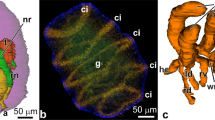
Abstract
The action of the epithelium on differentiation of connective tissue cells of Xenopus small intestine during metamorphosis was investigated by using culture and morphological techniques. Connective tissue fragments isolated from the small intestine at stage 57 were cultivated in the presence or absence of homologous epithelium. In the presence of the epithelium, metamorphic changes in the connective tissue were fully induced by hormones including thyroid hormone (T3), as during spontaneous metamorphosis, whereas they were partially induced in the absence of the epithelium. Macrophage-like cells showing non-specific esterase activity in the connective tissue were much fewer in the absence of the epithelium than in the presence of it, and aggregates of fibroblasts possessing well-developed rough endoplasmic reticulum developed only in the presence of the epithelium. Just before the aggregation of the fibroblasts, the connective tissue close to the epithelium became intensely stained with concanavalin A (ConA) and wheat germ agglutinin (WGA). The present results indicate that the epithelium plays important roles in the differentiation of intestinal connective tissue cells, which in turn affect the epithelial transformation from larval to adult form during anuran metamorphosis. Thus, the tissue interaction between the epithelium and the connective tissue in the anuran small intestine is truly bidirectional.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aplin JD, Hughes RC (1981) Cell adhesion on model substrata: Threshold effects and receptor modulation. J Cell Sci 50:89–103
Baur PS, Barratt GF, Brown GM, Parks DH (1979) Ultrastructural evidence for the presence of “fibroblasts” and “myofibroclasts” in wound healing tissues. J Trauma 19:744–756
Fox H (1983) Amphibian metamorphosis. Humana Press, Clifton, pp 119–126
Fujita H, Ueda A, Nishida T, Otori T (1987) Uptake of india ink particles and latex beads by corncal fibroblasts. Cell Tissue Res 250:251–255
Fujita H, Nishii Y, Yamashita K, Kawamata S, Yoshikawa K (1988) The uptake and long-term storage of india ink particles and latex beads by fibroblasts in the dermis and subcutis of mice, with special regard to the non-inflammatory defense reaction by fibroblasts. Arch Histol Cytol 51:285–294
Fukamachi H, Mizuno T, Kim YS (1987) Gland formation of human colon cancer cells combined with foetal rat mesenchyme in organ culture: An ultrastructural study. J Cell Sci 87:615–621
Haffen K (1986) Fetal gut mesenchyme induces differentiation of cultured intestinal endoderm and crypt cells. Dev Biol 113:474–483
Hourdry J, Dauca M (1977) Cytological and cytochemical changes in the intestinal epithelium during anuran metamorphosis. Int Rev Cytol [Suppl] 5:337–385
Ishizuya-Oka A, Mizuno T (1984) Intestinal cytodifferentiation in vitro of chick stomach endoderm induced by the duodenal mesenchyme. J Embryol Exp Morphol 82:163–176
Ishizuya-Oka A, Shimozawa A (1987a) Development of the connective tissue in the digestive tract of the larval and metamorphosing Xenopus laevis. Anat Anz 164:81–93
Ishizuya-Oka A, Shimozawa A (1987b) Ultrastructural changes in the intestinal connective tissue of Xenopus laevis during metamorphosis. J Morphol 193:13–22
Ishizyya-Oka A, Shimozawa A (1990) Changes in lectin-binding pattern in the digestive tract of Xenopus laevis during metamorphosis: II. Small intestine. J Morphol 205:9–15
Ishizuya-Oka A, Shimozawa A (1991) Induction of metamorphosis by thyroid hormone in anuran small intestine cultured organotypically in vitro. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol 27A:853–857
Ishizuya-Oka A, Shimozawa A (1992a) Connective tissue is involved in adult epithelial development of the small intestine during anuran metamorphosis in vitro. Roux's Archiv Dev Biol 201:322–329
