Summary
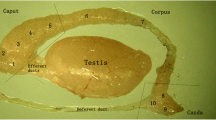
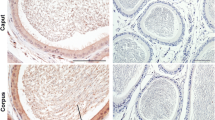
Prolactin (PRL) binds to the testis of mice and rats where it increases the number of luteinizing hormone receptors, increases the binding of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) to LH receptors, and enhances testosterone synthesis and secretion. PRL also binds to the prostate and seminal vesicles of rats and humans where it increases organ weight and stimulates growth and uptake of testosterone. PRL binds to the epididymis of rats but the effect of PRL on this organ is unknown. In the present study, a standard immunoperoxidase (PAP) technique was used to detect the binding of endogenous and exogenous PRL or PRL-like peptides to the epididymis of the mature mouse. Throughout the epididymal duct, a positive reaction for peroxidase, suggesting PRL or PRL-like binding, occurred in the Golgi area of principal cells. In segment 1, positive reactions were also visualized in the perinuclear area and in the region located between the Golgi area and the apical surface of the principal cells (supra-Golgi area). In the corpus and cauda epididymidis, scattered entire principal cells were also positive. Throughout the epididymal duct, the reactions indicating the binding of exogenous PRL were slightly stronger than those testing for binding of endogenous peptides. The significance of such binding to the epididymis is uncertain but PRL may perform the same functions in epididymal principal cells as it does in the testis, prostate, and seminal vesicles.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aafjes JH, Vreeburg JTM (1972) Distribution of 5 α-dihydrotestosterone in the epididymis of bull and boar, and its concentration in rat epididymis after ligation of efferent testicular ducts, castration, and unilateral gonadectomy. J Endocrinol 53:85–93
Abe K, Takano H, Ito T (1983) Ultrastructure of the mouse epididymal duct with special reference to the regional differences of the principal cells. Arch Histol Jpn 46:51–68
Adams CS, Brumlow WB (1989) Immunocytochemical detection of luteinizing hormone in epididymis of mature mouse. Histochemistry 91:495–499
Aragona C, Friesen HG (1975) Specific prolactin binding sites in the prostate and testis in rats. Endocrinology 97:677–684
Aragona C, Bohnet HG, Friesen HG (1977) Localization of prolactin binding in prostate and testis: the role of serum prolactin concentration on the testicular LH receptor. Acta Endocrinol 84:402–409
Barkey RJ, Shani J, Amit T, Barzilai D (1977) Specific binding of prolactin to seminal vesicle, prostate and testicular homogenates of immature, mature and aged rats. J Endocrinol 74:163–173
Bartke A (1971) Effects of prolactin on spermatogenesis in hypophysectomized mice. J Endocrinol 49:311–316
Bartke A (1976) Pituitary-testis relationships. In: Sperm action. Progress in reproductive biology, vol I. Karger, Basel, pp 136–152
Bartke A, Lloyd CW (1970) Influence of prolactin and pituitary isografts on spermatogenesis in dwarf mice and hypophysectomized rats. J Endocrinol 46:321–329
Bengmark S, Hesselsjo R (1964) Endocrine dependence of rat seminal vesicle tissue in tissue culture. Urol Int 17:84–92
Bohnet HG, Friesen HG (1976) Effect of prolactin and growth hormone on prolactin and LH receptors in the dwarf mouse. J Reprod Fertil 48:307–311
Boyns AR, Cole EN, Golder MP, Danutra V, Harper ME, Brownsey B, Cowley T, Jones GE, Griffiths K (1972) Prolactin studies with the prostate. In: Boyns AR, Griffiths K (eds) Prolactin and carcinogenesis, Proc of 4th Tenovus Workshop, Alpha Omega Alpha, Cardiff, Wales, pp 207–216
Brooks DE (1981) Secretion of proteins and glycoproteins by the rat epididymis: regional differences, androgen-dependence, and effects of protease inhibitors, procaine and tunicamycin. Biol Reprod 25:1099–1117
