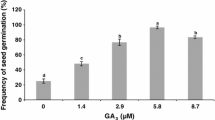
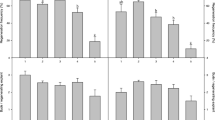
Abstract
Segments of hypocotyl and cotyledons of aseptically-grown seedlings of Pinus strobus L. (white pine) and P. echinata Mill (shortleaf pine) were used as explants for establishing tissue cultures. Growth and differentiation of callus were studied on a modified Murashige and Skoog's medium containing nutrients and plant growth regulators. Meristems below the surface of callus tissue of P. strobus could be induced on media supplemented with α-naphthaleneacetic acid alone or in combination with certain other plant growth regulators. Occasionally, differentiation of shoot buds also occurred on callus cultures. These shoot buds could be grown in vitro but roots did not develop.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ABA:
-
abscisic acid
- BA:
-
6-Benzyl-aminopurine
- 2-ip:
-
N6-(Δ2-isopentanyl)-adenine
- GD:
-
Gresshoff and Doy's medium
- GE:
-
Gamborg and Eveleigh's medium
- MS:
-
Modified Murashige and Skoog's medium
- NAA:
-
α-naphthaleneacetic acid
- SC:
-
Sommer and Caldas' medium
- TIBA:
-
2,3,5-Triiodobenzoic acid
References
Arnold SV, Eriksson T (1978) Physiol. Plant. 44:283–287.
Arnold SV, Eriksson T (1981) Can. J. Bot. 59:870–874.
Bonga JM (1974) N.Z. J. For. Sci. 4:253–260.
Cheng TY (1975) Plant Sci. Lett. 5:97–102.
David A, David H, Mateille T (1982) Physiol. Plant. 56:102–107.
Durzan DJ (1982) In: Bonga JM, Durzan DJ (eds) Tissue culture in forestry, Nijhoff/Junk Boston, pp 36–71.
Durzan, DJ, Campbell RA (1974) Can. J. For. Res. 4:151–174.
Gamborg OL, Eveleigh DE (1968) Can. J. Biochem. 46:417–421.
Gresshoff PM, Doy CH (1972) Planta 107:161–170.
Karnosky DF (1981) Bioscience 31:114–120.
Kasperbauer MJ, Reinert RA (1965) Physiol. Plant. 20:977–981.
Konar RN, Nagmani R (1974) N.Z. J. For. Sci. 4:279–290.
Minocha SC (1980) Can. J. Bot. 58:366–370.
Mott RL (1980) In: Conger BV (ed) Cloning agricultural plants via in-vitro techniques, CRC Press Inc., Boca Raton, Florida, pp 217–254.
Mott RL, Smeltzer RH, Mehra-Palta A, Zobel BJ (1977) Tappi 60:62–64.
Reilly K, Washer J (1977) N.Z. J. For. Sci. 7:199–206.
Shepard JF (1980) Plant Sci. Lett. 18:327–333.
Sommer HE, Brown CL, Kormanik PP (1975) Bot. Gaz. 136:196–200.
Sommer HE, Brown CL (1979) In: Sharp WR, Larsen PO, Paddock EF, Raghaven V (eds) Plant cell and tissue culture, principles, and applications, Ohio State University Press, Columbus, Ohio, pp 461–491.
Sommer HE, Caldas LS (1981) In: Thorpe TA (ed) Plant tissue culture methods and applications in agriculture, Academic Press, New York, pp 349–358.
Thorpe TA, Biondi S (1984) In: Sharp WR, Evans DA, Ammirato PA, Yamada Y (eds) Handbook of plant cell culture, vol. 2, crop species, Macmillan Publishing Company, New York, pp 435–470.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by I.K. Vasil
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaul, K., Kochhar, T.S. Growth and differentiation of callus cultures of Pinus . Plant Cell Reports 4, 180–183 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00269283
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00269283