 38:975–977
Aguado LI, Hancke JL, Rodriguez S, Rodriguez EM (1982) Changes in the luteinizing hormone content of the rat pars tuberalis during the estrus cycle and after lesions in the preoptic area. Neuroendocrinology 35:178–185
Antunes JL, Carmel PW, Zimmermann EA, Ferin M (1979) The pars tuberalis of the rhesus monkey secretes luteinizing hormone. Brain Res 166:49–55
Carmichael GC, McMaster GK (1980) The analysis of nucleic acids in gels using glyoxal and acridine orange. Methods Enzymol 65:380–388
Chafuen S, Cannata MA (1979) The adenohypophysial hormone content of the rat pars tuberalis. Experientia 35:1404–1405
Childs GV, Lloyd JM, Unabia G, Gharib SD, Wierman ME, Chin WW (1987) Detection of luteinizing hormone β messenger ribonucleic acid (RNA) in individual gonadotropes after castration: use of a new in situ hybridization method with a photobiotinylated complementary RNA probe. Mol Endocrinol 1:926–932
Childs GV, Unabia G, Wierman ME, Gharib SD, Chin WW (1990) Castration induces time-dependent changes in the follicle-stimulating hormone β-subunit messenger ribonucleic acid-containing gonadotrope cell population. Endocrinology 126:2205–2213
Counis R, Corbani M, Bérault A, Théoleyre M, Jansem de Almeida Catanho MT, Jutisz M (1981) Une microméthode permettant de préparer et de traduire l'acide ribonucléique messager à partir de cellules adénohypophysaires en culture. CR Acad Sci [III] 293:115–118
Dacheux F, Dubois MP (1976) Ultrastructural localization of prolactin, growth hormone and luteinizing hormone by immunocytochemical techniques in the bovine pituitary. Cell Tissue Res 174:245–260
D'Angelo-Bernard G, Moumni M, Jutisz M, Counis R (1990) Cloning and sequence analysis of the cDNA for the precursor of the beta subunit of ovine luteinizing hormone. Nucleic Acids Res 18:2175
Dellmann H-D, Stoeckel ME, Hindelang-Gertner C, Porte A, Stutinsky F (1974) A comparative ultrastructural study of the pars tuberalis of various mammals, the chicken and the newt. Cell Tissue Res 148:313–329
Dubois MP, Reviers M-M de, Courot M (1971) Activité gonadotrope de l'éminence médiane après hypophysectomie chez le rat. Etude en immunofluorescence. Exp Anim 4:213–226
Gross DS (1984) The mammalian hypophysial pars tuberalis: a comparative immunocytochemical study. Gen Comp Endocrinol 56:283–298
Gross DS, Page RB (1979) Luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone production in the pars tuberalis of hypophysectomized rats. Am J Anat 156:285–291
Gross DS, Turgeon JL, Waring DW (1984) The ovine pars tuberalis: a naturally occurring source of partially purified gonadotropes which secrete luteinizing hormone in vitro. Endocrinology 114:2084–2091
Leibold EA, Munro HN (1988) Cytoplasmic protein binds in vitro to a highly conserved sequence in the 5′untranslated region of ferritin heavy- and light-subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:2171–2175
Levine M, Rubin GM, Tjian R (1984) Human DNA sequences homologous to a protein coding region conserved between homeotic genes of Drosophila. Cell 38:667–673
McDonald PM, Struhl G (1986) A molecular gradient in early Drosophila embryos and tis role in specifying the body plan. Nature 324:537–545
Papavasiliou SS, Zmeili S, Herbon L, Duncan-Weldon J, Marshall JC, Landefeld TD (1986) α and luteinizing hormone β messenger ribonucleic acid (RNA) of male and female rats after castration: quantitation using an optimized RNA dot blot hybridization assay. Endocrinology 119:691–698
Reviers M-M de, Ravault JP, Tillet Y, Pelletier J (1989) Melatonin binding sites in the sheep pars tuberalis. Neurosci Lett 100:89–93
Simmons DM, Voss JW, Ingraham HA, Holloway JM, Broide RS, Rosenfeld MG, Swanson LW (1990) Pituitary cell phenotypes involve cell-specific Pit-1 mRNA translation and synergistic interactions with other classes of transcription factors. Genes Dev 4:695–711
Starzec A, Moumni M, D'Angelo-Bernard G, Lerrant Y, Jutisz M, Counis R (1989) Cyclic AMP enhances gene expression, synthesis and release of newly synthesized alpha and luteinizing hormone beta subunits in cultured rat anterior pituitary cells. Neurochem Int 15:259–264
Stoeckel ME, Porte A (1984) Fine structure and development of the pars tuberalis in mammals. In: Motta PM (ed) Ultrastructure of endocrine cells and tissues. Martinus Nijhoff, The Hague, pp 29–38
Stutinsky F, Porte A, Stoeckel ME (1964) Sur les modifications ultrastructurales de la pars tuberalis du rat après ultrastructurales de la pars tuberalis du rat après hypophysectomie. CR Acad Sci [III] 259:1765–1767
Tillet Y, Thibault J (1987) Early ontogeny of catecholaminergic structures in the sheep brain. Immunohistochemical study. Anat Embryol 177:173–181
Tillet Y, Pelletier J, Tramu G, Reviers M-M de (1990) The sheep pars tuberalis: an immunohistochemical study. Demonstration of the presence of glycoprotein and lipotropin hormones. Histochemistry 94:403–408
Watanabe YG (1986) A comparative in vitro study on LHRH responsiveness of LH cells of the pars tuberalis and pars distalis. Cell Tissue Res 245:369–375
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pelletier, J., Counis, R., de Reviers, MM. et al. Localization of luteinizing hormone β-mRNA by in situ hybridization in the sheep pars tuberalis. Cell Tissue Res 267, 301–306 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00302968
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00302968