Abstract
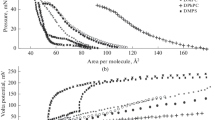
We have modelled a phospholipid bilayer as two monolayer sheets which interact with each other by a coupling which depends upon the states of the lipid hydrocarbon chains in each sheet. We make use of a model (Georgallas and Pink 1982a) and its parameters, already used to study monolayer phase changes at the LC-LE transition, in order to study the lipid main transition. Although the monolayer coexistence curve can be calculated exactly, we have made use of high-temperature series expansions to calculate the critical point of the bilayer. We also present the results of computer simulations on triangular lattices for the pressure-area isotherms. We find: (i) the interaction between the sheets of a DPPC bilayer is about 1.5–2% of the maximum interaction within the plane of each sheet; (ii) the internal lateral pressure of a DPPC bilayer is about 30.5 dyne/cm; (iii) the bilayer transition enthalpy depends sensitively upon the coupling between the sheets. Should this coupling vary from sample to sample (due, possibly, to its preparation) then very different values of transition enthalpy may be measured. (iv) We present a rough rule-of-thumb for estimating the internal lateral pressure of a bilayer from a knowledge of the corresponding monolayer pressure-area isotherms.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- LC-LE:
-
liquid condensed — liquid expanded
- DPPC:
-
dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine
- ΔQ:
-
transition enthalpy
References
Albrecht O, Gruler H, Sackmann E (1978) Polymorphism of phospholipid monolayers. J Phys (Paris) 39: 301–313
Baret JF (1981) Phase transitions in two-dimensional amphiphilic systems. Prog Surf Membr Sci 14:291–351
Bell GM, Combs LL, Dunne LJ (1981) Theory of cooperative phenomena in lipid systems. Chem Rev 81:15–48
Binder K (1979) Introduction: theory and “technical” aspects of Monte Carlo simulations. In: Binder K (ed) Monte Carlo methods in statistical physics. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 1–45
Blume A (1979) A comparative study of the phase transitions of phospholipid bilayers and monolayers. Biochim Biophys Acta 557:32–44
Cadenhead DA, Müller-Landau F, Kellner BMJ (1980) Phase transitions in insoluble one and two-component films at the air/water interface. In: Sinha SK (ed) Ordering in two-dimensions North-Holland, New York, pp 73–81
Chapman D (1975) Phase transitions and fluidity characteristics of lipids and cell membranes. Q Rev Biophys 8:185–235
Chapman D (1980) Studies using model biomembrane systems. In: Bittar E (ed) Membrane structure and function, vol 1. Wiley, London, pp 103–150
Dalton N, Wood DW (1969) Critical point behaviour of the Ising model with higher neighbour interactions present. J Math Phys 10:1271–1302
Dill KA, Flory PJ (1980) Interphase of chain molecules: monolayers and lipid bilayer membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77:3115–3119
Domb C, Sykes MF (1975) On the susceptibility of a ferromagnet above the Curie point. Proc R Soc London Ser A 240:214–228
Doniach S (1978) Thermodynamic fluctuations in phospholipid bilayers. J Chem Phys 68:4912–4916
Fisher ME, Au-Yang H (1979) Inhomogeneous differential approximants for power series. J Phys A 12:1677–1692
Fulford AJC, Peel WE (1980) Lateral pressures in biomembranes estimated from the dynamics of fluorescent probes. Biochim Biophys Acta 598:237–246
Gaines GL Jr (1966) Insoluble monolayers at liquid-gas interfaces. Wiley-Interscience, New York
Georgallas A, Pink DA (1982a) Phase transitions in monolayers of saturated lipids. Exact results and Monte Carlo simulations. J Colloid Interface Sci 89:107–116
Georgallas A, Pink DA (1982b) A new theory of the liquid condensed-liquid expanded phase transition in lipid monolayers. Can J Phys 60:1678–1681
Hunter DL (1969) Pade approximant analysis of the Ising model specific heat above the Curie point. J Phys C 2:941–947
Hunter DL, Baker GA Jr (1973) Methods of series analysis. I. comparison of current methods used in the theory of critical phenomena. Phys Rev B 7:3346–3376
Hunter DL, Baker GA Jr (1979) Methods of series analysis. II Integral approximant methods. Phys Rev B 19:3808–3821
Marčelja S (1974) Chain ordering in liquid crystals. II Structure of bilayer membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta 367:165–176
Meraldi J-P, Schlitter J (1981) A statistical mechanical treatment of fatty acyl chain ordering in phospholipid bilayers and correlation with experimental data. A: Theory. Biochim Biophys Acta 645:183–192; B: Dipalmitoyl-3-sn-phosphatidylcholine, 193–210
Nagle JF (1976) Theory of lipid monolayer and bilayer phase transitions: effect of headgroup interactions. J Membr Biol 27:233–250
Oitmaa J (1981) The square lattice Ising model with first and second neighbour interactions. J Phys A 14:1159–1168
Pink DA, Chapman D (1979) Protein-lipid interactions in bilayer membranes: A lattice model. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:1542–1547
Pink DA, Georgallas A, Zuckermann MJ (1980) Phase transitions and critical indices of a phospholipid bilayer model. Z Phys BCondensed Matter 40:103–110
Pink DA (1984a) Theoretical models of monolayers bilayers and biological membranes In: Chapman D (ed) Biomembrane structure and function, vol 4. McMillan Press, London, pp 319–354
Pink DA (1984b) Theoretical studies of phospholipid bilayers and monolayers. Perturbing probes, monolayer phase transitions and computer simulations of lipid-protein bilayers. Can J Biochem (in press)
Roskies RZ (1981) Reconciliation of high temperature series and renormalization group results by suppressing confluent singularies. Phys Rev B 24:5305–5317
Syozi I (1972) Transformation of Ising models. In: Domb C, Green MS (eds) Phase transitions and critical phenomena, vol 1. Academic Press, London, pp 269–329
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Work supported in part by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Georgallas, A., Hunter, D.L., Lookman, T. et al. Interactions between two sheets of a bilayer membrane and its internal lateral pressure. Eur Biophys J 11, 79–86 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00276622
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00276622