Abstract
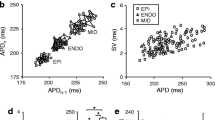
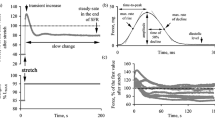
The effect of action potential duration and elevated cytosolic sodium concentration on the forcefrequency relationship in isolated rabbit, guinea pig and rat papillary muscle preparations was studied. Shortening of action potential duration in guinea pig and rabbit from 150–200 ms to values characteristic of rat (20–40 ms), using the K(ATP) channel activator levkromakalim (15 μmol·l−1), markedly reduced the force of contraction and converted the positive force-frequency relationship into negative one at longer pacing cycle lengths. This conversion was greatly enhanced in the presence of acetylstrophanthidin (0.2–1 μmol·l−1), an inhibitor of the Na-K pump. Acetylstrophanthidin (1 μmol·l−1) alone, however, had no effect on the forcefrequency relationship. Prolongation of action potential duration in rat with inhibitors of cardiac K channels (4-aminopyridine [10 mmol·l−1] plus tetraethylammonium [2 mmol·l−1) increased the force of contraction and abolished the negative force-frequency relationship observed in rat at longer pacing-cycle lengths. It is concluded that both action potential duration and cytosolic sodium concentration are major determinants of the force-frequency relationship in mammalian myocardium.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AC :
-
acetylstrophanthidin
- APD :
-
action potential duration
- APD 50 and APD 90 :
-
action potential duration measured at 50% and 90% level of repolarization, respectively
- SR :
-
sarcoplasmic reticulum
References
Attwell D, Cohen I, Eisner D, Ohba M, Ojeda C (1979) The steadystate TTX-sensitive (“window”) sodium current in cardiac Purkinje fibers. Pflügers Arch 379: 137–142
Bers DM (1991) Excitation-concentration coupling and contractile force. Kluwer, Dordrecht
Carmeliet E (1987) Slow inactivation of the sodium current in rabbit cardiac Purkinje fibers. Pflügers Arch 408: 18–26
Cohen CJ, Fozzard HA, Sheu SS (1982) Increase in intracellular sodium activity during stimulation in mammalian cardiac muscle. Circ Res 50: 651–662
Egan TM, Noble D, Noble S, Powell T, Spindler AJ, Twist VW (1989) Sodium-calcium exchange during the action potential in guinea-pig ventricular cells. J Physiol (London) 411: 639–661
Eisner DA, Lederer WJ (1985) Na-Ca exchange: Stochiometry and electrogenicity. Am J Physiol 248: C189–C202
Escande D, Thuringer D, LeGuern S, Courteix J, Laville M, Caveno I (1989) Potassium channel openers act through an activation of ATP sensitive K+ channels in guinea-pig cardiac myocytes. Pflügers Arch 414: 669–675
Hirano Y, Moscussi A, January CT (1992) Direct measurement of L-type Ca2+ window current in heart cells. Circ Res 70: 445–455
Morad M, Trautwein W (1968) The effect of the duration of the action potential on concentration in the mammalian heart muscle. Pflügers Arch 299: 66–82
Negretti N, Varró A, Eisner DA (1996) Estimate of net calcium fluxes and sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium content during systole in rat ventricular myocytes. J Physiol (London) (in press)
Ochi R, Nishiye H (1974) Effect of intracellular tetraethylammonium ion on action potential in the guinea pig's myocardium Pflügers Arch 348: 305–316
Schwartz A, Lindenmayer GE, Allen JC (1975) The sodium-potassium adenosine triphosphatase: pharmacological, physiological and biochemical aspects. Pharmacol Rev 37: 1–137
Shattock MJ, Bers DM (1989) Rat versus rabbit ventricle: Ca flux and intracellular Na assessed by ion-selective microelectrodes. Am J Physiol 256: C813–C822
Spurgeon HA, Isenberg G, Talo A, Stern MD, Capogrossi MC, Lakatta EG (1988) Negative staircase in cytosolic Ca2+ in rat myocytes is modulated by depolarization duration. Biophys J 53: 601A
Stanfield PR (1983) Tetraethylammonium ions and the potassium permeability of excitable cells. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol 97: 1–67
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Szigligeti, P., Pankucsi, C., Bányász, T. et al. Action potential duration and force-frequency relationship in isolated rabbit, guinea pig and rat cardiac muscle. J Comp Physiol B 166, 150–155 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00301179
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00301179