Abstract
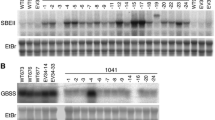
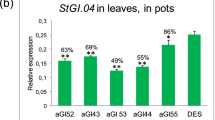
Inhibition of expression of specific genes by means of antisense RNA is widely used, although little information is available regarding conditions that affect the efficacy of inhibition. In this study, inhibition of granule-bound starch synthase (GBSS), a key enzyme in starch biosynthesis, is used as a model system. Eleven antisense constructs derived from the full-length GBSS cDNA, the genomic GBSS coding region (gDNA) or fragments of each of these sequences, were analysed with respect to their inhibitory effect. Introduction of full-length gDNA constructs yielded a lower percentage of transgenic clones showing complete inhibition than did introduction of the full-length cDNA constructs. This may be caused by a lower antisense binding capacity of the former due to the relatively low GC content in intron sequences present in the gDNA constructs. The presence of multiple T-DNA insertions was related to a higher degree of inhibition. Putative polyadenylation signals on the antisense strand of the GBSS gene resulted in a premature stop of transcription of some of the antisense genes, as demonstrated by the expression of smaller antisense RNA transcripts. Introduction of antisense constructs driven by the promoter of the (target) GBSS gene resulted in a higher percentage of clones with complete inhibition than introduction of antisense constructs driven by the 35S CaMV promoter. Complete antisense inhibition was achieved in 25% of the clones carrying the antisense construct pKGBA 50, which is based on the GBSS promoter and the full-length GBSS cDNA. Thus, it is concluded that the use of pKGBA50 is very suitable for the modification of the composition of potato tuber starch via antisense RNA.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Assaad FA, Tucker KL, Signer ER (1993) Epigenetic repeat-induced gene silencing (RIGS) in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol Biol 22:1067–1085
Bird CR, Ray JA, Fletcher JD, Boniwell JM, Bird AS, Teulieres C, Blain I, Bramley PM, Schuch W (1991) Using antisense RNA to study gene function: inhibition of carotenoid biosynthesis in transgenic tomatoes. Biotechnology 9:635–639
Boyer HW, Roulland-Dussoix D (1969) A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol 41:459–472
Casadaban MJ, Cohen SN (1980) Analysis of gene control signals by DNA fusion and cloning in E. coli. J Mol Biol 138:174–207
Chambers SP, Prior SE, Barstow DA, Minton NP (1988) The pMTL nic- cloning vectors. I. Improved pUC polylinker regions to facilitate the use of sonicated DNA for nucleotide sequencing. Gene 68:139–149
Dellaporta SL, Wood J, Hicks JB (1983) A plant DNA minipreparation: version II. Plant Mol Biol Rep 1:19–21
Ditta G, Stanfield S, Corbin D, Helinski DR (1980) Broad host range DNA cloning system for gram negative bacteria: construction of a gene bank of Rhizobium mehloti. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77:7374–7351
Dolfini S, Consonni G, Mereghetti M, Tonelli C (1993) Antiparallel expression of the sense and antisense transcripts of maize α-tubulin genes. Mol Gen Genet 241:161–169
Frandsen NO (1968) Die Plastidenzahl als Merkmal bei der Kartoffel. Theor Appl Genet 38:153–167
Hamilton AJ, Lycett GW, Grierson D (1990) Antisense gene that inhibits synthesis of the hormone ethylene in transgenic plants. Nature 346:284–287
Hergersberg M (1988) Molekulare Analyse des waxy Gens aus Solanum tuberosum and Expression von waxy antisense RNA in transgenen Kartoffeln. PhD dissertation, University of Cologne, Germany
Hobbs SLA, Kpodar P, DeLong CMO (1990) The effect of TDNA copy number, position and methylation on reporter gene expression in tobacco transformants. Plant Mol Biol 15:851–864
Hobbs SLA, Warkentin TD, DeLong CMO (1993) Transgene copy number can be positively or negatively associated with transgene expression. Plant Mol Biol 21:17–26
Höfgen R, Willmitzer L (1988) Storage of competent cells for Agrobacterium transfromation. Nucleic Acids Res 16:9877
