Abstract
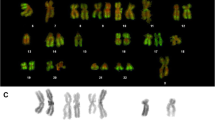
A monoclonal antibody against histone 2B (anti-H2B) was used as a reagent to stain isolated chromosomes for analysis using flow cytometry. Chromosome suspensions were treated with a mouse monoclonal antibody specific for the histone 2B (clone HBC-7) and then with a fluorescein-labeled goat anti-mouse-IgM antibody. The chromosomes were also stained for DNA content with either Hoechst 33258 or propidium iodide. The amount of antibody and the amount of DNA-specific stain bound to each chromosome were measured simultaneously using flow cytometry. The order of the steps in the staining protocol is important. Propidium iodide prevents anti-H2B from binding to chromosomes, and therefore must be added only after antibody labeling is completed. In contrast, the addition of Hoechst 33258 before antibody labeling reduces antibody binding by only 20%–30%. Binding of anti-H2B was proportional to the DNA content of both human and Chinese hamster chromosomes. Human chromosomes bind an average of three to four times more anti-H2B than do Chinese hamster or mouse chromosomes of the same DNA content. This was determined by analyzing mixtures of human and Chinese hamster chromosomes and human and mouse chromosomes. The results demonstrate that it is possible to label the proteins of chromosomes in suspension with fluorescent antibodies and to use these reagents for the analysis of chromosome structure by flow cytometry.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bustin M, Kurth PD, Moudrianakis EN, Goldblatt D, Sperling, Rizzo WB (1978) Immunological probes for chromatin structure. Cold Spring Harbor Symp XLII:379–388
Cantor C, Schimmel P (1980) Biophysical chemistry. Vol 3. The behavior of biological macromolecules. W.F. Freeman, San Francisco
Carrano AV, Gray JW, Langlois RG, Burkhart-Schultz K, Van Dilla MA (1979) Measurement and purification of human chromosomes by flow cytometry and sorting. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:1382–1384
Comings D (1975) Mechanisms of chromosome banding. VIII. Hoechst 33258-DNA interaction. Chromosoma 52:229–243
Compton LL, Bellard M, Chambon P (1976) Biochemical evidence of variability in the DNA repeat length in the chromatin of higher eukaryotes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 73:4382–4386
Davies KE, Young BD, Elles EG, Hill ME, Williamson R (1981) Cloning of a representative genomic library of the human X chromosome after sorting by flow cytometry. Nature 293:374–376
Dean P, Pinkel D (1978) High resolution dual laser flow cytometry. J Histochem Cytochem 26:622–627
Elgin SCR, Schilling J, Hood LE (1979) Sequence of histone 2B in Drosophila melanogaster. Biochemistry 18:5679–5685
Gray JW, Carrano AV, Steinmetz LL, Van Dilla MA, Moore II DH, Mayall BH, Mendelsohn ML (1975) Chromosome measurement and sorting by flow systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 72:1231–1234
Gray JW, Langlois RG, Carrano AV, Burkhart-Schultz K, Van Dilla MA (1979) High resolution chromosome analysis in one and two parameter flow cytometry. Chromosoma 73:9–27
Martinage A, Mangeat P, Santiere P, Marchiz-Mouren G, Biserte E (1979) Amino acid sequence of rat thymus histone H2B and identification of the in vitro phosphorylation sites. Biochimie 61:61–70
Mazrimas JA, Balhorn R (1983) Reversed phase HPLC separation of somatic histones. Liquid Chromatography 1:104–105
McGhee JD, Felsenfeld G (1980) Nucleosome structure. Ann Rev Biochem 49:1115–1156
Ohe Y, Hayaishi H, Awai K (1979) Human spleen histone H2B: isolation and amino acid sequence. J Biochem 86:615–624
Sell S (1978) Immunology, immunopathology and immunity. Harper and Row, New York
Silver LM, Wu CEC, Elgin SCR (1978) Immunofluorescent techniques in the analysis of chromosomal proteins. Methods Cell Biol 18:151–167
Spiker S, Isenberg I (1978) Evolutionary conservation of histone-histone binding sites: Evidence for interkingdom complex formation. Cold Spring Harbor Symp XLII:157–163
Turner BM (1981) Isolation of monoclonal antibodies to chromatin and preliminary characterization of target antigens. Eur J Cell Biol 24:266–274
Turner BM (1982) Immunofluorescent staining of human metaphase chromosomes with monoclonal antibody to histone H2B. Chromosoma 87:345–357
van den Engh GJ, Trask B, Cram S, Bartholdi M (1984) Preparation of chromosome suspensions for flow cytometry. Cytometry 5:108–117
Von Holt C, Strickland WN, Brandt WF, Strickland MS (1979) More histone structures. FEBS Lett 100:201–218
Worcel A (1978) Molecular architecture of the chromatin fiber. Cold Spring Harbor Symp XLII:313–324
Young BD, Ferguson-Smith MA, Sillar R, Boyd E (1981) High resolution analysis of human peripheral lymphocyte chromosomes by flow cytometry. Proc Natl Acad Sci 78:7727–7731
Yu L-C, Aten J, Gray JW, Carrano AV (1981) Human chromosome isolation from short-term lymphocyte culture for flow cytometry. Nature 293:154–155
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Trask, B., van den Engh, G., Gray, J. et al. Immunofluorescent detection of histone 2B on metaphase chromosomes using flow cytometry. Chromosoma 90, 295–302 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00287038
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00287038