Catt KJ, Harwood JP, Clayton RN, Davies TF, Chan V, Katikineni M, Nozu K, Dufau ML (1980) Regulation of peptide hormone receptors and gonadal steroidogenesis. Recent Prog Horm Res 36:557–622
Charreau EH, Attramadal A, Torjesen PA, Calandra R, Purvis K, Hansson V (1977) Androgen stimulation of prolactin receptors in the rat prostate. Mol Cell Endocrinol 7:1–7
Christensen AK, Gillem SW (1969) The correlation of fine structure and function in steroid-secreting cells, with emphasis on those of the gonads. In: McKerns KW (ed) The gonads. Appleton-Century-Crofts, New York, pp 415–488
Dravland E, Joshi MS (1981) Sperm-coating antigens secreted by the epididymis and seminal vesicle of the rat. Biol Reprod 25:649–658
Farnsworth WE (1970) The normal prostate and its control. In: Griffiths K, Pierrepoint CG (eds) Some aspects of the aetiology and biochemistry of prostatic cancer. Proc 3rd Tenovus Workshop. Alpha Omega Alpha, Cardiff, Wales, pp 3–15
Fleischer B, Fleischer S, Ozawa H (1969) Isolation and characterization of Golgi membranes from bovine liver. J Cell Biol 43:59–79
Flickenger CJ, Wilson KM, Gray HD (1984) The secretory pathway in the mouse epididymis as shown by electron microscope radioautography of principal cells exposed to monensin. Anat Rec 210:435–448
Frankel AI, Eik-Nes KB (1970) Testosterone and dehydroepiandrosterone in the epididymis of the rabbit. J Reprod Fertil 23:441–445
Friend DS, Farquhar MC (1967) Functions of coated vesicles during protein absorption in the rat vas deferens. J Cell Biol 35:357–376
Gloyna RE, Wilson JD (1969) A comparative study of the conversion of testosterone to 17-β hydroxy-5 α androstan-3-one (dihydrotestosterone) by the prostate and the epididymis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 29:970–977
Gunesakar PG, Kumaran B, Govindarajulu P (1988) Prolactin and Leydig cell steroidogenic enzymes in the bonet monkey (Macaca radiata). Int J Androl 11:53–59
Hafiez AA, Philpott JE, Bartke A (1971) The role of prolactin in the regulation of testicular function: the effect of prolactin and luteinizing hormone on 3 β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase activity in the testes of mice and rats. J Endocrinol 50:619–623
Hafiez AA, Bartke A, Lloyd CW (1972) The role of prolactin in the regulation of testis function: the synergistic effects of prolactin and luteinizing hormone on the incorporation of [1-14C] acetate into testosterone and cholesterol by testes from hypophysectomized rats in vitro. J Endocrinol 53:223–230
Hamilton DW (1971) Steroid function in the mammalian epididymis. J Reprod Fertil [Suppl] 13:89–97
Hamilton DW, Fawcett DW (1970) In vitro synthesis of cholesterol and testosterone from acetate by rat epididymis and vas deferens. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 133:693–695
Hamilton DW, Jones AL, Fawcett DW (1969) Cholesterol biosynthesis in the mouse epididymis and ductus deferens: a biochemical and morphological study. Biol Reprod 1:167–184
Hanlin ML, Yount AP (1975) Prolactin binding in the rat ventral prostate. Endocr Res Commun 2:489–502
Harper ME, Sibley PEC, Peeling WB, Griffiths K (1981) The immunocytochemical detection of GH and prolactin in human prostatic tissue. In: Murphy GP, Sandberg AA, Karr JP (eds) Prostatic cell: structure and function part B. Progress in clinical biological research, vol 75. Alan R Liss, New York, pp 115–130
Hussein MO, Zipf WB (1988) Temporal relationship of the prolactin-dependent LH-induced LH receptor to the LH stimulus. J Cell Physiol 134:137–142
Janszen FHA, Cooke BA, van der Molen HJ (1977) Specific protein synthesis in isolated rat testis Leydig cells. Influence of luteinizing hormone and cyclohexamide. Biochem J 162:341–346
