Summary
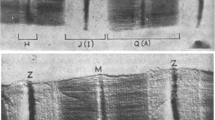
Nebulin, a giant myofibrillar protein with size variants from 700 to 900 kDa in various skeletal muscles, has been proposed to constitute a set of inextensible filaments anchored at the Z-line and coextensive with actin filaments. To elucidate the architectural organization of this fourth set of myofilaments in the skeletal muscle sarcomere, we performed immunoelectron microscopic localization of epitope profiles of a number of site-specific monoclonal antibodies against cloned human nebulin fragments of known sequence loci. Monoclonal antibody N113, which is directed to fragment ND8 at approximately 300 residues away from the C-terminus, labelled the edges of Z-lines in both human quadriceps muscle and rabbit psoas muscle. Monoclonal antibody N101, which is directed to fragment NB5 near the N-terminal side, is localized to a single locus at 0.89 μm from the Z-line in human quadriceps muscle and 0.80μm from the Z-line in rabbit psoas muscle. Additionally, monoclonal antibody N109, which is directed to fragment NA3 on the carboxy side of the adjacent fragment NB5, is localized at 0.76 μm away from the Z-line in rabbit psoas muscle. This one-to-one correspondence between epitope loci and sequence loci demonstrates that a single nebulin polypeptide spans the length of the thin filament with its C-terminus anchored at the Z-line. The epitope spacings of site-specific antibodies are consistent with the notion that the nebulin filament is uniform in mass density along its length.
We conclude that the thin filament, as defined morphologically by electron microscopy, is a composite filament of the conventional actin thin filament (actin/tropomyosin/troponin) and coextensible nebulin polypeptides which act as full-length molecular templates that regulate or stabilize colaterally the actin filament in the skeletal muscle sarcomere.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
EPSTEIN, H. F. & FISCHMAN, D. A. (1991) Molecular analysis of protein assembly in muscle development. Science 251, 1039–44.
HUANG, Q.-Q. (1993) Monoclonal antibodies against cloned human nebulin fragments. Master Thesis, The University of Texas at Austin.
JIN, J.-P. & WANG, K. (1991a) Cloning, expression and protein interaction of human nebulin fragments composed of varying numbers of sequence modules. J. Biol. Chem. 266, 21215–23.
JIN, J.-P. & WANG, K. (1991b) Nebulin as a giant actin-binding template protein in skeletal muscle sarcomere: interaction of actin and cloned human nebulin fragments. FEBS Lett. 281, 93–6.
KOCH, C. A., ANDERSON, D., MORAN, M. F., Ellis, C. & Pawson, T. (1991) SH2 and SH3 domains: elements that control interactions of cytoplasmic signalling proteins. Science 252, 668–74.
KRUGER, M., WRIGHT, J. & WANG, K. (1991) Nebulin as a length regulator of thin filaments of vertebrate skeletal muscles: correlation of thin filament length, nebulin size and epitope profile. J. Cell Biol. 115, 97–107.
LABEIT, S., GIBSON, T., LAKEY, A. LEONARD, K., ZEVIANI, M., KNIGHT, P., WARDALE, J. & TRINICK, J. (1991) Evidence that nebulin is a protein-ruler in muscle thin filaments. FEBS Lett. 282, 313–16.
LABEIT, S., GAUTEL, M., LAKEY, A., & TRINICK, J. (1992) Towards a molecular understanding of titin. EMBO J. 11, 1711–16.
MARUYAMA, K., MATSUNO, A., HIGUCHI, H., SHIMAOKA, S., KIMURA, S. & SHIMIZU, T. (1989) Behaviour of connectin (titin) and nebulin in skinned muscle fibers released after extreme stretch as revealed by immunoelectron microscopy. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 10, 350–9.
PIEROBON-BORMIOLI, S., BETTO, R. & SALVIATI, G., (1989). The organization of titin (connectin) and nebulin in the sarcomeres: an immunolocalization study. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 10, 446–56.
TRINICK, J. (1992) Understanding the functions of titin and nebulin. FEBS Lett. 307, 44–8.
WALKER, S. M. & SCHRODT, G. R. (1974) I. Segment lengths and thin filament periods in skeletal muscle fibers of the Rhesus monkey and the human. Anat. Rec. 178, 63–82.
WANG, K. (1984) Cytoskeletal matrix in striated muscle: the role of titin, nebulin and intermediate filaments. Muscle Cell Motil. 6, 285–305.
WANG, K. & WRIGHT, J. (1988) Architecture of the sarcomere matrix of skeletal muscle: immunoelectron microscopic evidence that suggests a set of parallel inextensible nebulin filaments anchored at the Z-line. J. Cell Biol. 107, 2199–212.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wright, J., Huang, QQ. & Wang, K. Nebulin is a full-length template of actin filaments in the skeletal muscle sarcomere: an immunoelectron microscopic study of its orientation and span with site-specific monoclonal antibodies. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 14, 476–483 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00297210
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00297210