Abstract
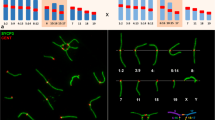
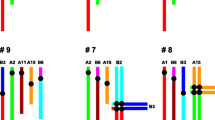
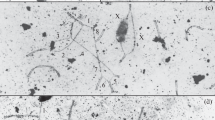
The patterns of chromosomal pairing and chiasma distribution were analyzed in male Sitka deer mice (Peromyscus sitkensis) polymorphic for terminally positioned pericentric inversions of chromosomes 6 and 7. Gand C-banding of somatic metaphases indicated that the inversions involved 30% and 40% of chromosomes 6 and 7, respectively. Analysis of silver-stained synaptonemal complexes in surface-spread zygotene and pachytene nuclei from heterozygous individuals revealed that inversion loops were not formed. The inverted segments proceeded directly to heterosynapsis without an intervening homosynaptic phase, and the heteromorphic bivalents remained straight-paired throughout pachynema. C-banded pachytene nuclei corroborated the occurrence of heterosynapsis, as the heteromorphic bivalents exhibited nonaligned centromeres. Analysis of diplonema and diakinesis indicated that crossing over had not occurred within the heterosynapsed inverted segments. The observation of chiasma suppression within the inversions indicates that pericentric inversion heterozygosity does not lead to the production of unbalanced gametes. Heterosynapsis of the inverted segments during zygonema and pachynema and the resulting chiasma suppression therefore represent a meiotic mechanism for the maintenance of pericentric inversion polymorphisms in this population of P. sitkensis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashley T, Moses MJ, Solari AJ (1981) Fine structure and behaviour of a pericentric inversion in the sand rat, Psammomys obesus. J Cell Sci 50:105–119
Baker RJ, Gardner AL, Patton JL (1972) Chromosomal polymorphism in the phyllostomatid bat, Mimon crenulatum (Geoffroy). Experientia 28:969–970
Bass RA (1979) Chromosomal polymorphism in cardinals Cardinalis cardinalis. Can J Genet Cytol 21:549–553
Bitgood JJ, Shoffner RN, Otis JS, Wang N (1982) Recombinant inversion chromosomes in phenotypically normal chickens. Science 215:409–411
Chandley AC (1982) A pachytene analysis of two male-fertile paracentric inversions in chromosome 1 of the mouse and in the male-sterile double heterozygote. Chromosoma 85:127–135
Cole CJ (1970) Karyotypes and evolution of the spinosus group of lizards in the genus Sceloporus. Am Mus Novit 2431:1–47
Committee for the Standardization of Chromosomes of Peromyscus (1977) Standardized karyotype of the deer mouse, Peromyscus (Rodentia). Cytogenet Cell Genet 19:38–43
Counce CJ, Meyer GF (1973) Differentiation of the synaptonemal complex and the kinetochore in Locusta spermatocytes studied by whole mount electron microscopy. Chromosoma 44:231–253
Davis KM, Smith SA, Greenbaum IF (1986) Evolutionary implications of chromosomal polymorphisms in Peromyscus boylii from southwestern Mexico. Evolution 40:645–649
Davisson MT, Poorman PA, Roderick TH, Moses MJ (1981) A pericentric inversion in the mouse. Cytogenet Cell Genet 30:70–76
Dobzhansky T (1970) Genetics of the evolutionary process. Columbia University Press, New York
Dresser ME, Moses MJ (1980) Synaptonemal complex karyotyping in spermatocytes of the Chinese hamster (Cricetulus griseus): IV. Light and electron microscopy of synapsis and nucleolar development by silver staining. Chromosoma 76:1–22
Elder FFB, Pathak S (1980) Light microscopic observations on the behavior of silver-stained trivalents in pachytene cells of Sigmodon fulviventer (Rodentia, Muridae) heterozygous for centric fusion. Cytogenet Cell Genet 27:31–38
Greenbaum IF, Reed MJ (1984) Evidence for heterosynaptic pairing of the inverted segment in pericentric inversion heterozygotes of the deer mouse (Peromyscus maniculatus). Cytogenet Cell Genet 38:106–111
Greenbaum IF, Baker RJ, Bowers JH (1978) Chromosomal homology and divergence between sibling species of deer mice: Peromyscus maniculatus and P. melanotis (Rodentia, Cricetidae). Evolution 32:334–341
Greenbaum IF, Hale DW, Fuxa KP (1986a) The mechanism of autosomal synapsis and the substaging of zygonema and pachynema from deer mouse spermatocytes. Chromosoma 93:203–212
Greenbaum IF, Hale DW, Fuxa KP (1986b) Synaptic adaptation in deer mice: A cellular mechanism for karyotypic orthoselection. Evolution 40:208–213
Guichaoua MR, Delafontaine D, Taurelle R, Taillemite JL, Morazzani MR, Luciani JM (1986) Loop formation and synaptic adjustment in a human male heterozygous for two pericentric inversions. Chromosoma 93:313–320
Gunn SJ, Greenbaum IF (1986) Systematic implications of karyotypic and morphologic variation in mainland Peromyscus from the Pacific Northwest. J Mammal 67:294–304
Hale DW, Greenbaum IF (1986) The behavior and morphology of the X and Y chromosomes during prophase I in the Sitka deer mouse (Peromyscus sitkensis). Chromosoma 94:235–242
