Summary
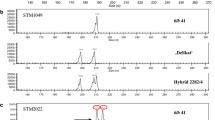
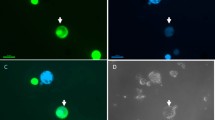
Irradiated mesophyll protoplasts from nine different accessions of B. juncea, B. nigra and B. carinata, all resistant to Phoma lingam, were used as gene donors in fusion experiments with hypocotyl protoplasts isolated from B. napus as the recipient. A toxin, sirodesmin PL, was used to select those fusion products in which the resistant gene(s) was present. In the fusion experiments different gene donors, various irradiation dosages and toxin treatments were combined. Symmetric and asymmetric hybrid plants were obtained from the cell cultures with and without toxin selection. Isozymes were used to verify hybrid characters in the symmetric hybrids, whereas two DNA probes were used to identify donor-DNA in the asymmetric hybrids. Resistance to P. lingam was expressed in all symmetric hybrids, and in 19 of 24 toxin-selected asymmetric hybrids, while all the unselected asymmetric hybrids were susceptible.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banks MS, Evans PK (1976) A comparison of the isolation and culture of mesophyll protoplasts from several Nicotiana species and their hybrids. Plant Sci Lett 7:409–416
Bates GW, Hasenkampf CA, Contolini CL, Piastuch WC (1987) Asymmetric hybridization in Nicotiana by fusion of irradiated protoplasts. Theor Appl Genet 74:718–726
Blonstein AD, King PJ (1985) Plant mutant isolation via protoplasts. In: Fowke LC, Constable F (eds) Plant protoplasts. CRC Press, Florida, pp 151–168
Crossway A, Oakes JV, Irvine JM, Ward B, Knauf VC, Shewmaker CK (1986) Integration of foreign DNA following microinjection of tobacco protoplasts. Mol Gen Genet 202:179–185
Dellaporta SK, Wood J, Hicks JB (1983) A plant DNA minipreparation: version II. Plant Mol Biol Rep 1:19–21
Deshayes A, Herrera-Estrelle L, Caboche M (1985) Liposomemediated transformation of tobacco mesophyll protoplasts by an Escherichia coli plasmid. EMBO J 4:2731–2737
Dudits D, Fejer O, Hadlaczky G, Koncz C, Lazar GB, Horvarth G (1980) Intergeneric gene transfer mediated by plant protoplast fusion. Mol Gen Genet 179:283–288
Dudits D, Maroy E, Praznovszky T, Olah Z, Gyorgyey J, Cella R (1987) Transfer of resistant traits from carrot into tobacco by asymmetric somatic hybridization: Regeneration of fertile plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:8434–8438
Ericsson M (1988) Seed storage proteins; studies on the structure, molecular genetics and intracellular localization of napin from Brassica napus. PhD Thesis, Swedish University of Agricultural Sciences, Part V, pp 1–19
Fahleson J, Dixelius J, Sundberg E, Glimelius K (1988) Correlation between flow cytometric determination of nuclear DNA content and chromosome number in somatic hybrids within Brassicaceae. Plant Cell Rep 7:74–77
Glimelius K (1984) High growth rate and regeneration capacity of hypocotyl protoplasts in some Brassicaceae. Physiol Plant 61:38–44
Glimelius K, Djupsjöbacka M, Fellner-Feldegg H (1986) Selection and enrichment of plant protoplast hetero-karyons of Brassicaceae by flow sorting. Plant Sci 45:133–141
Hinnisdaels S, Negrutiu I, Jacobs M, Sidorov V (1988) Plant somatic cell hybridizations: evaluations and prospectives. IAPTC Newslett 55:1–10
Hoffmann F, Adachi T (1981) Arabidobrassica: chromosomal recombination and morphogenesis in asymmetric intergeneric hybrid cells. Planta 153:586–593
Horsch R, Fraley R, Rogers S, Fry J, Klee H, Shah D, McCormick S, Niedermeyer J, Hoffman N (1987) Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of plants. In: Green CE, Somers DA, Hackett WP, Biesboer DD (eds) Plant tissue and cell culture. Alan Liss, New York, pp 317–329
