Summary
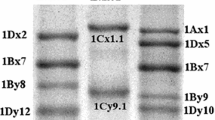
The high molecular weight (HMW) subunit composition of glutenin was analysed by sodium dodecyl sulphate, polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) in the A genome of 497 diploid wheats and in 851 landraces of bread wheat. The material comprised 209 accessions of wild Triticum monococcum ssp. boeoticum from Greece, Turkey, Lebanon, Armenia, Iraq, and Iran; 132 accessions of the primitive domesticate T. monococcum ssp. monococcum from many different germplasm collections; one accession of free-threshing T. monococcum ssp. sinskajae; 155 accessions of wild T. urartu from Lebanon, Turkey, Armenia, Iraq, and Iran; and landraces of T. aestivum, mainly from the Mediterranean area and countries bordering on the Himalayan Mountains. Four novel HMW glutenin sub-units were discovered in the landraces of bread wheat, and the alleles that control them were designated Glu-Ald through Glu-Alg, respectively. The HMW subunits of T. monococcum ssp. boeoticum have a major, “x” subunit of slow mobility and several, less prominent, “y” subunits of greater mobility, all of which fall within the mobility range of HMW subunits reported for bread wheat. In T. monococcum ssp. monococcum the range of the banding patterns for HMW subunits was similar to that of ssp. boeoticum. However, two accessions, while containing “y” subunits were null for “x” subunits. The single accession of Triticum monococcum ssp. sinskajae had a banding pattern similar to that of most ssp. boeoticum and ssp. monococcum accessions. The HMW subunit banding patterns of T. urartu accessions were distinct from those of T. monococcum. All of them contained one major “x” and most contained one major “y” subunit. In the other accessions a “y” subunit was not expressed. The active genes for “y” subunits, if transferred to bread wheat, may be useful in improving bread-making quality.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dorofeev VF, Korovina ON (1979) Flora of cultivated plants in wheat. Kolos, Leningrad, USSR
Forde J, Malpica J-M, Halford NG, Shewry PR, Anderson OD, Greene FC, Miflin BJ (1985) The nucleotide sequence of a HMW glutenin subunit gene located on chromosome 1A of wheat (Triticum aestivum). Nucleic Acids Res 13:6817–6832
Harberd NP, Bartels D, Thompson RD (1986) DNA restriction fragment variation in the gene family encoding high molecular weight (HMW) glutenin subunits of wheat. Biochem Genet 24:579–596
Holt LM, Astin R, Payne PI (1981) Structural and genetical studies on the high-molecular-weight subunits of wheat glutenin. 2. relative isoelectric points determined by two-dimensional fractionation in polyacrylamide gels. Theor Appl Genet 60:237–243
Johnson BL (1975) Identification of the apparent B-genome donor of wheat. Can J Genet Cytol 17:21–39
Johnson BL, Dhaliwal HS (1976) Reproductive isolation of Triticum boeoticum and T. urartu and the origin of the tetraploid wheats. Am J Bot 63:1088–1094
Law CN, Payne PI (1983) Genetical aspects of breeding for improved grain protein content and type in wheat. J Cereal Sci 1:79–93
Payne PI, Law CN, Mudd EE (1980) Control by homoeologous group 1 chromosomes of the high-molecular-weight subunits of glutenin, a major protein of wheat endosperm. Theor Appl Genet 58:113–120
Payne PI, Holt LM, Law CN (1981) Structural and genetical studies on the high-molecular-weight subunits of wheat glutenin. 1. Allelic variation in subunits amongst varieties of wheat (Triticum aestivum). Theor Appl Genet 60:229–236
Payne PI, Corfield KG, Holt LM, Blackman JA (1981) Correlations between the inheritance of certain high-molecular-weight subunits of glutenin and bread-making quality in progenies of six crosses of bread wheat. J Sci Food Agric 32:51–60
Payne PI, Holt LM, Thompson RD. Bartels D, Harberd NP, Harris PA, Law CN (1983) The high-molecular-weight subunits of glutenin: classical genetics, molecular genetics and the relationship to bread-making quality. In: Sakomoto S (ed) Proc 6th Int Wheat Genet Symp. Kyoto, Japan, pp 827–834
Payne PI, Lawrence GJ (1983) Catalogue of alleles for the complex gene loci, Glu-A1, Glu-B1 and Glu-D1 which code for high-molecular-weight subunits of glutenin in hexaploid wheat. Cereal Res Commun 11:29–35
Payne PI, Holt LM, Jackson EA, Law CN (1984) Wheat storage proteins: their genetics and their potential for manipulation by plant breeding. Philos Trans R Soc London, Ser B 304:359–371
Sharma HC, Waines JG (1981) The relationships between male and female fertility and among taxa in diploid wheats. Am J Bot 68:449–451
Thompson RD, Bartels D, Harberd NP, Flavell RB (1983) Characterisation of the multigene family coding for HMW glutenin subunits in wheat using cDNA clones. Theor Appl Genet 67:87–96
Waines (1983) Genetic resources in diploid wheats: the case for diploid commercial wheats. In: Sakomoto S (ed) Proc 6th Int Wheat Genet Symp. Kyoto, Japan, pp 115–122
Witcombe JR (1975) Wheat and barley from two Himalayan regions. Euphytica 24:431–434
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by H.F.Linskens
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Waines, J.G., Payne, P.I. Electrophoretic analysis of the high-molecular-weight glutenin subunits of Triticum monococcum, T. urartu, and the A genome of bread wheat (T. aestivum). Theoret. Appl. Genetics 74, 71–76 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00290086
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00290086