Josefsberg Z, Posner BI, Patel B, Bergeron JJM (1978) The uptake of prolactin into female rat liver. J Biol Chem 254:209–214
Keenan EJ, Klase PA, Thomas JA (1981a) Interaction between prolactin and androgens in the accessory sex organs of male mice. J Endocrinol 90:323–330
Keenan EJ, Ramsey EE, Kemp ED (1981b) The role of prolactin in growth of the prostate gland. In: Murphy GP, Sandberg AA, Karr JP (eds) Prostatic cell: structure and function part B. Progress in clinical biological research, vol 75. Alan R Liss, New York, pp 9–18
Kharroubi AT, Slaunwhite WR (1984) Hormonal regulation of prolactin receptors in male rat target tissues: the effect of hypothyroidism and adrenalectomy. Endocrinology 115:1283–1288
Kledzick GS, Marshall S, Campbell GA, Gelato M, Meites J (1976) Effects of castration, testosterone, estradiol, and prolactin on specific prolactin-binding activity in ventral prostate of male rats. Endocrinology 98:373–379
Lasnitzki I (1972) The effect of prolactin on rat prostate glands in organ culture. In: Boyns AR, Griffiths K (eds) Prolactin and carcinogenesis, Proc of 4th Tenovus Workshop. Alpha Omega Alpha, Cardiff, Wales, pp 200–206
L'Hermite-Baleriaux M, L'Hermite M (1984) Prolactin receptors in human tissues. In: Saxena BB, Catt KJ, Birnbaumer L, Martini L (eds) Hormone receptors in growth and reproduction. Raven Press, New York, pp 291–305
Lockett MF, Nail B (1965) A comparative study of the renal actions of growth and lactogenic hormones in rats. J Physiol (Lond) 180:147–156
Moore HDM (1980) Localization of specific glycoproteins secreted by the rabbit and hamster epididymis. Biol Reprod 22:705–718
Posner BI, Bergeron JJM (1975) Polypeptide hormone receptors in Golgi fractions from rat liver. Clin Res 23:617A
Prakash A, Moore HDM (1982) Localization of 5Δ-3 β-and 17 β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase activity in the efferent ducts, epididymis and vas deferens of the rabbit, hamster and marmoset monkey. J Reprod Fertil 66:95–100
Ramsey DH, Bern HA (1972) Stimulation by ovine prolactin of fluid transfer in everted sacs of rat small intestine. J Endocrinol 53:453–459
Smith C, Assimos D, Lee C, Grayhack JT (1985) Metabolic action of prolactin in regressing prostate: independent of androgen action. Prostate 6:49–59
Vernon RB, Muller CH, Herr JC, Feuchter FA, Eddy EM (1982) Epididymal secretion of a mouse sperm surface component recognized by a monoclonal antibody. Biol Reprod 26:523–535
Wahlstrom T, Huhtaniemi I, Hovatta O, Seppala M (1983) Localization of LH, FSH, prolactin and their receptors in human and rat testis using immunohistochemistry and radioreceptor assay. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 57:825–830
Welsh TH, Kasson BG, Hsueh AJW (1986) Direct biphasic modulation of gonadotropin-stimulated testicular androgen biosynthesis by prolactin. Biol Reprod 34:796–804
Witorsch RJ (1981) Visualization of prolactin binding sites in prostate tissue. In: Murphy GP, Sandberg AA, Karr JP (eds) Prostatic cell: structure and function part B. Progress in clinical biological research, vol 75. Alan R Liss, New York, pp 89–114
Zipf WB, Berntson G (1981) Hormone-dependent subpopulation of rat testicular luteinizing hormone (LH) receptors. Biol Reprod 24:306–310
Zipf WB, Payne AH, Kelch RP (1978) Prolactin, growth hormone and luteinizing hormone in the maintenance of testicular luteinizing hormone receptors. Endocrinology 103:595–600
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brumlow, W.B., Adams, C.S. Immunocytochemical detection of prolactin or prolactin-like immunoreactivity in epididymis of mature male mouse. Histochemistry 93, 299–304 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00266392
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00266392