Installé P, Negrutiu I, Jacobs M (1985) Protoplast-derived plants in Nicotiana plumbaginifolia viviani: Improving the regeneration response of wild type and mutant cultures. J Plant Physiol 119:443–454
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrook J (1982) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor/NY
Menczel L, Nagy I, Kizz ZsR, Maliga P (1981) Streptomycinresistant and sensitive somatic hybrids of Nicotiana tabacum+Nicotiana knightiana: correlation of resistance to N. tabacum plastids. Theor Appl Genet 59:191–195
Neuhaus G, Spangenberg G, Mittelsten Scheid O, Schwiger H-G (1987) Transgenic rapeseed plants obtained by the microinjection of DNA into microspore-derived embryoids. Theor Appl Genet 75:30–36
Potrykus I, Paszkowski J, Saul MW, Negrutiu I, Shillito RD (1987) Direct gene transfer to plants: facts and future. In: Green CE, Somers DA, Hackett WP, Biesboer DD (eds) Plant tissue and cell culture. Alan Liss, New York, pp 289–302
Schieder O, Gupta PP, Krumbiegel-Schroener G, Hein T, Steffen A (1985) Novel techniques in handling and manipulating cells. Hereditas (Suppl) 3:65–75
Scofield SR, Crouch ML (1987) Nucleotide sequence of a member of the napin storage protein family from Brassica napus. J Biol Chem 262:12202–12208
Shields CR, Orton TJ, Stuber CW (1983) An outline of general resource needs and procedures for the electrophoretic separation of active enzymes from plant tissue. In: Tanksley SD, Orton TJ (eds) Isozymes in plant genetics and breeding, part A. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 443–479
Sjödin C, Glimelius K (1988) Screening for resistance to blackleg Phoma lingam (Tode ex Fr.) Desm. within Brassicaceae. J Phytopathol 123:322–332
Sjödin C, Glimelius K (1989a) Differences in response to the toxin sirodesmin PL produced by Phoma lingam (Tode ex Fr.) Desm. on protoplasts, cell aggregates and intact plants of resistant and susceptible Brassica accessions. Theor Appl Genet 77:76–80
Sjödin C, Glimelius K (1989b) Brassica naponigra, a somatic hybrid resistant of Phoma lingam. Theor Appl Genet 77:651–656
Sjödin C, Nyhammar T, Glimelius K (1988) Effects of toxic metabolites produced by Phoma lingam (Tode ex Fr.) Desm. on protoplasts, cells and plants of hosts and non-hosts to the pathogen. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 32:301–312
Sundberg E, Glimelius K (1986) A method for production of interspecific hybrids within Brassiceae via somatic hybridization, using resynthesis of Brassica napus as a model. Plant Sci 43:155–162
Sundberg E, Landgren M, Glimelius K (1987) Fertility and chromosome stability in Brassica napus resynthesised by protoplast fusion. Theor Appl Genet 75:96–104
Yakura K, Kato A, Tanifuji S (1984) Length heterogeneity of the large spacer of Vicia faba rDNA is due to the differing number of a 325 bp repetitive sequence element. Mol Gen Genet 401–405
Zelcer A, Aviv D, Galun E (1978) Interspecific transfer of cytoplasmic male sterility by fusion between protoplasts of normal Nicotiana sylvestris and X-ray irradiated protoplasts of male-sterile N. tabacum. Z Pflanzenphysiol 90:397–407
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by G. Wenzel
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sjödin, C., Glimelius, K. Transfer of resistance against Phoma lingam to Brassica napus by asymmetric somatic hybridization combined with toxin selection. Theoret. Appl. Genetics 78, 513–520 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00290835
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00290835