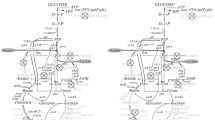
Summary
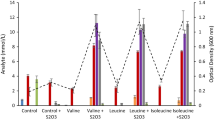
Mutants of Alcaligenes eutrophus, which are defective in the intracellular accumulation of poly(β-hydroxybutyric acid), PHB, were cultivated in the presence of excess carbon source after growth had ceased due to depletion of ammonium, sulphate, phosphate, potassium, magnesium, or iron. Under these conditions all mutants excreted large amounts of pyruvate into the medium. Excretion of pyruvate occurred with lactate, gluconate or fructose as carbon sources; the highest rate of pyruvate excretion (8 mmol/1 per hour) was obtained with lactate. The rate of pyruvate excretion by strain N9A-PHB-02-HB-1 on gluconate amounted to 2.5–6.3 mmol/g protein per hour depending on the depleted nutrient. The ratios of the molar rates for the utilization of the substrates versus those for the excretion of pyruvate were 1.9, 1.0 or 0.7, respectively. Wild-type strains did not excrete even traces of pyruvate, but accumulated PHB. Depending on the limiting nutrient, strain N9A accumulated PHB at a rate of 0.21–0.49 g/g protein per hour. On a molar basis (β-hydroxybutyrate monomers versus pyruvate) the ratios for the rates for accumulation of PHB in the wild-type and for excretion of pyruvate in PHB-negative mutants were 0.9–1.4. The fermentation enzymes alcohol dehydrogenase and lactate dehydrogenase were not synthesized in cells starved of a nutrient; they were only detectable in cells cultivated under conditions of restricted oxygen supply. The latter conditions caused accumulation of PHB in the wild-type and excretion of pyruvate by the PHB-negative mutant.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andreeva RI, Vysotskii ES, Ridicheva EK, Shchbakova GY (1981) Production of pyruvic acid by the luminescent bacterium Photobacterium mandapamensis. Microbiology 50:435–445
Bahl H, Andersch W, Braun K, Gottschalk G (1982) Effect of pH and butyrate concentration on the production of acetone and butanol by Clostridium acetobutylicum grown in continuous culture. Eur J Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 14:17–20
Bergmeyer HU, Bernt E (1974) α-Ketoglutarat. UV-spectroskopische Bestimmung. In: Bergmeyer HU (ed) Methoden der enzymatischen Analyse, 3rd edn. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, pp 1624–1627
Blackkolb F, Schlegel HG (1968) Regulation der Glucose-6-phosphat dehydrogenase aus Hydrogenomonas H16 durch ATP und NADH2. Arch Mikrobiol 63:177–196
Bohlken G (1969) Zur Speicherung von Reservestoffen in Bacillus megaterium. II. Untersuchungen an Poly-β-hydroxybuttersäure-freien Mutanten. Zentralbl Bakteriol Parasitenkd Abt II 123:16–29
Bormann EJ (1966) Stoffwechselregulation und Brenztraubensäurestauung bei Antibiotika-bildenden Streptomyceten. Arch Mikrobiol 53:218–230
Bormann EJ, Hermann R (1968) Zur Pyruvat- und α-Ketoglutaratausscheidung durch Streptomyces rimosus. Arch Mikrobiol 63:41–52
Bowien B, Schlegel HG (1972) Isolierung und Charakterisierung katabolischer Defektmutanten von Hydrogenomonas eutropha Stamm H16. II. Mutanten mit einem Defekt in der 2-Keto-3-desoxy-6-phosphogluconat-Aldolase. Arch Mikrobiol 87:221–234
Bowien B, Cook AM, Schlegel HG (1974) Evidence for the in vivo regulation of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase activity in Hydrogenomonas eutropha H16 from measurements of the intracellular concentrations of metabolic intermediates. Arch Microbiol 97:273–281
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Codd GA, Bowien B, Schlegel HG (1976) Glycollate production and excretion by Alcaligenes eutrophus. Arch Microbiol 110:167–171
Coleman RJ, Nord FF (1954) Application of mixed substrates to the study of pyruvic acid formation by Fusarium lini Bolley. Arch Mikrobiol 20:230–234
