Abstract
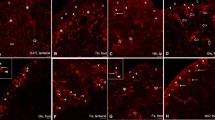
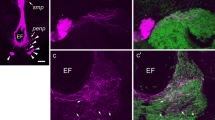
The light yellow neuropeptidergic cell system of the basommatophoran snail Lymnaea stagnalis is homologous to the R3-R14 system of the opisthobranch Aplysia californica, and produces three different neuropeptides. Systems homologous to the light yellow cells of Lymnaea stagnalis have been investigated morphologically in two Basommatophora (Lymnaea ovata, Bulinus truncatus) and three Stylommatophora (Helix aspersa, Cepaea nemoralis, Deroceras reticulatum). To this end, an antibody to synthetic light-yellow-cell peptide-II and oligonucleotides to mRNAs encoding parts of peptide-I and peptide-III, were used. The in situ hybridization probes gave negative results. On the other hand, neuronal cell clusters were observed in the central nervous system of all specias studied by immunocytochemistry. These clusters were located in the ganglia of the visceral complex. The neurons project axons into all nerves of these ganglia, especially into the pallial nerves, into the connective tissue of the central nervous system, and into the neuropile of various ganglia. The morphology of the systems is similar to that of the light-yellow-cell system of Lymnaea stagnalis. In all species, the wall of the aorta was innervated by immunoreactive axons. Peripheral innervation by the light-yellow-cell system was investigated in Helix aspersa and Deroceras reticulatum. Serial and alternate sections of whole snails were studied. Reconstructions were made of the heart-kidney-lung complex of these animals. In both species, the muscular vessels of the pulmonary system at the right side of the body were strongly innervated by immunoreactive axons. Furthermore, immunopositive innervation was observed to muscles in the secondary ureter-pneumostome area. The light-yellow-cell system of pulmonates is thus probably involved in the regulation of blood pressure and urine release.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bekius R (1972) The circulatory system of Lymnaea stagnalis (L.) Neth J Zool 22:1–58
Boer HH, Algera NH, Lommerse AW (1973) Ultrastructure of possible sites of ultrafiltration in some Gastropoda, with particular reference to the auricle of the freshwater prosobranch Viviparus viviparus L. Z Zellforsch 143:329–341
Boer HH, Roubos EW, Dalen H van, Groesbeek JRFT (1977) Neurosecretion in the basommatophoran snail Bulinus truncatus (Gastropoda, Pulmonata). Cell Tissue Res 176:56–67
Boer HH, Montagne-Wajer C, Minnen J van, Ramkema M, Boer P de (1992) Functional morphology of the neuroendocrine sodium influx-stimulating peptide system of the pond snail Lymnaea stagnalis, studied by in situ hybridization and immunocytochemistry. Cell Tissue Res 268:559–566
Boer HH, Montagne-Wajer C, Smith FG, Parish DC, Ramkema MD, Hoek RM, Minnen J van, Benjamin PR (1994) Functional morphology of the light yellow cell and yellow cell (sodium influx-stimulating peptide) neuroendocrine systems of the pond snail Lymaea stagnalis. Cell Tissue Res 275:361–368
Bouillon J, Delhaye W (1970) Histophysiologie comparée des cellules rénales de quelques gastéropodes pulmonés terrestres et dulcaquicoles. Ann Sci Nat Zool Biol Animale 12:1–26
Campanelli JT, Scheller RH (1987) Histidine-rich basic peptide: a cardioactive neuropeptide from Aplysia neurons R3-R14. J Neurophysiol 57:1201–1209
Delhaye W, Bouillon J (1972) L'évolution et l'adaptation de l'organe excréteur chez les mollusques gastéropodes pulmonés. Bull Biol CVI:45–77
Drozdowski A (1970) Vergleichende Studien über die Lungenmorphologie bestimmter Schneckenarten (Gastropoda, Pulmonata). Zool Pol 20:217–256
Hoek RM, Li KW, Minnen J van, Geraerts WPM (1992) Chemical characterization of a novel peptide from the neuroendocrine light yellow cells of Lymnaea stagnalis. Mol Brain Res 16:71–74
Kerkhoven RM, Croll RP, Ramkema MD, Minnen J van, Bogerd J, Boer HH (1992) The VD1/RPD2 neuronal system in the central nervous system of the pond snail Lymnaea stagnalis studied by in situ hybridization and immunocytochemistry. Cell Tissue Res 267:551–559
