Summary
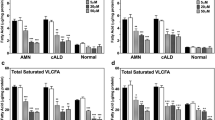
Cerebro-hepato-renal (Zellweger) syndrome, adrenoleukodystrophy, and Refsum's disease patients can be divided into at least five distinct groups, according to the nature of their plasma changes and their fibroblast phytanic acid oxidase activities. The biochemical changes in the plasma vary from an increase in a single metabolite or group of structurally related metabolites, such as in X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy (ALD) and classical Refsum's disease, to an increase in a number of structurally distinct metabolites, as in neonatal ALD/Zellweger syndrome, and infantile Refsum's disease. All patients, with the exception of those with the X-linked form of adrenoleukodystrophy are deficient in phytanic acid oxidase activity. The great similarity observed in neonatal adrenoleukodystrophy/Zellweger syndrome and infantile Refsum's disease suggests that the basic biochemical lesion in each may be similar or at least closely related.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berkovic SF, Zajac JD, Warburton DJ, Merory JD, Fellenberg AJ, Poulos A, Pollard AC (1983) Adrenomyeloneuropathy in clinical and biochemical diagnosis. Aust NZ J Med 13:594–600
Borst P (1983) Animal peroxisomes (microbodies) lipid biosynthesis and the Zellweger syndrome. Trends Biochem Sci 8:269–272
Brown FR, McAdams AJ, Cullins JW, Konkol R, Singh I, Moser AB, Moser HW (1982) Cerebro-hepato-renal (Zellweger) syndrome and neonatal adrenoleukodystrophy. Similarities in phenotype and accumulation of very long chain fatty acids. Johns Hopkins Med J 151:344–351
Burton BK, Reed SP, Remy WT (1981) Hyperpipecolic acidemia: Clinical and biochemical observations in two male siblings. J Pediatr 99:729–734
Danks DM, Tippett P, Adams C, Campbell P (1975) Cerebro-hepatorenal syndrome of Zellweger. A report of eight cases with comments upon the incidence, liver lesion and a fault in pipecolic acid metabolism. J Pediatr 86:328–387
Eldjarn L, Stokke P, Try K (1975) Biochemical aspects of Refsum's disease and principles for the dietary treatment. In: Vinken PJ, Bruyn GW (eds) Handbook of clinical neurology. Metabolic disorders of the nervous system. North Holland Publishing, Amsterdam
Farrell K, Dimmick JE, Applegarth DA, Wong LE, Tze WJ, McCormich AQ, Jan JE, Moser HW (1983) Peroxisomal abnormalities in neonatal adrenoleukodystrophy. Ann Neurol 4:379–380
Folch J, Lees M, Sloane-Stanley J (1957) A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissues. J Biol Chem 226:497–509
Gatfield PD, Taller E, Hinton GG, Wallace AC, Abdelnour GM, Haust MD (1968) Hyperpipecolatemia: A new metabolic disorder associated with neuropathy and hepatomegaly. Can Med Assoc J 99:1215–1233
Goldfischer S (1982) Peroxisomes and human metabolic diseases. The cerebro-hepato-renal syndrome (CHRS), cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis and Schilder's disease (adrenoleukodystrophy). Ann NY Acad Sci 386:526–529
Hanson RF, Isenberg JN, Williams JC, Hackey D, Szczepanik P, Klein PD, Sharp HL (1975) The metabolism of 3α, 7α, 12α-trihydroxy-5B-cholestan-26-oic acid in two siblings with cholestasis due to intrahepatic duct abnormalities. J Clin Invest 56:577–587
Hanson RF, Szcepanik-van Leeuwen P, Williams GC, Grabowski G, Sharp HL (1979) Defects of bile acid synthesis in Zellweger's syndrome. Science 203:1107–1108
Heymans H, Bosch HVD, Schutgens RBH, Tegelaers WHH, Walther JV, Muller-Hocker J, Borst P (1984) Deficiency of plasmalogens in the cerebro-hepato-renal (Zellweger) syndrome. Eur J Pediatr 142:10–15
Inomata M, Takaku F, Nagai Y, Saita M (1982) Assay of polyunsaturated fatty acids by argentation — thin layer chromatography using commercial thin-layer plates. Anal Biochem 125:197–202
Jaffe R, Crumrine P, Hashida Y, Moser HW (1982) Neonatal adrenoleukodystrophy: Clinical, pathologic and biochemical delineation of a syndrome affecting both males and females. Am J Pathol 108:100–111
Kelley RI (1983) The cerebrohepatorenal syndrome of Zellweger, morphologic and metabolic aspects. Am J Med Genet 16:503–517
