Abstract
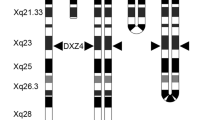
The following hypothesis is put forward: X chromatin in man condenses around a center which is situated on Xq at a short distance from the centromere. The hypothesis is based on, and explains, two classes of observations. (1) Abnormal X chromosomes that have the assumed center in duplicate form bipartite Barr bodies in part of the cells. The frequency of bipartite bodies and the distance between the two parts seem to be determined by the distance between the postulated centers. (2) A large number of variously abnormal X chromosomes have been described. Almost all of them possess the postulated center and it seems possible that the very few apparent exceptions represent misidentifications of chromosome Xq — as isochromosome i(Xp). According to the hypothesis, chromosomes lacking the center would form no Barr body and therefore presumably would not be inactivated, thus leaving the cell severely unbalanced. Furthermore, absence of the center might interfere with the viability of the chromosome itself.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Caspersson, T., Lindsten, J., Zech, L.: The nature of structural X chromosome aberrations in Turner's syndrome as revealed by quinacrine mustard fluorescence analysis. Hereditas (Lund) 66, 287–292 (1970).
Chapelle, A. de la, Schröder, J., Pernu, M.: Isochromosome for the short arm of X, a human 46, XXpi syndrome. Ann. hum. Genet. 36, 79–87 (1972).
Cohen, M. M., Lin, C.-C., Sybert, V., Orecchio, E. J.: Two human X-autosome translocations identified by autoradiography and fluorescence. Amer. J. hum. Genet. 24, 583–597 (1972).
Distèche, C., Hagemeijer, A., Frederic, J., Progneaux, D.: An abnormal large human chromosome identified as an end-to-end fusion of two X's by combined results of the new banding techniques and microdensitometry. Clin. Genet. 3, 388–395 (1972).
Paris Conference 1971: Standardization in human cytogenetics. Birth Defects: Original Article Series, VIII: 7. The National Foundation, New York 1972.
Sarto, G. E.: Cytogenetics of 50 patients with primary amenorrhea. Amer. J. Obstet. Gynec. in press, 1974.
Sears, E. R.: Misdivision of univalents in common wheat. Chromosoma (Berl.) 4, 535–550 (1952).
Southern, D. I.: Stable telocentric chromosomes produced following centric mis-division in Myrmeleotettix maculatus (Thunb.). Chromosoma (Berl.) 26, 140–147 (1969).
Steinitz-Sears, L. M.: Somatic instability of telocentric chromosomes in wheat and the nature of the centromere. Genetics 54, 241–248 (1966).
Summitt, R. L., Martens, P. R., Wilroy, R. S., Jr.: X-autosome translocation in normal mother and effectively 21-monosomic daughter. J. Pediat. (in press, 1973).
Therman, E., Sarto, G. E., Patau, K.: Apparently isodicentric but functionally monocentric X chromosome in man. Amer. J. hum. Genet. 26 (in press, 1974).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Paper no. 1687 from the Genetics Laboratory, University of Wisconsin. Supported by grants GM 15422 and HD 3084 from the National Institutes of Health, Washington, D. C.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Therman, E., Sarto, G.E. & Patau, K. Center for Barr body condensation on the proximal part of the human Xq: a hypothesis. Chromosoma 44, 361–366 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00284895
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00284895