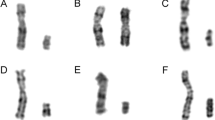
Summary
A very small sex chromosome was identified prenatally as a Y chromosome by using molecular hybridization in conjunction with conventional cytogenetics techniques. The combination of R-banding, Q-banding, distamycin-DAPI staining suggested that the chromosome might be a de novo deletion of the Y chromosome as the father's Y chromosome was normal. Restriction enzyme analysis of amniotic fluid cell DNA using a Y chromosome repetitive probe confirmed the origin of this chromosome.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Borgaonkar DS, Hollander DH (1971) Quinacrine fluorescence of the human Y chromosome. Nature 230:52
Bühler EM (1980) A synopsis of the human Y chromosome. Hum Genet 55:145–175
Caspersson T, Zech L, Johansson C, Modest EJ (1970) Identification of human chromosomes by DNA-binding fluorescent agents. Chromosoma 30: 215–227
Chang H-C, Jones OW, Masui M (1982) Human amniotic fluid cells grown in a hormone-supplemented medium: suitability for prenatal diagnosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 79:4795–4799
Cooke HJ (1976) Repeated sequence specific to human males. Nature 262:182–186
Cooke HJ, Noel B (1979) Confirmation of Y autosome translocations using recombinant DNA. Hum Genet 50:39–44
Hoar DI, Haslam DB, Starezik DM (1984) Improved direct molecular diagnosis and rapid fetal sexing. Prenatal Diagn (in press)
Magenis E, Donlon T (1982) Non-fluorescent Y chromosomes: cytologic evidence of origin. Hum Genet 60:133–138
McKay RDG, Heritage J, Bobrow M, Cooke HJ (1978) Endonuclease analysis of Y chromosome DNA. Cytogenet Cell Genet 22:357–358
Page D, De Martinville B, Barker D, Wyman A, White R, Francke U, Botstein D (1982) Single-copy sequence hybridizes to polymorphic and homologous loci on human X and Y chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 79:5352–5356
Schmid M, Gall H, Schempp W, Weber L, Schmidtke J (1981) Characterization of a new aberration of the human Y chromosome by banding methods and DNA restriction endonuclease analysis. Hum Genet 59:26–35
Schmidtke J, Schmid M (1980) Regional assignment of a 2.1 kb repetitive sequence to the distal part of the human Y heterochromatin. Hum Genet 55:255–257
Schweizer D, Ambros P, Andrle M (1978) Modifications of DAPI banding on human chromosomes by prestaining with a DNA binding oligopeptide antibiotic distamycin A. Exp Cell Res 111:327–332
Sehested J (1974) A single method for R-banding of human chromosomes, sharing a pH-dependent connection between R and G-bands. Humangenetik 21:55–58
Smith KK. Personal communication
Szabo P, Kunkel L, Yu LC, George D, Smith KK (1980) Chromosomal distribution of DNA sequences derived from the human Y chromosome in human higher primates. Cytogenet Cell Genet 25:212–213
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Disteche, C., Luthy, D., Haslam, D.B. et al. Prenatal identification of a deleted Y chromosome by cytogenetics and a Y-specific repetitive DNA probe. Hum Genet 67, 222–224 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00273007
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00273007