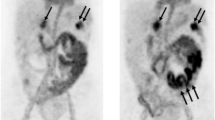
Abstract
Monoclonal antibodies (MoAbs) 17-1A and 19-9, which specifically bind human colorectal carcinoma (CRC) cells, were tested for their usefulness in localizing colorectal tumors in nude mice. One of the 131I-labeled MoAbs and an irrelevant 125I-labeled immunoglobulin of the same isotype were injected into nude mice simultaneously bearing a human CRC and a human melanoma. The percentage of the injected dose of antibody per gram of tissue, the CRC/tissue ratios of antibody distribution, and the localization indices were calculated at various time intervals (2 h to 9 days). For both MoAbs, labeling to a specific activity of 10 μCi/μg by the iodogen method gave optimum immunoreactivity. The accumulation of MoAb 17-1A in CRC reached its maximum at 5 days and remained at this level for up to 9 days postinjection. For MoAb 19-9, which detects a circulating antigen shed by the tumor into the serum, the accumulation in the CRC was maximum at 24 h, and decreased thereafter. The CRC/organ ratios and localization indices for both MoAbs increased with time in the CRC tissue, but remained low and unchanged in the melanoma and normal tissues. Using F(ab′)2 antibody fragments, faster kinetics with earlier maximum accumulation, higher tumor/organ ratios, and better localization indices were achieved than with intact MoAbs. The data obtained was useful in defining parameters which must be considered before radiolabeled MoAbs are used in cancer patients for diagnostic purposes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ballou B, Levine G, Hakala T, Solter D (1979) Tumor location detected with radioactivity labeled monoclonal antibody and external scintigraphy. Science 206:844–847
Epenetos AA, Mather S, Granowska M, Nimmon CC, Hawkins CR, Britton KE, Shepherd J, Taylor-Papadimitriou J, Durbin H, Malpas JS, Bodmer WF (1982) Targeting of iodine-123-labelled tumour-associated monoclonal antibodies to ovarian, breast and gastrointestinal tumours. Lancet 2:999–1004
Farrands PA, Pimm MV, Embleton MJ, Perkins AC, Hardy JD, Baldwin RW, Hardcastle JD (1982) Radioimmunodetection of human colorectal cancers by anti-tumor monoclonal antibody. Lancet 2:397–400
Fraker PJ, Speck JC (1978) Protein and cell membrane iodinations with a sparingly soluble chloramide 1,3,4,6-tetrachloro 3a-6a-diphenyl-glycouril. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 80:849–857
Gold P, Freedman SO (1965) Demonstration of tumor specific antigens in human colonic carcinoma by immunological and adsorption techniques. J Exp Med 121:439–462
Goldenberg DM, Deland F, Evishin K, Bennett S, Primus FJ, Van Nagel JR, Estes N, De Simone P, Rayburn P (1978) Use of radiolabeled antibodies to carcinoembryonic antigen for the detection and localization of diverse cancer by external photoscanning. N Engl J Med 298:1384–1388
Goldenberg DM, Kim EE, Deland FH, Spremulli E, Nelson MO, Gackerman JP, Primus FJ, Corgan RL, Alpert E (1980) Radioimmunodetection of cancer with radioactive antibodies to carcinoembryonic antigen. Cancer Res 40:2984–2992
Kohler G, Milstein C (1975) Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature 256:495–497
Koprowski H, Steplewski Z, Mitchell K, Herlyn M, Herlyn D, Fuhrer P (1979) Colorectal carcinoma antigens detected by hybridoma antibodies. Somatic Cell Genet 5:957–972
Levine G, Ballou B, Reiland J, Solter D, Gumerman M, Hakala T (1980) Localization of I-131-labeled tumor-specific monoclonal antibody in the tumor-bearing BALB/c mouse. J Nucl Med 21:570–573
Mach JP, Carrel S, Forni M, Ritschard J, Donath A, Alberto P (1980) Tumor localization of radiolabeled antibodies against carcinoembryonic antigen in patients with carcinoma. N Engl J Med 303:5–10
Magnani JL, Brockhaus M, Smith DF, Ginsburg V, Blasczcyk M, Mitchell KF, Steplewski Z, Koprowski H (1981) A monosialoganglioside is a monoclonal antibody defined antigen of colon carcinoma. Science 212:55–56
Moshakis V, McIlhinney R, Raghavan D, Neville AM (1981) Monoclonal antibodies to detect human tumours: an experimental approach. J Clin Pathol 34:314–319
Pressman D (1957) Radiolabeled antibodies. Ann NY Acad Sci 69:644–650
Primus FJ, Wang RH, Goldenberg DM, Hansen HJ (1973) Localization of human GW39 tumours in hamsters by radiolabeled heterospecific antibody to carcinoembryonic antigen. Cancer Res 33:2977–2982
Stuhlmiller GM, Sullivan D, Vervaert C, Vervaert CE, Crocker BP, Harris CC, Seigler HF (1981) In vivo tumor localization using tumor specific monkey xenoantibody, alloantibody and murine monoclonal xenoantibody. Ann Surg 194:592–601
Tompkins WA, Watrach AM, Schmale JD, Schultz RM, Harris JA (1974) Cultural and antigenic properties of newly established cell strains derived from adenocarcinomas of human colon and rectum. J Natl Cancer Inst 52:1101–1110
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Douillard, JY., Chatal, JF., Saccavini, J.C. et al. Pharmacokinetic study of radiolabeled anti-colorectal carcinoma monoclonal antibodies in tumor-bearing nude mice. Eur J Nucl Med 11, 107–113 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00265042
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00265042