Summary
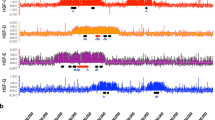
A cloned alphoid sequence, p82H, hybridizes in situ to the centromere of every human chromosome. After washing under stringent conditions, no more than 8% of the grains are located on any specific chromosome. p82H thus differs from other centromeric sequences which are reported to be chromosome specific, because it detects sequences that are conserved among the chromosomes. Two experimental approaches show that the p82H sequences are closely associated with the centromere. First, p82H remains with the relocated centromeres in an inv(19) and an inv(6) chromosome. Second, p82H hybridizes at the centromere but not to the centromeric heterochromatin of chromosomes 1, 9 and 16 that have elongated 1qh, 9qh and 16qh regions produced by short growth in 5-azacytidine. The only noncentromeric site of hybridization is at the distal end of the 9qh region.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bobrow M, Madan K, Pearson PL (1972) Staining of some specific regions of human chromosomes, particularly the secondary constriction of no. 9. Nature 238:122–124
Cooke HJ, Hindley J (1979) Cloning of human satellite III DNA: different components are on different chromosomes. Nucleic Acids Res 6:3177–3197
Devilee P, Slagboom P, Cornelisse CJ, Pearson PL (1986) Sequence heterogeneity within the human alphoid repetitive DNA family. Nucleic Acids Res 14:2059–2073
Dewald GW, Boros SJ, Conroy MM, Dahl RJ, Spurbeck JL, Vitek HA (1979) A tdic(5;15)(p13;p11) chromosome showing variation for constriction in the centromeric regions in a patient with the cri du chat syndrome. Cytogenet Cell Genet 24:15–26
Gray KM, White JW, Costanzi C, Gillespie D, Schroeder WT, Calabretta B, Saunders GF (1985) Recent amplification of an alpha satellite DNA in humans. Nucleic Acids Res 13:521–535
Harper ME, Saunders GF (1981) Localisation of single copy DNA sequences on G-banded human chromosomes by in situ hybridisation. Chromosoma 83:431–439
Hieter P, Pridmore D, Hegemann JH, Thomas M, Davis RW, Philippsen P (1985) Functional selection and analysis of yeast centromere DNA. Cell 42:913–921
Jabs EW, Wolf SF, Migeon BR (1984) Characterization of a cloned DNA sequence that is present at centromeres of all human autosomes and the X chromosome and shows polymorphic variation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:4884–4888
Jorgensen AL, Bostock CJ, Bak AL (1986) Chromosome-specific subfamilies within human alphoid repetitive DNA. J Mol Biol 187:185–196
McDermid HE, Duncan AMV, Higgins MJ, Hamerton JL, Rector E, Brasch KR, White BN (1986) Isolation and characterization of an α-satellite repeated sequence from human chromosome 22. Chromosoma 94:228–234
Manuelidis L (1978) Chromosomal localization of complex and simple repeated human DNAs. Chromosoma 66:1–21
Miller DA, Choi Y-C, Miller OJ (1983) Chromosome localization of highly repetitive human DNAs and amplified rDNA by use of restriction enzymes. Science 219:395–397
Mitchell AR, Beauchamp RS, Bostock CJ (1979) A study of sequence homologies in four satellite DNAs of man. J Mol Biol 135:127–149
Mitchell AR, Gosden JR, Miller DA (1985) p82H: A cloned sequence of the alphoid repeated DNA family found at the centromeres of all human chromosomes. Chromosoma 92:369–377
Mitchell AR, Ambros P, McBeath S, Chandley AC (1986) Molecular hybridization to meiotic chromosomes in man reveals sequence arrangement on the no. 9 chromosomes and provides clues to the nature of “parameres”. Cytogenet Cell Genet 41:89–95
Prosser J, Frommer M, Paul C, Vincent PC (1986) Sequence relationships of three human satellite DNAs. J Mol Biol 187:145–155
Rassoulzadegan M, Leopold P, Vailly J, Cuzin F (1986) Germ line transmission of autonomous genetic elements in transgenic mouse strains. Cell 46:513–519
Rigby P, Dieckmann M, Rhodes C, Berg P (1977) Labeling of DNA to high specific activity by in vitro nick translation with DNA polymerase. I. J Mol Biol 113:237–251
Sahar E, Latt SA (1978) Enhancement of banding patterns in human metaphase chromosomes by energy transfer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 75:5650
Schmid M, Grunert D, Haaf T, Engel W (1983) A direct demonstration of somatically paired heterochromatin of human chromosomes. Cytogenet Cell Genet 36:554–561
Sumner AT, Evans HJ, Buckland RA (1971) A new technique for distinguishing between human chromosomes. Nature New Biol 232:31
Waye JS, Willard HF (1985) Chromosome-specific alpha satellite DNA: Nucleotide sequence analysis of a 2.0 kilobase-pair repeat from the human X chromosome. Nucleic Acids Res 13:2731–2743
Waye JS, Wilard HF (1986) Structure, organization, and sequence of alpha satellite DNA from human chromosome 17: evidence for evolution by unequal crossing-over and an ancestral pentamer repeat shared with the human X chromosome. Mol Cell Biol 6:3156–3165
Willard HF (1985) Chromosome-specific organization of human alpha satellite DNA. Am J Hum Genet 37:524–532
Wolfe J, Darling SM, Erickson RP, Craig I, Buckle V, Rigby PR, Willard HF, Goodfellow PN (1985) Isolation and characterization of an alphoid centromere repeat family from the human Y chromosome. J Mol Biol 182:477–483
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aleixandre, C., Miller, D.A., Mitchell, A.R. et al. p82H identifies sequences at every human centromere. Hum Genet 77, 46–50 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00284712
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00284712