Abstract
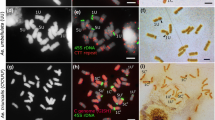
Two pairs of chromosomes (1U and 5U) in Aegilops umbellulata possess ribosomal RNA genes. This has been proven by studying wheat plants into which 1U and 5U chromosomes have been introduced separately. These plants have more ribosomal RNA genes than the recipient wheat plants and additional clusters of rDNA when examined by in situ hybridisation. The repeating rDNA unit in Aegilops umbellulata is longer than most of the units in the wheat variety Chinese Spring, the additional DNA probably being in the non-transcribed spacer. This was determined from restriction endonuclease maps of rDNA. In Chinese Spring plants possessing 1U or 5U chromosomes, the largest nucleoli are formed on 1U or 5U chromosomes and the wheat nucleolus organisers form micronucleoli. This is not because the nucleolus organisers on chromosomes 1U and 5U have many more rRNA genes than wheat nucleolus organisers. It is suggested that the Aegilops umbellulata nucleolus organisers are dominant over those of wheat because they compete more effectively for some limiting factor. — The partial inactivation of the wheat nucleolus organisers by chromosomes 1U or 5U does not result in a reduced total nucleolus volume in root tip or pollen mother cells, because of the compensation by the nucleolus organisers of chromosomes 1U or 5U. The amount of RNA in seedlings is not markedly affected by the partial inactivation of the wheat nucleolus organisers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appels, R., Driscoll, C.: Heterochromatin and highly repeated DNA sequences in rye (Secale cereale). Chromosoma (Bert.) 70, 67–89 (1978)
Appels, R., Gerlach, W.L., Dennis, E.S., Swift, H., Peacock W.J.: Molecular and chromosomal Organisation of DNA sequences coding for the ribosomal RNAs in cereals. Chromosoma (Berl.) 78, 293–311 (1980)
Bedbrook, J.R., Jones, J., O'Dell, M., Thompson, R., Flavell, R.B.: A molecular description of telomeric heterochromatin in Secale species. Cell 19, 545–560 (1980)
Bramwell, M.E., Handmaker, S.D.: Ribosomal RNA synthesis in human-mouse hybrid cells. Biochim biophys. Acta (Amst.) 232, 580–593 (1971)
Burton, K.: A study of the conditioning and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric determination of DNA. Biochem. J. 62, 315–323 (1956)
Eliceiri, G.L., Green, H.: Ribosomal RNA synthesis in human-mouse hybrid cells. J. molec. Biol. 41, 253–260 (1969)
Flavell, R.B., Martini, G.: The genetic control of nucleolus formation with special reference to common breadwheat. In: Society of exp. Biol. Symp. (C.A. Cullis, E.G. Jordan eds.) Cambridge, London: Cambridge University Press (1981)
Flavell, R.B., McPherson F.: The control of wheat malate dehydrogenase by rye chromosomes. Biochem. Genet. 7, 259–268 (1972)
Flavell, R.B., O'Dell, M.: Ribosomal RNA genes on homoeologous chromosomes of groups 5 and 6 in hexaploid wheat. Heredity 37, 377–385 (1976)
Flavell, R.B., O'Dell, M.: The genetic control of nucleolus formation in wheat. Chromosoma (Berl.) 71, 135–152 (1979)
Flavell, R.B., Smith, D.B.: Variation in nucleolar organiser rRNA gene multiplicity in wheat and rye. Chromosoma (Berl.) 47, 327–334 (1974a)
Flavell, R.B., Smith, C.B.: The role of homoeologous group 1 chromosomes in the control of rRNA genes in wheat. Biochem. Genet. 12, 271–279 (1974b)
Gerlach, W.L., Bedbrook, J.R.: Cloning and characterisation of ribosomal RNA genes from wheat and barley. Nucleic Acids Res. 7, 1869–1885 (1979)
Graham, D.E.: The isolation of high molecular weight DNA from whole organisms or large tissue masses. Anal. Biochem. 85, 609–613 (1978)
Honjo, T., Reeder, R.H.: Preferential transcription of Xenopus laevis ribosomal RNA in interspecies hybrids between Xenopus laevis and Xenopus mulleri. J. Molec. Biol. 80, 217–228 (1973)
Hutchinson, J.H., Miller, T.E., Chapman, V.: Chromosome pairing at meiosis in hybrids between Aegilops and Secale species: A study by in situ hybridisation using cloned DNA. Heredity 45, 245–254 (1980)
Kasha, K.J., Sadasivaich, R.S.: Genome relationships between Hordeum vulgare L. and H. bulbosum L. Chromosoma (Berl.) 35, 264–287 (1971)
Keep, E.: Satellite and nucleolar number in hybrids between Ribes nigrum and R. grossularia and in their backgrosses. Canad. J. Genet. Cytol. 4, 206–218 (1962)
Knowland, J., Miller, L.: Reduction of ribosomal RNA synthesis and ribosomal RNA genes in a mutant of Xenopus laevis which organises only a partial nucleolus. I. Ribosomal RNA synthesis in embryos of diploid nucleolus types. J. molec. Biol. 53, 321–328 (1970)
Loening, V.E., Ingle, J.: Diversity of RNA components in green plant tissues. Nature (Lond.) 215, 363–367 (1967)
Miller, L., Brown, D.D.: Variation in the activity of nucleolus organizers and their ribosomal gene content. Chromosoma (Berl.) 28, 430–444 (1969)
Miller, D.A., Dev, V.G., Tantravah, R., Miller, O.J.: Suppression of human nucleolus organizer activity in mouse-human somatic hybrid cells. Exp. Cell Res. 101, 235–243 (1976)
Miller, L., Knowland, J.: Reduction of Ribosomal RNA synthesis and ribosomal RNA genes in a mutant of Xenopus laevis which organises only a partial nucleolus. II. The number of ribosomal RNA genes in animals of different nucleolar types. J. molec. Biol. 53, 329–338 (1970)
Miller, O.J., Miller, D.A.: Expression of human suppression of mouse nucleolus organiser activity in mouse-human somatic cell hybrids. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.) 12, 4531–4535 (1976)
Miller, T.E., Gerlach, W.L., Flavell, R.B.: Nucleolus organiser variation in wheat and rye revealed by in situ hybridisation. Heredity 45, 377–382 (1980)
Mohan, J., Flavell, R.B.: Ribosomal RNA cistron multiplicity and nucleolar organizers in hexaploid wheat. Genetics 76, 33–44 (1974)
Phillips, R.L., Kleese, R.A., Wang, S.S.: The nucleolus organiser region of maize (Zea mays L.). Chromosomal site of DNA complementary to ribosomal RNA. Chromosoma (Berl.) 36, 79–88 (1971)
Rattenbury, J.A.: A specific staining of nucleolar substance with aceto-carmine. Stain Technol. 27, 113 (1952)
Southern, E.M.: Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J. molec. Biol. 98, 503–517 (1975)
Wallace, H., Langridge, W.H.R.: Differential amphiplasty and the control of ribosomal RNA synthesis. Heredity 27, 1–13 (1971)
Wilkinson, J.: The cytology of Salix in relation to its taxonomy. Ann. Bot. 8, 269–284 (1944)
Yeh, B.P., Peloquin, S.J.: The nucleolus associated chromosome of Solanum species and hybrids. Amer. J. Bot. 52, 626 (1965)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martini, G., O'Dell, M. & Flavell, R.B. Partial inactivation of wheat nucleolus organisers by the nucleolus organiser chromosomes from Aegilops umbellulata . Chromosoma 84, 687–700 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00286334
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00286334