Abstract
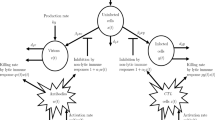
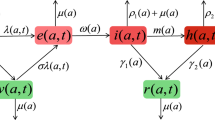
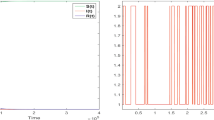
In this study, we investigate systematically the role played by the reproductive number (the number of secondary infections generated by an infectious individual in a population of susceptibles) on single group populations models of the spread of HIV/AIDS. Our results for a single group model show that if R ⩽ 1, the disease will die out, and strongly suggest that if R > 1 the disease will persist regardless of initial conditions. Our extensive (but incomplete) mathematical analysis and the numerical simulations of various research groups support the conclusion that the reproductive number R is a global bifurcation parameter. The bifurcation that takes place as R is varied is a transcritical bifurcation; in other words, when R crosses 1 there is a global transfer of stability from the infection-free state to the endemic equilibrium, and vice versa. These results do not depend on the distribution of times spent in the infectious categories (the survivorship functions). Furthermore, by keeping all the key statistics fixed, we can compare two extremes: exponential survivorship versus piecewise constant survivorship (individuals remain infectious for a fixed length of time). By choosing some realistic parameters we can see (at least in these cases) that the reproductive numbers corresponding to these two extreme cases do not differ significantly whenever the two distributions have the same mean. At any rate a formula is provided that allows us to estimate the role played by the survivorship function (and hence the incubation period) in the global dynamics of HIV. These results support the conclusion that single population models of this type are robust and hence are good building blocks for the construction of multiple group models. Our understanding of the dynamics of HIV in the context of mathematical models for multiple groups is critical to our understanding of the dynamics of HIV in a highly heterogeneous population.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, R. M.: The epidemiology of HIV infection: variable incubation plus infectious period and heterogeneity in sexual activity. J. R. Stat. Soc. A 151, 66–93 (1988)
Anderson, R. M., May, R. M.: Transmission dynamics of HIV infection. Nature 326, 137–142 (1987)
Anderson, R. M., May, R. M., Medley, G. F., Johnson, A.: A preliminary study of the transmission dynamics of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), the causative agent of AIDS. IMA J. Math. Med. Biol. 3, 229–263 (1986)
Barré-Sinoussi, F., Chermann, J.-C., Rey, F., Nugeyre, M. T., Chamaret, S., Gruest, J., Dauguet, C., Axler-Blin, C., Brun-Vézinet, F., Rouzioux, C., Rozenbaum, W., Montagnier, L.: Isolation of a T-lymphotropic retrovirus from a patient at risk for acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). Science 220, 868–870 (1983)
Blythe, S. P., Anderson, R. M.: Distributed incubation and infectious periods in models of the transmission dynamics of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). IMA J. Math. Med. Bio. 5, 1–19 (1988)
Castillo-Chavez, C., Cooke, K., Huang, W., Levin, S. A.: The role of long periods of infectiousness in the dynamics of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. In: Castillo-Chavez, C., Levin, S. A., Shoemaker, C. (eds.) Mathematical approaches to resource management and epidemiology. (Lect. Notes Biomath., in press) Berlin Heidelberg New York: Springer 1989a
Castillo-Chavez, C., Cooke, K., Huang, W., Levin, S. A.: Results on the dynamics for models for the sexual transmission of the human immunodeficiency virus. Appl. Math. Lett., in press (1989b)
Dietz, K., Hadeler, K. P.: Epidemiological models for sexually transmitted diseases. J. Math. Biol. 26, 1–26 (1988)
