Summary
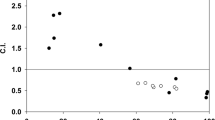
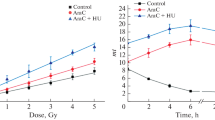
We report on the individual and combined effects of doxorubicin (DOX) and hyperthermia (HYP) on nucleoid sedimentation and poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) activity of L1210 cells. The effects of HYP and DOX on nucleoid sedimentation (increased sedimentation) were similar and correlated with cell viability. No correlation of PARP activity with cell toxicity was evident; the activity of PARP was inhibited by HYP (42°C; 1–3 h) and stimulated by DOX (1–10 μM; 30 min). The HYP-induced inhibition of PARP was actually ameliorated by simultaneous exposure to DOX. Although separate studies have previously suggested that chromatin alterations or the inhibition of PARP might play a role in the effect of HYP, the correlation of nucleoid changes (rather than PARP activity) with cell viability emphasizes the contribution of the former. Furthermore, the results suggest that the nucleoid technique may prove useful in screening potential treatment modalities.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adwankar MK, Chitnis MP (1984)Effect of hyperthermia alone or in combination with anticancer drugs in the viability of P388 leukemia cells Tumori 70:231
Althaus FR, Lawrence SD, Sattler GL, Pitot HC (1980) The effect of nicotinamide on unscheduled DNA synthesis in cultured hepatocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 95:1063
Ben-Hur E, Elkind MM, Bronk BV (1974) Thermally enhanced radioresponse of cultured Chinese hamster cells: Inhibition of repair of sublethal damage and enhancement of lethal damage. Radiat Res 58:38
Benjamin RC, Gill DM (1980) Poly (ADP-ribise) synthesis in vitro programmed by damaged DNA. J Biol Chem 255:10502
Berger NA, Sikorski GW (1980) Nicotinamide stimulates repair of DNA damage in human lymphocytes. Biochem Biphys Res Commun 95:67
Bodell WJ, Cleaver JE, Roti Roti JL (1984) Inhibition by hyperthermia of repair synthesis and chromatin reassembly of ultraviolet-induced damage to DNA. Radiat Res 100:87
Bowden GT, Kasunic MD (1981) Hyperthermic potentiation of the effect of a clinically significant X-ray dose on cell survival, DNA damage and DNA repair. Radiat Res 87:109
Cook PR, Brazell IA (1975) Supercoils in human DNA. J Cell Sci 19:261
Cook PR, Brazell IA (1976) Detection and repair of single strand breaks in nuclear DNA. Nature 263:679
Corry PM, Robinson S, Getz S (1977) Hyperthermic effects of DNA repair mechanisms. radiology 123:475
Durkacz BW, Omidiji O, Gray DA, Shall S (1980) ADP-ribose participates in DNA excision repair. Nature 283:593
Durkacz BW, Irwin J, Shall S (1981) The effect of inhibition of (ADP-ribose) biosynthesis on DNA repair assayed by the nucleoid technique. Eur J Biochem 121:65
Hayaishi Y, Ueda K (1977) Poly (ADP-ribose) and ADP-ribosylation of proteins. Ann Rev Biochem46:95
Herman TS, Sweets CC, White DM, Gerner EW (1982) Effect of heating on the lethality due to hyperthermia and selected chemotherapeutic drugs. J Natl Cancer Inst 68:487
James MR, Lehmann AR (1982) Role of poly (adenosine diphosphate ribose) in deoxyribonuclear acid repair in human fibroblasts. Biochemistry 21:4007
Kulkarni MS, Heideprim PM, Yeilding KL (1980) Production by lithocholic acid of DNA strand breaks in L1210 cells. Cancer Res 40:2666
Leith JT, Miller RC, Gerner EW, Boone MLM (1977) Hyperthermic potentiation: Biological aspects and applications to radiation therapy. Cancer 39:766
Li GC, Kal HB (1977) Effect of hyperthermia on the radiation response of two mammalian cell lines. Eur J Cancer 13:65
Lindahl T (1982) DNA repair enzymes. Ann Rev Biochem 51:61
Mills MD, Meyn RE (1981) Effects of hyperthermia on repair of radiation-induced DNA strand breaks. Radiat Res 87:314
Miwa M, Kanai M, Kondo T, Hoshino H, Ishihara K, Sugimura T (1981) Inhibitors of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase enhace unscheduled DNA synthesis in human peripheral lymphocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 100:463
Nagle WA, Moss AJ Jr (1983) Inhibitors of poly (ADP-ribose) synthetase enhance the cytotoxicity of 42°C and 45°C hyperthermia in cultured Chinese hamster cells. Int J Radial Biol 44:475
Nduka N, Skidmore CJ, Shall S (1980) The enhancement of cytotoxicity of N-methyl-N-nitrosourea and of γ-radiation by inhibitors of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase. Eur J Biochem 105:525
Nolan NL, Kidwell WR (1982) Effect of heat shock on poly (ADP-ribose) synthetase and DNA repair in Drosophila cells. Radiat Res 90:187
Romagna F, Kulkarni MS, Anderson MW (1985) Detection of repair of chemically-induced DNA damage in vivo by the nucleoid sedimentation method. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 127:56
Ross WE, Glaubiger DL, Kohn KW (1978) Protein-associated DNA breaks in cells treated with adriamycin or ellipticine. Biochim Biophys Acta 519:23
Roti Roti JL, Painter RB (1982) Effect of hyperthermia on the sedimentation of nucleoids from HeLa cells in sucrose gradients. Radiat Res 89:166
Sapareto SA, Hopwood LE, Dewey WC (1978) Combined effects of X irradiation and hyperthermia on CHO cells for various temperatures and orders of applications. Radiat Res 73:221
Simpson TA Jr, LaRussa PG, Mullins DW Jr, Daugherty JP (1987) Restoration of hyperthermia-associated increased protein to DNA ratio of nucleoids. Int J Hyperthermia 3:49
Skidmore CJ, Davies MI, Goodwin PM, Halldorsson H, Lewis PJ, Shall S, Zia'ee AA (1979) The involvement of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase in the degradation of NAD caused by gamma-radiation and N-methyl-N-nitroso-urea. Eur J Biochem 101:135
Smulson ME, Schein PS, Mullins DW, Sudhakar S (1977) A putative role for nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-promoted nuclear protein modification in the antitumor activity of N-methyl-N-nitrosourea. Cancer Res 37:3006
Someya A, Tanaka N (1979) DNA strand scission induced by adriamycin and aclacinomycin A. J Antibiot 3:839
Tamulevicius P, Schmidt K, Streffer C (1984) The effects of X irradiation, hyperthermia, and combined modality treatment on poly (ADPR) synthetase activity in human melanoma cells.Radiat Res 100:65
Van Wijk R (1982) Regulation of DNA synthesis in cultured rat hepatoma cells. Int Rev Cytol 85:63
Waldes H, Center MS (1982) Adriamycin-induced compaction of isolated chromatin. Biochem Pharmacol 31:1057
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Daugherty, J.P., Simpson, T.A. & Mullins, D.W. Effect of hyperthermia and doxorubicin on nucleoid sedimentation and poly (ADP-ribose) Polymerase activity in L1210 cells. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 21, 229–232 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00262775
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00262775