Summary
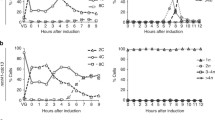
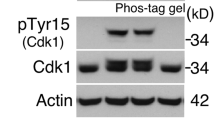
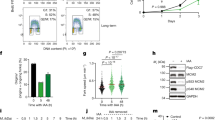
The product of the CDC7 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae has multiple cellular functions, being needed for the initiation of DNA synthesis during mitosis as well as for synaptonemal complex formation and commitment to recombination during meiosis. The CDC7 protein has protein kinase activity and contains the conserved residues characteristic of the protein kinase catalytic domain. To determine which of the cellular functions of CDC7 require this protein kinase activity, we have mutated some of the conserved residues within the CDC7 catalytic domain and have examined the ability of the mutant proteins to support mitosis and meiosis. The results indicate that the protein kinase activity of the CDC7 gene product is essential for its function in both mitosis and meiosis and that this activity is potentially regulated by phosphorylation of the CDC7 protein.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bahman AM, Buck V, White A, Rosamond -J (1988) Characterisation of the CDC7 product of Saccharomyces cerevisiae as a protein kinase needed for the initiation of DNA synthesis. Biochim Biophys Acta 951:335–343
Booher R, Beach D (1986) Site-specific mutagenesis of cdc2 +, a cell cycle control gene of the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Mol Cell Biol 6:3523–3530
Brill SJ, Stillman B (1989) Yeast replication factor-A functions in the unwinding of the SV40 origin of DNA replication. Nature 342:92–95
Bryant BL, Parsons JT (1984) Amino acid alterations within a highly conserved region of the Rous sarcoma virus src gene product pp60src inactivate tyrosine protein kinase activity. Mol Cell Biol 4:862–866
Carter P, Bedouelle H, Winter G (1985) Improved oligonucleotideinduced mutagenesis using M13 vectors. Nucleic Acids Res 13:4431–4443
Ham J, Moore D, Rosamond J, Johnston IR (1989) Transcriptional analysis of the CDC7 protein kinase gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res 17:5781–5792
Hanks SK, Quinn AM, Hunter T (1988) The protein kinase family: conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domain. Science 241:42–52
Hannink M, Donoghue DJ (1985) Lysine residue 121 in the proposed ATP-binding site of the v-mos protein is required for transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:7894–7898
Hartwell LH (1973) Three additional genes required for deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol 115:966–974
Hereford LM, Hartwell LH (1974) Sequential gene function in the initiation of S. cerevisiae DNA synthesis. J Mol Biol 84:445–461
Hollingsworth RE, Sclafani RA (1990) DNA metabolism gene CDC7 from yeast encodes a serine (threonine) protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:6272–6276
Humphreys GO, Willshaw GA, Anderson ES (1975) A simple method for the preparation of large quantities of pure plasmid DNA. Biochim Biophys Acta 383:457–463
Jazwinski SM (1988) CDC7-dependent protein kinase activity in yeast replicative-complex preparations. Proc Nail Acad Sci USA 85:2101–2105
Kamps MP, Taylor SS, Sefton BM (1984) Direct evidence that oncogenic tyrosine kinases and cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinases have homologous ATP binding sites. Nature 310:589–592
Krek W, Nigg EA (1991) Differential phosphorylation of vertebrate p34cdc2 kinase at the G1/S and G2/M transitions of the cell cycle. Identification of major phosphorylation sites. EMBO J 10:305–316
Lucchini G, Francesconi S, Foiani M, Badaracco G, Plevani P (1987) Yeast DNA polymerase-DNA primase complex: cloning of PRI1, a single essential gene related to DNA primase activity. EMBO J 6:737–742
Maxam AM, Gilbert W (1977) A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74:560–564
Miller JH (1972) Experiments in molecular genetics. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Njagi GDE, Kilbey BJ (1982) cdc7-1, a temperature-sensitive cell-cycle mutant which interferes with induced mutagenesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet 186:478–481
Patterson MN, Sclafani RA, Fangman WL, Rosamond J (1986) Molecular characterization of cell cycle gene CDC7 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol 6:1590–1598
Rose MD, Novick P, Thomas JH, Botstein D, Fink GR (1987) A Saccharomyces cerevisiae genomic plasmid bank based on a centromere-containing shuttle vector. Gene 60:237–243
Sanger F, Nicklen S, Coulson AR (1977) DNA sequencing with chain terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74: 5463–5467
Schild D, Byers B (1987) Meiotic effects of DNA defective cell division cycle mutations of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Chromosoma 70:109–130
Sclafani RA, Patterson M, Rosamond J, Fangman WL (1988) Differential regulation of the yeast CDC7 gene during mitosis and meiosis. Mol Cell Biol 8:293–300
Sherman F, Fink GR, Hicks J (1979) Methods in yeast genetics. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Simchen G (1974) Are mitotic functions required in meiosis? Genetics 76:745–753
Synder MA, Bishop JM, McGrath JP, Levinson AD (1985) A mutation at the ATP-binding site of pp60v-src abolishes kinase activity, transformation and tumorigenicity. Mol Cell Biol 5:1772–1779
Tschumper G, Carbon J (1983) Copy number control by a yeast centromere. Gene 23:221–232
Warren G, Sherratt D (1978) Incompatibility and transforming efficiency of Co1E1 and related plasmids. Mol Gen Genet 161:39–47
Weinmaster G, Zoller MJ, Pawson T (1986) A lysine in the ATPbinding site of p130gap-fps is essential for protein-tyrosine kinase activity. EMBO J 5:69–76
Wierenga RK, Hol WGJ (1983) Predicted nucleotide-binding properties of p21 protein and its cancer-associated variant. Nature 302:842–844
Yanisch-Perron C, Vieira J, Messing J (1985) Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mpl8 and pUC19 vectors. Gene 33:103–119
Zoller MJ, Nelson NC, Taylor SS (1981) Affinity labelling of cAMP-dependent protein kinase with p-fluorosulfonylbenzoyl adenosine. J Biol Chem 256:10837–10842
Zoller MJ, Smith M (1984) Oligonucleotide directed mutagenesis: a simple method using two oligonucleotide primers and a singlestranded DNA template. DNA 3:479–488
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by. B.J. Kilbey
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Buck, V., White, A. & Rosamond, J. CDC7 protein kinase activity is required for mitosis and meiosis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae . Molec. Gen. Genet. 227, 452–457 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00273937
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00273937