Abstract
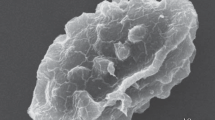
Conditions for microcycle sporogenesis in two streptomycete strains without shifting the culture were found. The sporulation in Streptomyces granaticolor took place after 24 h of cultivation. The dry mass was increasing till 32 h probably due to production of a hydrophobic substance resembling fibrous sheath of aerial hyphae and spores. Ultrathin section of microcycle spores are presented.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson JG, Smith JE (1971) The production of conidiophores and conidia by newly germinated conidia of Aspergillus niger (microcycle conidiation). J Gen Microbiol 69:185–197
Carvajal F (1947) The production of spores in submerged cultures by some Streptomyces. Mycologia 39:426–440
Cortat M, Turian G (1974) Conidiation of Neurospora crassa in submerged culture without mycelial phase. Arch Microbiol 95:305–309
Gashinsky VV, Vojtsekhovsky VG (1978) Repeated microcycle of Bacillus cereus. Mikrobiologiya (Moscow) 47:304–305
Grund AD, Ensign JC (1985) Properties of the germination inhibitor of Streptomyces viridochromogenes spores. J Gen Microbiol 131:833–847
Kellenberger E, Ryter A, Sechaud J (1958) Electron microscope study of DNA containing plasms. II. Vegetative and phage DNA as compared with normal bacterial nucleoids in different physiological states. J Biophys Biochem Cytol 4:671–679
Keynan A (1973) The transformation of bacterial endospores into vegetative cells. In: Microbial differentiation, Proc 23rd Symp Soc Gen Microbiol, London, pp 85–123
Koepsel R, Ensign JC (1984) Microcycle sporulation of Streptomyces viridochromogenes. Arch Microbiol 140:9–14
MacKechnie I, Hanson RS (1968) Microcycle sporogenesis of Bacillus cereus in a chemically defined medium. J Bacteriol 95:355–359
McBride M, Ensign JC (1987) Effects of intracellular trehalose content on Streptomyces griseus spores. J Bacteriol 169:4995–5001
Pažout J, Schroder P (1988) Microcycle conidiation in submerged cultures of Penicillium cyclopium attained without temperature changes. J Gen Microbiol 134:2685–2692
Sekiguchi J, Gaucher GM, Costerton JW (1975) Microcycle conidiation in Penicillium urticae: an ultrastructural investigation of spherical spore growth. Can J Microbiol 21:2048–2058
Št'astná J (1977) A method of rapid wetting and synchronous germination of streptomycete spores. Folia Microbiol 22:137–138
Št'astná J, Janda I (1983) Production, long-term preservation and synchronous germination of aerial spores of Streptomyces. J Microbiol Methods 1:267–273
Vinter V, Slepecky RA (1965) Direct transition of outgrowing bacterial spores to new sporangia without intermediate cell division. J Bacteriol 90:803–807
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Št'astná, J., Kvapil, P., Čáslavská, J. et al. Microcycle sporogenesis in some streptomycetes without shift down treatment. Arch. Microbiol. 156, 263–265 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00262995
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00262995