Cook AM, Schlegel HG (1978) Metabolite concentrations in Alcaligenes eutrophus H16 and a mutant defective in poly-β-hydroxybutyrate synthesis. Arch Microbiol 119:231–235
Cook AM, Urban E, Schlegel HG (1976) Measuring the concentrations of metabolites in bacteria. Anal Biochem 72:191–201
Czok R, Lamprecht W (1974) Pyruvat, Phosphoenolpyruvat und d-Glycerat-2-phosphat. In: Bergmeyer HU (ed) Methoden der enzymatischen Analyse, 3rd edn. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, pp 1491–1496
Dawes EA (1986) Microbial energetics, 1st edn. Blackie, Glasgow
Dawes EA, Senior P (1973) Energy reserve polymers in microorganisms. Arch Microbiol Physiol 14:203–266
Dische Z (1962) Colour reactions of hexoses. In: Whistler RL, Wolfram ML (eds) Methods in carbohydrate chemistry, vol. 1. Academic Press, New York, pp 488–494
Dorn M (1976) Vergärung von Fumarat und Malatdurch Clostridium formicoaceticum. Ph. D. Thesis. University of Göttingen
Doskocil J, Sikiia B, Kasparowa J, Doskocilowa D, Zajicek J (1958) Development of culture of Str. rimosus in submerged fermentation. J Gen Microbiol 18:302–313
Eagon RG, Cho HW (1965) Major products of glucose dissimlation by Pseudomonas natriegens. J Bacteriol 89:1209–1211
Eschenbruch R, Dittrich HH (1970) Die Acetoinbildung von Lactobacillus plantarum in Abhängigkeit von Thiamin, Liponsäure, l-Valin und l-Isoleucin. Arch Mikrobiol 70:303–312
Gawehn K, Bergmeyer HU (1974) d(−)-Lactat. In: Bergmeyer HU (ed) Methoden der enzymatischen Analyse, 3rd edn. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, pp 1538–1541
Gutmann I, Wahlefeld AW (1974) l(+)-Lactat. Bestimmung mit Lactat Dehydrogenase und NAD. In: Bergmeyer HU (ed) Methoden der enzymatischen Analyse, 3rd edn. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, pp 1510–1514
Hall AN (1963) Miscellaneous oxidative transformations. In: Rainbow C, Rose AH (eds) Biochemistry of industrial micro-organisms. Academic Press, London, pp 607–628
Hastings JW, Nealson KH (1977) Bacterial luminescence. Ann Rev Microbiol 31:549–595
Haywood GW, Anderson AJ, Chu L, Dawes EA (1988a) Characterization of two 3-ketothiolases possessing differing substrate specificities in the polyhydroxyalkanoate synthesizing organisms Alcaligenes eutrophus. FEMS Microbiol Lett 52:91–96
Haywood GW, Anderson A, Chu L, Dawes EA (1988b) The role of NADH- and NADPH-linked acetoacetyl-CoA reductases in the poly-3-hydroxybutyrate synthesizing organism Alcaligenes eutrophus. FEMS Microbiol Lett 52:259–264
Izumi Y, Matsumura Y, Tani Y, Yamada H (1982) Pyruvic acid production from 1,2-propandiol by thiamine requiring Acinetobacter sp 80-M. Agric Biol Chem 46:2673–2678
Jüttner RR, Lafferty RM, Knackmuss HJ (1975) A simple method for the determination of poly-β-hydroxybutyric acid in microbial biomass. Eur J Appl Microbiol 1:233–237
Kodaki I, Murakami H, Taguchi M, Izui K, Katsuki H (1981) Stringent control of intermediatry metabolism in Escherichia coli: pyruvate excretion by cells grown on succinate. J Biochem 90:1437–1444
Lemoigne M (1926) Produits de deshydration et de polymerisation de l'acide β-oxybutyrique. Bull Soc Chim Biol 8:770–782
Möllering H, Bergmeyer HU (1974) d-Gluconat. In: Bergmeyer HU (ed) Methoden der enzymatischen Analyse, 3rd edn. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, pp 1205–1209
Morinaga Y, Yamanaka S, Ishizaki A, Hiros Y (1978) Growth characteristics and cell composition of Alcaligenes eutrophus in chemostat culture. Agric Biol Chem 42:439–444
Moriguchi M (1982) Fermentative production of pyruvic acid from citrus peel extract by Debaryomyces coudertii. Agric Biol Chem 46:955–961
Nataka HM (1963) Effect of pH on intermediates produced during growth and sporulation of Bacillus cereus. J Bacteriol 86:577–581