Martin AW, Stewart DM, Harrison FM (1965) Urine formation in a pulmonate land snail, Achatina fulica. J Exp Biol 42:99–123
Meester I, Ramkema MD, Minnen J van, Boer HH (1992) Differential expression of four genes encoding molluscan insulin-related peptides in the central nervous system of the pond snail Lymnaea stagnalis. Cell Tissue Res 269:183–188
Minnen J van, Schallig HDFH (1990) Demonstration of insulin-related substances in the central nervous system of pulmonates and Aplysia californica. Cell Tissue Res 260:381–386
Minnen J van, Schallig HDFH, Ramkema M (1992) Identification of putative egg-laying hormone containing neuronal systems in gastropod molluscs. Gen Comp Endocrinol 86:96–102
Nagle GT, Knock SL, Painter SD, Blankenship JE, Fritz RR, Kurosky A (1989) I. Aplysia californica neurons R3-R14: primary structure of the myoactive histidine-rich basic peptide and peptide-I. Peptides 10:849–857
Nambu JR, Taussig R, Mahon AC, Scheller RH (1983) Gene isolation with cDNA probes from identified Aplysia neurons: neuropeptide modulators of cardiovascular physiology. Cell 35:47–56
Price CH, McAdoo JT (1979) Anatomy and ultrastucture of the axons and terminals of neurons R3-R14 in Aplysia. J Comp Neurol 188:647–677
Rittenhouse AR, Price CH (1986 a) Anatomical and elctrophysiological study of multitransmitter neuron R14 of Aplysia. J Comp Neurol 247:447–456
Rittenhouse AR, Price CH (1986 b) Electrophysiological and antomical identification of the peripheral axons and target tissues of Aplysia neurons R3-14 and their status as multifunctional multimessenger neurons. J Neurosci 6:2071–2084
Rolle G (1907) Die Renopericardialverbindung bei einheimischen Nacktschnecken und anderen Pulmonaten. Jena Z Naturwiss 43:373–416
Sawada M, Blankenship JE, McAdoo DJ (1981) Neural control of a molluscan blood vessel, anterior aorta of Aplysia. J Neurophysiol 46:967–986
Smit AB, Hoek RM, Geraerts WPM (1993) The isolation of a cDNA encoding a neuropeptide prohormone from the light yellow cells of Lymnaea stagnalis. Cell Mol Neurobiol 13:263–270
Sonetti D, Heumen WRA van, Roubos EW (1992) Light-and electron-microscopic immunocytochemistry of a molluscan insulinrelated peptide in the central nervous system of Planorbarius corneus. Cell Tissue Res 267:473–481
Swichgem H van (1979) On the endogenous bursting properties of ‘light yellow’ neurosecretory cells in the freshwater snail Lymnaea stagnalis (L.). J Exp Biol 80:55–67
Swichgem H van (1981) Electrotonic coupling within a cluster of neurosecretory endogenous oscillators in Lymnaea stagnalis (L.). Comp Biochem Physiol [A] 68:199–201
Vorhwohl G (1961) Zur Funktion der Exkretionsorgane von Helix pomatia L. und Achatina ventricosa Gould. Z Vergl Physiol 45:12–49
Wendelaar Bonga SE (1970) Ultrastructure and histochemistry of neurosecretory cells and neurohaemal areas in the pond snail Lymnaea stagnalis (L.). Z Zellforsch 108:190–224
Wendelaar Bonga SE, Boer HH (1969) Ultrastructure of the renopericardial system in the pond snail Lymnaea stagnalis (L.). Z Zellforsch 94:513–529
Wijdenes J, Minnen J van, Boer HH (1980) A comparative study on neurosecretion demonstrated by the Alcian blue-Alcian yellow technique in three terrestrial pulmonates (Stylommatophora). Cell Tissue Res 210:47–56
With ND de, Berg HA van den (1992) Neuroendocrine control of hydromineral metabolism in molluscs, with special emphasis on the pulmonate freshwater snail, Lymnaea stagnalis. Adv Comp Endocrinol 1:83–89
With ND de, Schors RC van den, Boer HH, Ebberink RHM (1993) The sodium influx stimulating peptide of the pulmonate freshwater snail Lymnaea stagnalis. Peptides 14:783–789
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boer, H.H., Montagne-Wajer, C. Functional morphology of the neuropeptidergic light-yellow-cell system in pulmonate snails. Cell Tissue Res 277, 531–538 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00300226
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00300226