Moser HW, Moser AB, Kawamura N, Murphy J, Suzuki K, Schaumburg H, Kishimoto Y (1980) Adrenoleukodystrophy: Elevated C26 fatty acid in cultured skin fibroblasts. Ann Neurol 7:542–549
Moser HW, Moser AB, Frayer KK, Chen W, Schulman JD, O'Neill BP, Kishimoto Y (1981) Adrenoleukodystrophy: Increased plasma content of saturated very long chain fatty acids. Neurology (NY) 31:1241–1249
Moser AB, Singh I, Brown FR, Solish GI, Kelley RI, Benke PJ, Moser HW (1984) The cerebrohepatorenal (Zellweger) syndrome: Increased levels and impaired degradation of very long chain fatty acids and their use in prenatal diagnosis. N Engl J Med 310:1141–1146
Noetzel MJ, Clark B, Moser HW (1983) Neonatal adrenoleukodystrophy with prolonged survival. Ann Neurol 14:379–380
Oftebro H, Bjorkhem I, Skrede S, Schreiner A, Pedersen JI (1980) Cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis, a defect in mitochondrial 26-hydroxylation required for normal biosynthesis of cholic acid. J Clin Invest 65:1418–1430
Poulos A (1981) Diagnosis of Refsum's disease using [1-14C] phytanic acid as substrate. Clin Genet 20:247–253
Poulos A, Sharp P (1984) Plasma and skin fibroblasts C26 fatty acids in infantile Refsum's disease. Neurology (NY) 34:1606–1609
Poulos A, Whiting M (to be published) Identification of 3,7,12-trihydroxy-5-cholestan-26-oic acid, and intermediate in cholic acid synthesis, in the plasma of patients with infantile Refsum's disease. J Inherited Metab Dis
Poulos A, Sharp P, Whiting M (1984a) Infantile Refsum's disease (phytanic acid storage disease). A variant of Zellweger's syndrome? Clin Genet 26:579–586
Poulos A, Pollard AC, Mitchell JD, Wise G, Mortimer G (1984b) Patterns of Refsum's disease. Phytanic acid oxidase deficiency. Arch Dis Child 59:222–229
Refsum S (1975) Heredopathia atactica polyneuritiformis. Phytanic acid storage disease (Refsum's disease). In: Vinken PJ, Bruyn GW (eds) Handbook of clinical neurology: Metabolic disorders of the nervous system. North Holland Publishing, Amsterdam, pp 181–229
Schaumburg HH, Powers JM, Raine CS (1975) Adrenoleukodystrophy: A clinical and pathological study of 17 cases. Arch Neurol 32:577–591
Schutgens RBH, Romeyn GJ, Wanders RJA, van den Bosch H, Schrakamp G, Heymans HSA (1984) Deficiency of acyl-CoA dihydroxyacetone phosphate acyltransferase in patients with Zellweger (cerebro-hepato-renal) syndrome. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 120:179–184
Scotto JM, Hadchouel M, Odievre M, Laudat MH, Saudubray JM, Dulac P, Beucler I, Beaune P (1982) Infantile phytanic acid storage disease, a possible variant of Refsum's disease. Three cases including ultrastructural studies of the liver. J Inherited Metab Dis 5:83–90
Singh I, Moser AE, Moser HW, Kishimoto Y (1984) Adrenoleukodystrophy—impaired oxidation of very long chain fatty acids in white blood cells, cultured skin fibroblasts and amniocytes. Pediatr Res 18:286–289
Steinberg D (1978) Phytanic acid storage disease: Refsum's syndrome. In: Stanbury JB, Wyngaarden JB, Fredrickson DS (eds) The metabolic basis of inherited disease. McGraw-Hill Book Co, New York, pp 688–706
Thomas GH, Haslam RHA, Batshaw ML, Capute AJ, Niedengard L, Ransom JL (1975) Hyperpipecolic acidemia associated with hepatomegaly, mental retardation, optic dysplasia and progressive neurological disease. Clin Genet 8:376–382
Tsai SC, Avigan J, Steinberg D (1969) Studies on the α-oxidation of phytanic acid by rat liver mitochondria. J Biol Chem 244:2628–2692
Woody NC, Pupene MB (1970) Excretion of pipecolic acid by infants and by patients with hyperlysinemia. Pediatr Res 4:89–95
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Poulos, A., Sharp, P., Fellenberg, A.J. et al. Cerebro-hepato-renal (Zellweger) syndrome, adrenoleukodystrophy, and Refsum's disease: Plasma changes and skin fibroblast phytanic acid oxidase. Hum Genet 70, 172–177 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00273077
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00273077