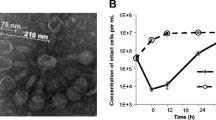
Summary
Different strains of E. coli commonly used in genetic studies were exposed to ozone and the results described in this paper indicate that exrA and (lex), but not uvrA genes affect sensitivity to ozone. No relationship between this latter property and the capacity to repair UV-damaged infecting phage (host cell reactivation) was also found. The hypothesis is proposed that the association of ozone sensitivity and X-rays sensitivity in the same mutants may reflect common steps in the mechanism of DNA repair.
Similar content being viewed by others
Bibliographie
Christensen, E., Giese, A. C.: Changes in adsorption spectra of nucleic acids and their derivatives following exposure to ozone and ultraviolet radiations. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 51, 208–216 (1954)
Chung, Y. S., Greenberg, J.: Genes affecting sensitivity to ultraviolet light in the malB region of the chromosome of Escherichia coli. Genetics 59, 11–22 (1968)
Chung, Y. S., Hamelin, C.: The locus of the lex mutation in Escherichia coli (en préparation)
Davis, I.: Microbiologic studies with ozone: Mutagenesis of ozone for Escherichia coli. U.S.A.F. School of Aerospace Medicine Report No. SAM-TR-61-60, 1-9 (1961)
Fairchild, E. J., Murphy, S. D., Stokinger, H. E.: Protection by sulphur compounds against the air pollutants ozone and nitrogen dioxide. Science 130, 861–862 (1959)
Fetner, R. H.: Chromosome breakage in Vicia faba by ozone. Nature (Lond.) 181, 504–505 (1958)
Fetner, R. H.: Ozone-induced chromosome breakage in human cell cultures. Nature (Lond.) 194, 793–794 (1962)
Giese, A. C., Christensen, E.: Effect of ozone on organisms. Physiol. Zool. 27, 101–115 (1954)
Greenberg, J.: Loci for radiation sensitivity in Escherichia coli strain Bs-1. Genetics 55, 193–201 (1967)
Hamelin, C., Chung, Y. S.: Résistance à l'ozone chez Escherichia coli: I. Etude comparative de différentes souches B et B/r. Rev. Canad. Biol. 32, 169–176 (1973)
Howard-Flanders, P.: Molecular mechanisms in the repair of irradiated DNA. J. Genet. 40, 256–263 (1964)
Howard-Flanders, P., Boyce, R. P.: DNA repair and genetic recombination: Studies on mutants of Escherichia coli defective in these processes. Radiat. Res., Suppl. 6, 156–184 (1966)
Howard-Flanders, P., Boyce, R. P., Theriot, L.: Three loci in Escherichia coli K-12 that control the excision of pyrimidine dimers and certain other mutagen products from DNA. Genetics 53, 1119–1136 (1966)
McGrath, R. A., Williams, R. W.: Reconstruction in vivo of irradiated Escherichia coli deoxyribonucleic acid; the rejoining of broken pieces. Nature (Lond.) 212, 534–535 (1966)
Mount, D. W., Kosel, C.: Properties of strains of Escherichia coli K12 carrying mutant lex-1 and uvrA6 alleles. Molec. gen. Genet. 120, 291–299 (1973)
Prat, R., Nofre, Cl., Cier, A.: Effets de l'hypochlorite de sodium, de l'ozone et des radiations ionisantes sur les constituants pyrimidiques de Escherichia coli. Ann. Inst. Pasteur. 114, 595–607 (1968)
Sachsenmaier, W., Siebs, W., Tjong-An-Tan: Effects of ozone upon mouse ascites tumor cells and upon chick fibroblasts in tissue culture. Z. Krebsforsch. 67, 113–126 (1965)
Scott, D. B., Lesher, E. C.: Effect of ozone on survival and permeability of Escherichia coli. J. Bact. 85, 567–576 (1963)
Setlow, R. B., Carrier, W. L.: The disappearance of thymine dimers from DNA. An error correcting mechanism. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.) 51, 226–231 (1964)
Wangermann, E., Lacey, H. J.: Some effects of ultraviolet radiation on Lemna minor. Nature (Lond.) 170, 126–127 (1942)
Zelac, R. E., Cromroy, H. L., Bolch, W. E., Dunavant, B. G., Bevis, H. A.: Inhaled ozone as a mutagen: I. Chromosome aberrations induced in chinese hamster lymphocytes. Environ. Res. 4, 262–282 (1971a)
Zelac, R. E., Cromroy, H. L., Bolch, W. E., Dunavant, B. G., Bevis, H. A.: Inhaled ozone as a mutagen: II. Effect on the frequency of chromosome aberrations observed in irradiated chinese hamster. Environ. Res. 4, 325–342 (1971b)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Ce travail a pu être réalisé grâce à l'assistance financière du Conseil National de Recherches du Canada.
Boursier du Conseil National de Recherches du Canada.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hamelin, C., Chung, Y.S. Résistance à l'ozone chez Escherichia coli . Molec. Gen. Genet. 129, 177–184 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00268630
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00268630