Abstract
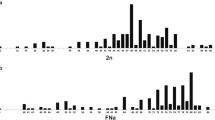
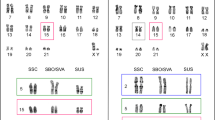
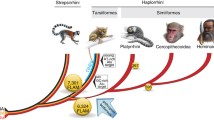
Callimico goeldii (Goeldi's marmoset) is a neotropical primate with 2n=47,X1X2Y in the male, and 2n=48,X1X1X2X2 in the female, due to a Y-autosome translocation. Karyological comparisons of Callimico, Callithrix jacchus and Cebus apella suggest that Callimico is a member of the Callitrichidae. Isozyme data and restriction mapping of LINE-1 repetitive elements in these species and in a variety of other neotropical primates confirm these findings and supply strong evidence for including Callimico in the Callitrichidae.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armada JLA, Barroso CML, Lima MMC, Muniz JAPC, Seuánez HN (1987) Chromosome studies in Alouatta belzebul. Am J Primatol 13:283–296
Bender MA, Chu EHY (1963) The chromosomes of Primates. In: Buettner-Janusch J (ed) Evolutionary and genetic biology of the Primates. Academic Press, London, New York
Bender MA, Mettler LE (1960) Chromosome studies of Primates: Callithrix, Leontocebus and Callimico. Cytologia 25:400–404
Benirschke K, Anderson JM, Brownhill LE (1962) Marrow chimerism in marmosets. Science 138:513–515
Benirschke K, de Boer LEM, Bogart M (1976) The karyotype of two uakari species Cacajao calvus and C. rubicundus (Primates, Platyrrhini). Genen Phaenen 19:1–6
Casavant NC, Hardies SC, Funk FD, Comer MB, Edgell MH, Hutchison III CA (1988) Extensive movement of LINE ONE sequences in beta-globin loci of Mus caroli and Mus domesticus. Mol Cell Biol 8:4669–4674
de Boer LEM (1974) Cytotaxonomy of the Platyrrhini. Genen Phaenen 17:1–115
Dutrillaux B, Descailleux L, Viegas-Pequignot E, Couturier J (1981) Y-autosome tanslocation in Cacajao calvus rubicundus (Platyrrhini). Ann Genet 24:197–201
Egozcue J, Perkins EM, Hagemenas F (1968) Chromosomal evolution in marmosets, tamarins and pinches. Folia Primat 9:81–94
Fanning TG, Singer MF (1987a) LINE-1: a mammalian transposable element. Biochim Biophys Acta 910:203–212
Fanning TG, Singer MF (1987b) The LINE-1 DNA sequences in four mammalian orders predict proteins that conserve homologies to retrovirus proteins. Nucleic Acids Res 15:2251–2260
Ford SM (1980) Callitrichids as phyletic dwarfs, and the place of the Callitrichidae in Platyrrhini. Primates 21:31–43
Gengozian N, Brewen JG, Preston RJ, Batson JS (1980) Presumptive evidence for the lack of functional germ cell chimerism in the marmoset. J Med Primatol 9:9–27
Harris H, Hopkinson DA (1978) Handbook of enzyme electrophoresis in human genetics. North Holland, Amsterdam New York Oxford
Hattori M, Kuhara S, Takenaka O, Sakaki Y (1986) L1 family of repetitive DNA sequences in primates may be derived from a sequence encoding a reverse transcriptase-related protein. Nature 321:625–628
Hershkovitz P (1977) Living New World monkeys (Platyrrhini), vol. 1. University of Chicago Press, Chicago
Hsu TC, Hampton SH (1970) Chromosomes of Callithricidae with special reference to an XX/“XO” sex chromosome system in Goeldi's marmoset (Callimico goeldii Thomas 1904). Folia Primatol 13:183–195
Ikeuchi T (1984) Inhibitory effect of ethidium bromide on mitotic chromosome condensation and its application to high resolution chromosome banding. Cytogenet Cell Genet 38:56–61
Koiffmann CP (1977) Variabilidae cromossomica na familia Cebidae (Platyrrhini, Primata). Ph. D. Dissertation, University of Sao Paulo
Loeb DD, Padgett RW, Hardies SC, Shehee WR, Comer MB, Edgell MH, Hutchison III CA (1986) The sequence of a large L1Md element reveals a tandemly repeated 5′ end and several features found in retrotransposons. Mol Cell Biol 6:168–182
Ma NSF, Jones TC, Thorington RW, Miller A, Morgan L (1975) Y-autosome translocation in the howler monkey, Alouatta palliata. J Med Primatol 4:299–307
Ma NSF, Elliot MW, Morgan L, Miller A, Jones TC (1976) Translocation of Y chromosome to an autosome in the Bolivian owl monkey, Aotus. Am J P Anthropol 45:191–202
Ma NSF, Hall R, Sehgal PK, Simeone T, Jones TC (1980) XX/“XO” sex determination system in a population of Peruvian owl monkeys, Aotus. J Hered 71:336–342
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrook J (1982) Molecular cloning. A laboratory manual, Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Martin SL, Voliva CF, Hardies SC, Edgell MH, Hutchison III CA (1985) Tempo and mode of concerted evolution in the L1 repeat family of mice. Mol Biol Evol 2:127–140
Matayoshi T, Seuánez HN, Nasazzi N, Nagle C, Armada JL, Freitas L, Alves G, Barroso CML, Howlin E (1987) Heterochromatic variation in Cebus apella (Cebidae, Platyrrhini) of different geographic regions. Cytogenet Cell Genet 44:158–162
Sanger F, Nicklen S, Coulson AR (1977) DNA sequencing with chain terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74:5463–5467
Sarich VM, Cronin JE (1980) South American mammal molecular systematics, evolutionary clocks, and continental drift. In: Ciochon RL, Chiarelli AB (eds) Evolutionary biology of the New World monkeys and continental drift. Plenum Press, New York, NY, pp 399–421
Scott AF, Schmeckpeper BJ, Abdelrazik M, Comey CT, O'Hara B, Rossiter JP, Cooley T, Heath P, Smith KD, Margolet L (1987) Origin of the human L1 elements: proposed progenitor genes deduced from a consensus DNA sequence. Genomics 1:113–125
Seuánez HN, Forman L, Alves G (1988) Comparative chromosome morphology in three Callitrichid genera: Cebuella, Callithrix, and Leontopithecus. J Hered 79:418–424
Shehee WR, Chao SF, Loeb DD, Comer MB, Hutchison III CA, Edgell MH (1987) Determination of a functional ancestral sequence and definition of the 5′ end of A-type mouse L1 elements. J Mol Biol 196:757–767
Skowronski J, Fanning TG, Singer MF (1988) Unit-length Line-1 transcripts in human teratocarcinoma cells. Mol Cell Biol 8:1385–1397
Wayne RK, O'Brien SJ (1987) Allozyme divergence within the Canidae. Syst Zool 36:339–355
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
On leave from: Genetics Section, Instituto Nacional do Cancer (Rio de Janeiro)/Department of Genetics, Universidade Federal do Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seuánez, H.N., Forman, L., Matayoshi, T. et al. The Callimico goeldii (Primates, Platyrrhini) genome: Karyology and middle repetitive (LINE-1) DNA sequences. Chromosoma 98, 389–395 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00292783
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00292783