Höfgen R, Willmitzer L (1992) Transgenic potato plants depleted for the major tuber protein patatin via expression of antisense RNA. Plant Sci 87:45–54
Hovenkamp-Hermelink JHM, Jacobsen E, Pijnacker LP, de Vries JN, Witholt B, Feenstra WJ (1988a) Cytological studies on adventitious shoots and minitubers of a monoploid potato clone. Euphytica 39:213–219
Hovenkamp-Hermelink JHM, de Vries JN, Adamse P, Jacobsen E, Witholt B, Feenstra WJ (1988b) Rapid estimation of the amylose/amylopectin ratio in small amounts of tuber and leaf tissue in potato. Potato Res 31:241–246
Jacobsen E, Hovenkamp-Hermelink JHM, Krijgsheld HT, Nijdam H, Pijnacker LP, Witholt B, Feenstra WJ (1989) Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of an amylose-free starch mutant of the potato. Euphytica 44:43–48
Jefferson RA, Kavanagh TA, Bevan MW (1987) GUS fusions: beta glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants. EMBO J 6:3901–3907
Kuipers GJ, Vreem JTM, Meyer H, Jacobsen E, Feenstra WJ, Visser RGF (1991) Field evaluation of antisense RNA-mediated inhibition of GBSS gene expression in potato. Euphytica 59:83–91
Kuipers AGJ, Jacobsen E, Visser RGF (1994) Formation and deposition of amylose in the potato tuber starch granule are affected by the reduction of granule-bound starch synthase gene expression. Plant Cell 6:43–52
Linn F, Heidemann I, Saedler H, Meyer P (1990) Epigenetic changes in the expression of the maize Al gene in Petunia hybrida: role of number of integrated gene copies and state of methylation. Mol Gen Genet 222:329–336
Müller-Röber B, Sonnewald U, Willmitzer L (1992) Inhibition of the ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase in transgenic potatoes leads to sugar-storing tubers and influences tuber formation and expression of tuber storage protein genes. EMBO J 11:1229–1238
Müllner EW, Kühn LC (1988) A stem-loop in the 3′ untranslated region mediates iron-dependent regulation of transferrin receptor mRMA stability in the cytoplasm. Cell 53:815–825
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Oeller PW, Min-Wong L, Taylor LP, Pike DA, Theologis A (1991) Reversible inhibition of tomato fruit senescence by antisense RNA. Science 254:437–439
Ooms G, Hooykaas PJJ, van Veen RJM, van Bellen P, Regensburg-Tuink TJG, Schilperoort RA (1982) Octopine Ti-plasmid deletion mutants of Agrobacterium tumefaciens with emphasis on the right side of the T-region. Plasmid 7:15–29
Peach C, Velten J (1991) Transgene expression variability (position effect) of CAT and GUS reporter genes driven by linked divergent T-DNA promoters. Plant Mol Biol 17:49–60
Rodermel SR, Abbott MS, Bogorad L (1988) Nuclear-organelle interactions: nuclear antisense gene inhibits ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase enzyme levels in transformed tobacco plants. Cell 55:673–681
Rogers JC (1988) RNA complementarity to alpha-amylase RNA in barley. Plant Mol Biol 11:125–138
Salehuzzaman SNIM, Jacobsen E, Visser RGF (1992) Cloning, partial sequencing and expression of a cDNA coding for branching enzyme in cassava. Plant Mol Biol 20:809–819
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Sandler SJ, Staynton M, Townsend JA, Ralston ML, Bedbrook JR, Dunsmuir P (1988) Inhibition of gene expression in transformed plants by antisense RNA. Plant Mol Biol 11:301–310
Sheehy RE, Kramer M, Hiatt WR (1988) Reduction of polygalacturonase activity in tomato fruit by antisense RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:8805–8809
Shimada H, Tada Y, Kawasaki T, Fujimura T (1993) Antisense regulation of the rice waxy gene expression using a PCR-amplified fragment of the rice genome reduces the amylose content in grain starch. Theor Appl Genet 86:665–672
Smith CJS, Watson CF, Ray J, Bird CR, Morris PC, Schuch W, Grierson D (1988) Antisense RNA inhibition of polygalacturonase gene expression in transgenic tomatoes. Nature 334:724–726
Smith CJS, Watson CF, Morris PC, Bird CR, Seymour GB, Gray JE, Arnold C, Tucker GA, Schuch W, Harding S, Grierson D (1990) Inheritance and effect on ripening of antisense polygalacturonase genes in transgenic tomatoes. Plant Mol Biol 14:369–379