Ishizuya-Oka A, Shimozawa A (1992b) Programmed cell death and heterolysis of larval epithelial cells by macrophage-like cells in the anuran small intestine in vivo and in vitro. J Morphol 213:185–195
Kedinger M, Simon-Assmann P, Lacroix B, Marxer A, Hauri HP, Alexandie E, Haffen K (1987) Importance of a fibroblastic support for in vitro differentiation of intestinal endodermal cells and for their response to glucocorticoids. Cell Differ 20:171–182
Kedinger M, Simon-Assmann P, Bouziges F, Haffen K (1988) Epithelial-mesenchymal interactions in intestinal epithelial differentiation. Scand J Gastroenterol 23 [Suppl] 151:62–69
Kerr JFR, Wyllie AH Currie AR (1972) Apoptosis: a basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging implications in tissue kinetics. Br J Cancer 26:239–257
Kinoshita T, Takahama H, Sasaki F (1991) Changes in the function of dermal fibroblasts in the tadpole tail during anuran metamorphosis. J Exp Zool 257:166–177
Li CY, Lam KW, Yam LT (1973) Esterase in human leukocytes. J Histochem Cytochem 21:1–12
Nieuwkoop PD, Faber J (1967) Normal table of Xenopus laevis (Daudin). North-Holland, Amsterdam
Niki K, Namiki H, Kikuyama S, Yoshizato K (1982) Epidermal tissue requirement for tadpole tail regression induced by thyroid hormone. Dev Biol 94:116–120
Niki K, Yoshizato K, Namiki H, Kikuyama S (1984) In vitro regression of tadpole tail by thyroid hormone. Dev Growth Differ 26:329–338
Nishikawa A, Yoshizato (1986) Characterization of macrophages in the tail of the anuran tadpole. J Exp Zool 239:133–137
Rauvala H, Carter WG, Hakomori S (1981) Studies on cell adhesion and recognition. I. Extent and specificity of cell adhesion triggered by carbohydrate-reactive proteins (glycosidases and lectins) and by fibronectin. J Cell Biol 88:127–137
Svoboda ELA, Deporter DA (1980) Phagocytosis of exogenous collagen by cultured murine fibroblasts and macrophages: A quantitative electron microscopic comparison. J Ultrastruc Res 72:169–173
Takahama H, Kinoshita T, Sasaki F (1992) Structural and endocytotic differences of fibroblasts and macrophages in the tail fin of amphibian larvae during metamorphosis. Arch Histol Cytol 55:437–448
Vernon-Robers B (1972) The macrophage. Cambridge University Press, New York
Yam LT, Li CY, Crosly WH (1971) Cytochemical identification of monocytes and granulocytes. Am J Clin Pathol 55:283–290
Yaoita Y, Shi Y-B, Brown DD (1990) Xenopus laevis and thyroid hormone receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:7090–7094
Yasugi S (1993) Role of epithelial-mesenchymal interactions in differentiation of epithelium of vertebrate digestive organs. Dev Growth Differ 35:1–9
Yagusi S, Mizuno T (1990) Mesenchymal-epithelial interactions in the organogenesis of digestive tract. Zool Sci 7:163–174
Yoshizato K (1989) Biochemistry and cell biology of amphibian metamorphosis with a special emphasis on the mechanism of removal of larval organs. Int Rev Cytol 119:97–149
Yoshizato K (1992) Death and transformation of larval cells during metamorphosis of anura. Dev Growth Differ 34:607–612
Yoshizato K, Kikuyama S, Shioya N (1980) Stimulation of glucose utilization and lactate production in cultured human fibroblasts by thyroid hormone. Biochim Biophys Acta 627:23–29
Yui S, Yamazaki M (1985) Induction of macrophage growth by effete cells. J Leukocyte Biol 39:489–497
Yui S, Yamazaki M (1986) Induction of macrophage growth by lipids. J Immunol 136:1334–1338
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ishizuya-Oka, A., Shimozawa, A. Inductive action of epithelium on differentiation of intestinal connective tissue of Xenopus laevis tadpoles during metamorphosis in vitro. Cell Tissue Res 277, 427–436 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00300215
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00300215