Howell WM, Black DA (1980) Controlled silver staining of nucleolus organizer regions with a protective colloidal developer: A 1-step method. Experientia 36:1014–1015
Kaelbling M, Fechheimer NS (1985) Synaptonemal complex analysis of a pericentric inversion in chromosome 2 of the domestic fowl, Gallus domesticus. Cytogenet Cell Genet 39:82–86
Kaiser P (1984) Pericentric inversions: Problems and significance for clinical genetics. Hum Genet 68:1–47
Lande R (1979) Effective deme sizes during long-term evolution estimated from rates of chromosomal rearrangement. Evolution 33:234–251
Lande R (1984) The expected fixation rate of chromosomal inversions. Evolution 38:743–752
Lee MR, Elder FFB (1980) Yeast stimulation of bone marrow mitosis for cytogenetic investigations. Cytogenet Cell Genet 26:36–40
Mahadevaiah S, Mittwoch U, Moses MJ (1984) Pachytene chromosomes in male and female mice heterozygous for the Is(7; 1)4OH insertion. Chromosoma 90:163–169
Mascarello JT, Warner JW (1974) Chromosome variations in the plains woodrat: A pericentric inversion involving constitutive heterochromatin. Experientia 30:90–91
Matthey R (1966) Une inversion pericentrique a l'origine d'un polymorphisme chromosomique non-Robertsonien dans une population de Mastomys (Rodentia-Murinae). Chromosoma 18:188–200
Moses MJ (1977) Synaptonemal complex karyotyping in spermatocytes of the Chinese hamster (Cricetulus griseus): I. Morphology of the autosomal complement in spread preparations. Chromosoma 60:99–125
Moses MJ, Poorman PA (1981) Synaptonemal complex analysis of mouse chromosomal rearrangements: II. Synaptic adjustment in a tandem duplication. Chromosoma 81:519–535
Moses MJ, Poorman PA (1984) Synapsis, synaptic adjustment and DNA synthesis in mouse oocytes. Chromosomes Today 8:90–103
Moses MJ, Karatsis PA, Hamilton AE (1979) Synaptonemal complex analysis of heteromorphic trivalents in Lemur hybrids. Chromosoma 70:141–160
Moses MJ, Poorman PA, Roderick TH, Davisson MT (1982) Synaptonemal complex analysis of mouse chromosomal rearrangements: IV. Synapsis and synaptic adjustment in two paracentric inversions. Chromosoma 84:457–474
Ohno S, Weiler C, Poole J, Christian L, Stenius C (1966) Autosomal polymorphism due to pericentric inversions in the deer mouse (Peromyscus maniculatus) and some evidence of somatic segregation. Chromosoma 18:177–187
Pengilly D, Jarrell GH, MacDonald SO (1983) Banded karyotypes of Peromyscus sitkensis from Baranof Island, Alaska. J Mammal 64:682–685
Poorman PA, Moses MJ, Davisson MT, Roderick TH (1981) Synaptonemal complex analysis of mouse chromosomal rearrangements: III. Cytogenetic observations on two paracentric inversions. Chromosoma 83:419–429
Roderick TH, Hawes NL (1974) Nineteen paracentric chromosomal inversions in mice. Genetics 76:109–117
Rogers DS, Greenbaum IF, Gunn SJ, Engstrom MD (1984) Cytosystematic value of chromosomal inversion data in the genus Peromyscus (Rodentia: Cricetidae). J Mammal 65:457–465
Seabright M (1971) A rapid banding technique for human chromosomes. Lancet ii:971–972
Sharp PJ (1986) Synaptic adjustment at a C-band heterozygosity. Cytogenet Cell Genet 41:56–57
Shields GF (1973) Chromosomal polymorphism common to several species of Junco (Aves). Can J Genet Cytol 15:461–471
Shields GF (1976) Meiotic evidence for pericentric inversion polymorphism in Junco (Aves). Can J Genet Cytol 18:747–751
Sites JW (1983) Chromosome evolution in the iguanid lizard Sceloporus grammicus. I. Chromosome polymorphisms. Evolution 37:38–53
Sumner AT (1972) A simple technique for demonstrating centromeric heterochromatin. Exp Cell Res 75:304–306
Tease C, Fisher G (1986) Further examination of the production-line hypothesis in mouse foetal oocytes: I. Inversion heterozygotes. Chromosoma 93:447–452
Thorneycroft HB (1975) A cytogenetic study of the white-throated sparrow, Zonotrichia albicollis (Gmelin). Evolution 29:611–621
Turner BJ, Grudzien TA, Adkisson KP, Worrell RA (1985) Extensive chromosomal divergence within a single river basin in the goodeid fish, Ilyodon furcidens. Evolution 39:122–134
White MJD (1973) Animal cytology and evolution. Cambridge University Press, London
White MJD (1978) Modes of speciation. Freeman, San Francisco
Yosida TH (1977) Frequencies of chromosome polymorphism in pairs no. 1, 9, and 13 in three geographical variants of black rats, Rattus rattus. Chromosoma 60:391–398
Yosida TH, Tsuchiya K, Moriwaki K (1971) Frequency of chromosome polymorphism in Rattus rattus collected in Japan. Chromosoma 33:30–40
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hale, D.W. Heterosynapsis and suppression of chiasmata within heterozygous pericentric inversions of the Sitka deer mouse. Chromosoma 94, 425–432 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00292751
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00292751