Stockhaus J, Höfer M, Renger G, Westhoff P, Wydrzynski T, Willmitzer L (1990) Antisense RNA efficiently inhibits formation of the 10 kd polypeptide of photosystem 11 in transgenic potato plants: analysis of the role of the 10 kd protein. EMBO J 9:3013–3021
Tautz D, Renz M (1983) An optimized freeze-squeeze method for the recovery of DNA fragments from agarose gels. Anal Biochem 132:14–19
Tieman DM, Harriman RW, Ramamohan G, Handa AK (1992) An antisense pectin methylesterase gene alters pectin chemistry and soluble solids in tomato fruit. Plant Cell 4:667–679
Van Blokland R, De Lange P, Mol JNM, Kooter JM (1993) Modulation of gene expression in plants by antisense genes. In: LeBlue B (ed) Antisense research and applications. CRC Press, London, pp 125–148
Van der Krol AR, Mol JNM, Stuitje AR (1988a) Modulation of eukaryotic gene expression by complementary RNA or DNA sequences. Biotechniques 6:958–976
Van der Krol AR, Lenting PE, Veenstra J, van der Meer IM, Kroes RE, Gerats AGM, Mol JNM, Stuitje AR (1988b) An antisense chalcone synthase gene in transgenic plants inhibits flower pigmentation. Nature 333:866–869
Van der Krol AR, Mur LA, de Lange P, Mol JNM, Stuitje AR (1990) Inhibition of flower pigmentation by antisense CHS genes: promoter and minimal sequence requirements for the antisense effects. Plant Mol Biol 14:457–466
Van der Leij FR, Visser RGF, Ponstein AS, Jacobsen E, Feenstra WJ (1991) Sequence of the structural gene for granule-bound starch synthase of potato (Solanum tuberosum L) and evidence for a single point deletion in the amf allele. Mot Gen Genet 228:240–248
Van der Leij FR, Abeln ECA, Hesseling-Meinders A, Feenstra WJ (1993) A putative pseudogene behind the potato GBSS gene. Plant Mol Biol 21:567–571
paVan der Meer IM, Stam ME, van Tunen AJ, Mol JNM, Stuitje AR (1992) Antisense inhibition of flavonoid biosynthesis in petunia anthers results in male sterility. Plant Cell 4:253–262
Vieira J, Messing J (1982) The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene 19:259–268
Visser RGF (1991) Regeneration and transformation of potato by Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Plant Tissue Culture Manual 135:1–9
Visser RGF, Hergersberg M, van der Leij FR, Jacobsen E, Witholt B, Feenstra WJ (1989) Molecular cloning and partial characterization of the gene for granule-bound starch synthase from a wildtype and an amylose-free potato (Solanum tuberosum L). Plant Sci 64:185–192
Visser RGF, Somhorst I, Kuipers GJ, Ruys NJ, Feenstra WJ, Jacobsen E (1991a) Inhibition of the expression of the gene for granule-bound starch synthase in potato by antisense constructs. Mol Gen Genet 225:289–296
Visser RGF, Stolte A, Jacobsen E (1991b) Expression of a chimeric granule-bound starch synthase-GUS gene in transgenic potato plants. Plant Mol Biol 17:691–699
Vos-Scheperkeuter GH, de Boer W, Visser RGF, Feenstra WJ, Witholt B (1986) Identification of granule-bound starch synthase in potato tubers. Plant Physiol 82:411–416
Watson CF, Grierson D (1993) Antisense RNA in plants. In: Hiatt A (ed) Transgenic plants, fundamentals and applications. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 255–281
Williams PC, Kuzin FD, Hlynka I (1970) A rapid colorimetric procedure for estimating the amylose content of starches and flours. Cereal Chem 47:411–420
Zrenner R, Willmitzer L, Sonnewald U (1993) Analysis of the expression of potato uridinephosphate-glucosepyrophosphorylase and its inhibition by antisense RNA. Planta 190:247–252
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by H. Saedler
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuipers, A.G.J., Soppe, W.J.J., Jacobsen, E. et al. Factors affecting the inhibition by antisense RNA of granule-bound starch synthase gene expression in potato. Molec. Gen. Genet. 246, 745–755 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00290722
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00290722