Abstract
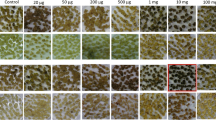
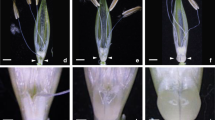
A white-flowered mutant (“WFM”) was regenerated from tissue culture of a purple-flowered plant of tetraploid alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). When WFM was recultured, many regenerated plants (>20%) were purple-flowered. Genetic analysis established that a functional allele, C2, of a locus required for anthocyanin pigmentation was in the simplex condition (C2c2c2c2) in the donor genotype when it mutated to an unstable recessive (“mutable”) allele, c2-m4, which is carried by WFM. Tissue culture experiments demonstrated that c2-m4 reverts to function at a high frequency in vitro. Results indicate that reversion occurs early in culture and may be the result of a genome shock associated with callus formation. Reversion also occurs in planta, but at a much lower frequency than in vitro. The c2-m4 allele is transmitted to progeny which revert in tissue culture. Revertant alleles, like the progenitor allele, are stable and are sexually transmitted. The action of a transposable element which is especially active in vitro is suggested.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bingham ET (1973) Crop Sci 13:393–394
Bingham ET, Hurley LV, Kaatz DM, Saunders JW (1975) Crop Sci 15:719–721
Burr B, Burr F (1981) Stadler Genet Symp 13:115–128
Chaleff RS (1983) Science 214:676–682
Clement WM (1964) Genetics 50:241–242 (Abstract)
Fedoroff NV (1983) In: Shapiro J (ed) Mobile genetic elements. Academic, New York, pp 1–63
Fincham JRS, Sastry GRK (1974) Ann Rev Genet 25:15–50
Freeling M (1984) Ann Rev Plant Physiol 35:277–298
Groose RW (1985) An unstable anthocyanin mutation in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) which reverts at high frequency in tissue culture. Ph.D. dissertation, Univ Wisconsin-Madison
Groose RW, Bingham ET (1984) Crop Sci 24:655–658
Groose RW, Bingham ET (1986) Plant Cell Rep in press
Larkin PJ, Scowcroft WR (1981) Theor Appl Genet 60:197–214
McClintock B (1978) Stadler Genet Symp 10:25–48
McClintock B (1984) Science 226:792–801
Neilson-Jones W (1969) Plant chimeras. Camelot, London
Orton TJ (1984) Stadler Genet Symp 16:427–468
Reisch B, Duke SH, Bingham ET (1981) Theor Appl Genet 59:89–94
Satina S, Blakeslee AF (1941) Am J Bot 28:862–871
Talbert LE, Bingham ET (1986) Crop Sci in press
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by J. M. Widholm
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Groose, R.W., Bingham, E.T. An unstable anthocyanin mutation recovered from tissue culture of alfalfa (Medicago sativa). Plant Cell Reports 5, 104–107 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00269245
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00269245