Summary
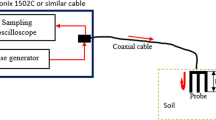
The principle of operation of a simple, manually controlled Time Domain Reflectometer (TDR meter) for soil moisture measurements, which operates with a needle pulse of 300 ps rise-time, is described. A block diagram and constructions are also given. Construction of a switchless multiple sensor probe, having an inherent delay reference, is presented. Results of measurements of the soil dielectric constant as related to water content, for soils having different bulk densities, textures and humus content show a high correlation. The results agree closely with other investigators measurements with different, more expensive, TDR instruments. The general principle of microprocessor-controlled TDR operated soil moisture meter is considered.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chudobiak WJ, Syrett BA, Hafez HM (1979) Recent advances in broad-band VHF and UHF transmission line methods for moisture content and dielectric constant measurement. IEEE Trans Instr Meas. IM-28, 4:284
Dasberg S, Dalton FN (1985) Time domain reflectrometry field measurements of soil water content and electrical conductivity. Soil Sci Soc Am J 49:293
Davis JL, Chudobiak WJ (1975) In situ meter for measuring relative permittivity of soils. Geol Survey of Canada. Energy, Mines and Resources of Canada, Ottawa, Paper 75-1A:75
Davis JL, Topp GC, Annan AP (1977) Electromagnetic detection of soil water content: Progress report II. In: Remote sensing of soil moisture and groundwater. Workshop proceedings, Canadian Aeronoutics and Space Institute, Ottawa, Nov. 1976, p 96
Fellner-Feldegg H (1969) The measurement of dielectrics in the time domain. J Phys Chem 73, 3:616
Hayhoe HN, Bailey WG (1985) Monitoring changes in total and unfrozen water content in seasonally frozen soil using Time-Domain Reflectrometry and neutron moderation techniques. Water Resour Res 21, 8:1077
Ryden BE (1986) Winter soil moisture regime monitored by the Time-Domain Reflectrometry technique (TDR). Geografiska Annalen, vol 68, ser. A. 3:175
Topp GC, Davis JL, Annan AP (1982) Electromagnetic determination of soil water content using TDR: I. Apptictions to wetting fronts and steep gradients. Soil Sci Soc Am J 4:672
Topp GC, Davis JL (1985) Measurement of soil water content using Time-Domain Reflectrometry (TDR): A field evaluation. Soil Sci Soc Am J 49:19
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Patent pending
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Malicki, M.A., Skierucha, W.M. A manually controlled TDR soil moisture meter operating with 300 ps rise-time needle pulse. Irrig Sci 10, 153–163 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00265691
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00265691