Francis, D. F., Feorino, P. M., Broderson, J. R., McClure, H. M., Getchell, J. P., McGrath, C. R., Swenson, B., McDougal, J. S., Palmer, E. L., Harrison, A. K., Barré-Sinoussi, F., Chermann, J.-C., Montagnier, L., Curran, J. W., Cabradilla, C. D., Kalyanaraman, V. S.: Infection of chimpanzees with lymphadenopathy-associated virus. Lancet 2, 1276–1277 (1984)
Gallo, R. C.: The first human retrovirus. Scientific American 255, 88–98 (1986)
Gallo, R. C.: The AIDS virus. Scientific American 256, 47–56 (1987)
Gallo, R. C., Salahuddin, S. Z., Popovic, M., Shearer, G. M., Kaplan, M., Haynes, B. F., Palker, T. J., Redfield, R., Oleske, J., Safai, B., White, G., Foster, P., Markhamet, P. D.: Frequent detection and isolation of sytopathic retroviruses (HTLV-III) from patients with AIDS and at risk for AIDS. Science 224, 500–503 (1984)
Hethcote, H. W., Stech, H. W., van den Driessche, P.: Nonlinear oscillations in epidemic models. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 40, 1–9 (1981)
Hethcote, H. W., van Ark, J. W.: Epidemiological methods for heterogeneous populations: proportional mixing, parameter estimation, and immunization programs. Math. Biosci. 84, 85–118 (1987)
Huang, W., Castillo-Chavez, C., Cooke, K., Levin, S. A.: On the role of long incubation periods of in the dynamics of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Part 2: Multiple group models. In: Castillo-Chavez, C. (ed.) Mathematical and statistical approaches to AIDS transmission and epidemiology. (Lect. Notes Biomath., in preparation) Berlin Heidelberg New York: Springer 1989a
Huang, W., Cooke, K., Castillo-Chavez, C.: Multiple group models for the dynamics of HIV/AIDS transmission with proportionate and preferred mixing, and multiple endemic equilibria (in preparation, 1989b)
Hyman, J.M., Stanley, E. A.: A risk base model for the spread of the AIDS virus. Math. Biosci. 90, 415–473 (1988)
Kingsley, R. A., Kaslow, R., Rinaldo, C. R., Jr., Detre, K., Odaka, N., Van Raden, M., Detels, R., Polk, B. F., Chimel, J., Kersey, S. F., Ostrow, D., Visscher, B.: Risk factors for seroconversion to human immunodeficiency virus among male homosexuals, Lancet 1, 345–348 (1987)
Lange, J. M. A., Paul, D. A., Huisman, H. G., De Wolf, F., Van den Berg, H., Roel, C. A., Danner, S. A., Van der Noordaa, J., Goudsmit, J.: Persistent HIV antigenaemia and decline of HIV core antibodies associated with transition to AIDS. Brit. Med. J. 293, 1459–62 (1986)
Medley, G. F., Anderson, R. M., Cox, D. R., Billiard, L.: Incubation period of AIDS in patients infected via blood transfusions. Nature 328, 719–721 (1987)
Miller, R. K.: On the linearization of Volterra integral equations. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 23, 198–208 (1968)
Miller, R. K.: Nonlinear Volterra integral equations. Menlo Park: Benjamin 1971
Pickering J., Wiley, J. A., Padian, N. S., et al.: Modeling the incidence of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) in San Francisco, Los Angeles, and New York. Math. Modelling 7, 661–688 (1986)
Salahuddin, S. Z., Groopman, J. E., Markham, P. D., Sarngaharan, M. G., Redfield, R. R., McLane, M. F., Essex, M., Sliski, A., Gallo, R. C.: HTLV-III in symptom-free seronegative persons. Lancet 2, 1418–1420 (1984)
Thieme, H., Castillo-Chavez, C., Cooke, K.: On the effects of variable infectivity in the dynamics of HIV/AIDS. In: Castillo-Chavez, C., Levin, S. A., Shoemaker, C. (eds.) Mathematical approaches to resource management and epidemiology. (Lect. Notes Biomath., in press) Berlin Heidelberg New York: Springer 1989
Wong-Staal, F., Gallo, R. C.: Human T-lymphotropic retroviruses. Nature 317, 395–403 (1985)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Castillo-Chavez, C., Cooke, K., Huang, W. et al. On the role of long incubation periods in the dynamics of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). J. Math. Biology 27, 373–398 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00290636
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00290636