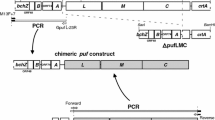
Summary
The transcription of the polycistronic puf operon which encodes pigment binding proteins of the reaction center and light-harvesting complex I of Rhodobacter capsulatus is regulated by the oxygen tension in the culture. A DNA sequence upstream of the puf transcriptional start was identified as a protein binding site. A DNA fragment carrying this DNA sequence participated in the formation of two DNA-protein complexes. The relative amounts of the two complexes were dependent on the oxygen tension in cultures from which the cytosolic fraction used for the in vitro binding studies was isolated. A single base pair transition within the protein binding site affected the oxygen-dependent expression of puf in vivo and the formation of DNA-protein complexes in vitro. The data suggest that the formation of specific DNA-protein complexes is involved in the oxygen-dependent regulation of the puf promoter. A DNA fragment containing the promoter region of the puc operon that encodes proteins of the light-harvesting complex II acted as a competitor for the formation of the DNA-protein complexes with the puf-specific fragment, indicating coregulation of the two operons.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams CW, Forrest ME, Cohen SN, Beatty T (1989) Structural and functional analysis of transcriptional control of the Rhodobacter capsulatus puf operon. J Bacteriol 171:473–482
Bauer CE, Marrs BL (1988) Rhodobacter capsulatus puf operon encodes a regulatory protein (PUFQ) for bacteriochlorophyll biosynthesis. Proc Nail Acad Sci USA 85:7074–7078
Bauer CE, Young DA, Marrs BL (1988) Analysis of the Rhodobacter capsulatus puf operon. Location of the oxygen-regulated promoter region and the identification of an additional puf-encoded gene. J Biol Chem 263:4820–4827
Beringer JE, Beynon JL, Buchanan-Wellaston AV, Johnston AWB (1978) Transfer of drug-resistance transposon Tn5 to Rhizobium. Nature 276:633–634
Belasco JG, Beatty JT, Adams CW, van Gabain A, Cohen SN (1985) Differential expression of photosynthetic genes in R. capsulata results from segmental differences in stability within a polycistronic transcript. Cell 40:171–181
Boyer HW, Roulland-Dussoix D (1969) A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in E. coli. J Mol Biol 41:459–472
Casadaban MJ, Cohen SN (1980) Analysis of gene control signals by DNA fusion and cloning in E. coli. J Mol Biol 138:174–207
Clark WG, Davidson E, Marrs BL (1984) Variation of levels of mRNA coding for antenna and reaction center polypeptides in Rhodopseudomonas capsulata in response to changes in oxygen concentration. J Bacteriol 157:945–948
Drews G (1983) Mikrobiologisches Praktikum. Springer Verlag, Berlin
Drews G, Oelze J (1981) Organization and differentiation of membranes from phototrophic bacteria. Adv Microbiol Physiol 22:1–97
Figurski DH, Helinski DR (1979) Replication of an origin-containing derivative of plasmid RK2 dependent on a plasmid function provided in trans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:1648–1652
von Gabain A, Belasco JG, Schottel JL, Chang ACY, Cohen SN (1983) Decay of mRNA in E. coli: investigation of the fate of specific segments of transcripts. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80:653–657
Innis MA, Myambo KB, Gelfand DH, Brow MAD (1988) DNA sequencing with Thermophilus aquaticus DNA polymerase and direct sequencing of polymerase chain reaction amplified DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:9436–9440
Kaufmann N, Hddig H, Drews G (1984) Transposon Tn5 mutagenesis of genes for the photosynthetic apparatus in R. capsulata. Mol Gen Genet 198:153–158
Klug G, Cohen SN (1988) Pleiotropic effects of localized Rhodobacter capsulatus puf operon deletions on the production of light-absorbing pigment-protein complexes. J Bacteriol 170:5814–5821
Klug G, Drews G (1984) Construction of a gene bank of R. capsulata using a broad host range cloning system. Arch Microbiol 139:319–325
Klug G, Kaufmann N, Drews G (1984) The expression of genes encoding proteins of B800-850 antenna complex and ribosomal RNA in Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. FEBS Lett 117:61–65
Klug G, Kaufmann N, Drews G (1985) Gene expression of pigment binding proteins of the bacterial photosynthetic apparatus: Transcription and assembly in the membrane of Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:6486–6489
Marrs BL (1981) Mobilization of genes for photosynthesis from Rhodopseudomonas capsulata by a promiscuous plasmid. J Bacteriol 146:1003–1012
Marrs BL (1974) Genetic recombination in Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 71:971–973
Miller JH (1972) Experiments in Molecular Genetics. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Narro ML, Adams CW, Cohen SN (1990) Isolation and characterization of mutants defective in oxygen regulation of the puf operon of Rhodobacter capsulatus. J Bacteriol 172:4549–4554
Ronson CW, Nison BT, Ausubel FM (1987) Conserved domains in bacterial regulatory proteins that respond to environmental stimuli. Cell 49:579–581
Southern EM (1975) Detection of specific DNA sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol 98:503–517
Suissa M (1983) Spectrophotometric quantitation of silver grain eluted from autoradiographs. Anal Biochem 133:511–514
Tichy HV, Oberle B, Stiehle H, Schiltz E, Drews G (1989) Genes downstream from pucA are essential for formation of the B800850 complex of R. capsulatus. J Bacteriol 171:4914–4922
Youvan DC, Ismail S (1985) Light harvesting 11 (B800-850 complex) structural genes from Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:58–62
Youvan DC, Bylina EJ, Alberti M, Begusch, Hearst JE (1984) Nucleotide and deduced polypeptide sequence of the photosynthetic reaction center, B870 antenna, and flanking polypeptides from Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. Cell 37:949–957
Youvan DC, Ismail ST, Bylina EJ (1985) Chromosomal deletion and plasmid complementation of the photosynthetic reaction center and light harvesting genes from Rhodopseudomonas capsulata. Gene 38:19–30
Yu P-L, Hohn B, Falk H, Drews G (1982) Molecular cloning of the ribosomal RNA genes of the photosynthetic bacterium R. capsulata. Mol Gen Genet 188:392–398
Zucconi AP, Beatty JT (1988) Posttranscriptional regulation by light of the steady-state levels of mature B800-850 light-harvesting complex in R. capsulatus. J Bacteriol 170:877–882
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by J.W. Lengeler
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Klug, G. A DNA sequence upstream of the puf operon of Rhodobacter capsulatus is involved in its oxygen-dependent regulation and functions as a protein binding site. Mol Gen Genet 226, 167–176 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00273600
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00273600