Summary
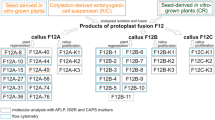
The fusion of Citrus sinensis cv. Hamlin (sweet orange) protoplasts isolated from an embryogenic suspension culture with Severinia disticha (Philippine box orange) protoplasts isolated from epicotyl-derived callus with organogenic potential, resulted in the regeneration of allotetraploid somatic hybrid plants. Plant regeneration was a function of complementation, combining the capacity for somatic embryogenesis of C. sinensis with the organogenic ability of S. disticha. Confirmation of somatic hybrid identity was based on leaf morphology, chromosome number, and analyses of phosphoglucose mutase (PGM) and malate dehydrogenase (MDH) zymograms. Hybrid plants were multiplied organogenically and exhibited morphology intermediate to that of the parents. This is the first example of somatic hybrid plants produced between sexually incompatible woody genera.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cardy BJ, Stuber CW, Goodman MM (1981) Techniques for starch gel electrophoresis of enzymes from maize (Zea mays L.). In: Institute of Statistics Mimeograph, Ser No 1317, North Carolina State University, Raleigh
Collins GB, Taylor NL, DeVerna JW (1984) In vitro approaches to interspecific hybridization and chromosome manipulation in crop plants. In: Gustafson, JP (ed) Gene manipulation in plant improvement. 16th Stadler Genet Symp, pp 323–383
Cooper WC (1961) Toxicity and accumulation of salts in citrus trees on various rootstocks in Texas. Proc Fla State Hortic Soc 74:95–104
Grosser JW, Chandler JL (1987) Aseptic isolation of leaf protoplasts from Citrus, Poncirus, CitrusXPoncirus hybrids and Severinia for use in somatic hybridization experiments. Sci Hortic 31:253–257
Grosser JW, Gmitter FG, Chandler JL (1988) Intergeneric somatic hybrid plants of Citrus sinenis cv. Hamlin and Poncirus trifoliata cv. Flying Dragon. Plant Cell Rep (in press)
Harms CT (1983) Somatic incompatibility in the development of higher plant somatic hybrids. Q Rev Biol 58:325–353
Hutchison DJ, Grimm GR (1983) Citrus clones resistant to Phytophthora parasitica: 1973 screening results. Proc Fla State Hortic Soc 86:88–91
Hutchison DJ, O'Bannon JH (1972) Evaluating the reaction of citrus selections to Tylenchulus semipenetrans. Plant Dis Rep 56:747–751
Kobayashi S, Uchimaya H, Ikeda I (1983) Plant regeneration from ‘Trovita’ orange protoplasts. Jpn J Breed 33:119–122
Menczel L, Nagy F, Kiss Z, Maliga P (1981) Streptomycin resistant and sensitive hybrids of Nicotiana tabacum and Nicotiana knightiana: Correlation of resistance with N. tabacum plastids. Theor Appl Genet 59:191–195
Murashige T, Tucker DPH (1969) Growth factor requirements of citrus tissue culture. Proc First Int Citrus Symp 3:1155–1161
Ohgawara T, Kobayashi S, Ohgawara E, Uchimaya H, Ishii S (1985) Somatic hybrid plants obtained by protoplast fusion between Citrus sinensis and Poncirus trifoliata. Theor Appl Genet 71:1–4
Soost RK, Torres AM (1981) Leaf isozymes as genetic markers in citrus. Proc Int Soc Citricult 1:7–10
Sundberg E, Glimelius K (1986) A method for production of interspecific hybrids within Brassiceae via somatic hybridization, using resynthesis of Brassica napus as a model. Plant Sci 43:155–162
Swingle WT, Reece PC (1967) The botany of citrus and its wild relatives, chap 3. In: Reuther W, Batchelor LD, Webber HJ (eds) The citrus industry, vol I. University of California Press, Berkeley, pp 190–430
Torres AM, Soost RK, Mau-Lastovicka T (1982) Citrus isozymes. J Hered 73:335–339
Vallejos CE (1983) Enzyme staining activity. In: Tanskley SA, Orton TJ (eds) Isozymes in plant genetics and breeding, part A. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 469–516
Vardi A, Speigel-Roy P, Galun E (1982) Plant regeneration from Citrus protoplasts: variability in methodological requirements among cultivars and species. Theor Appl Genet 62:171–176
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by P. Maliga
Florida Agricultural Experiment Station Journal Series No. 8198
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grosser, J.W., Gmitter, F.G. & Chandler, J.L. Intergeneric somatic hybrid plants from sexually incompatible woody species: Citrus sinensis and Severinia disticha . Theoret. Appl. Genetics 75, 397–401 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00276741
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00276741