O'Brien RW (1975) Induction of citrate lyase in Enterobacter cloacaae grown under aerated conditions and its effect on citrate metabolism. J Bacteriol 124:1084–1088
Payne WJ, Eagon RG, Williams AK (1960) Some observations on the physiology of Pseudomonas natriegens nov. spec. Antonie Leeuwenhoek J Microb Serol 27:121–128
Rehm HJ (1980) Industrielle Mikrobiologie. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York
Repaske R, Repaske AC (1976) Quantitative requirements for exponential growth of Alcaligenes eutrophus. J Appl Environ Microbiol 32:585–591
Ruby EG, Nealson KH (1977) Pyruvate production and excretion by the luminous marine bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 34:164–169
Ruhr EM (1977) Regulation der Biosynthese von Poly-β-hydroxybuttersäure in Alcaligenes eutrophus H16. Ph. D. Thesis, University of Göttingen
Ruhr EM, Schlegel HG (1975) Synthesis of poly-β-hydroxybutyrate in vivo and kinetics of β-ketothiolase in vitro in Alcaligenes eutrophus H16. Biochem Soc Trans 3:1093–1094
Schlegel HG, Steinbüchel A (1981) Die relative Belüftungstrate (RRR), ein neuer Belüftungsparameter. In: Lafferty RM (ed) Fermentation. Pringer, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York, pp 11–26
Schlegel HG, Vollbrecht D (1980) Formation of the dehydrogenases for lactate, ethanol and butanediol in the strictly aerobic bacterium Alcaligenes eutrophus. J Gen Microbiol 117:475–481
Schlegel HG, Gottschalk G, Bartha R von (1961) Formation and utilization of poly-β-hydrobutyric acid by Knallgas-bacteria (Hydrogenomonas). Nature 191:463–465
Schlegel HG, Lafferty R, Krauss I (1970) The isolation of mutants not accumulating poly-β-hydroxybutyric acid. Arch Microbiol 71:283–294
Schubert P, Steinbüchel A, Schlegel HG (1988) Cloning of the Alcaligenes eutrophus genes for the synthesis of poly-β-hydroxybutyric acid (PHB) and synthesis of PHB in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 170:5837–5847
Schuster E, Schlegel HG (1967) Chemolithotrophes Wachstum von Hydrogenomonas H16 im Chemostaten mit elektrolytischer Knallgaserzeugung. Arch Mikrobiol 58:380–409
Senior PJ, Dawes EA (1973) The regulation of poly-β-hydroxybutyrate metabolism in Azotobacter beijerinckii. Biochem J 134:225–238
Semor PJ, Beech GA, Ritchie GF, Dawes EA (1972) The role of oxygen limitation in the formation of poly-β-hydroxybutyrate during batch and continuous culture of Azotobacter beijerinckii. Biochem J 128:1193–1201
Sharma S, Tauro P (1987) Control of ethanol production by yeast: pyruvate accumulation in slow ethanol producing Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biotechnol Lett 9:585–586
Slater SC, Voige WH, Dennis DE (1988) Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of the Alcaligenes eutrophus H16 poly-β-hydroxybutyrate biosynthesis pathway. J Bacteriol 170:4431–4436
Steinbüchel A, Schlegel HG (1983) NAD-linked l(+)-lactate dehydrogenase from the strict aerobe Alcaligenes eutrophus. 1. Purification and properties. Eur J Biochem 130:321–328
Steinbüchel A, Schlegel HG (1984) A multifunctional fermentative alcohol dehydrogenase from the strict aerobe Alcaligenes eutrophus: purification and properties. Eur J Biochem 141:555–564
Steinbüchel A, Kuhn M, Niedrig M, Schlegel HG (1983) Fermentation enzymes in strictly aerobic bacteria: comparative studies on strains of the genus Alcaligenes and on Nocardia opaca and Xanthobacter autotrophicus. J Gen Microbiol 129:2825–2835
Vollbrecht D, El Nawawy MA (1980) Restricted oxygen supply and excretion of metabolites. I. Pseudomonas spec. and Paracoccus denitrificans. Eur J Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 8:135–143
Vollbrecht D, Schlegel HG (1979) Excretion of metabolites by hydrogen bacteria. III. d(−)-3-Hydroxybutaneoate. Eur J Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 7:259–266
Vollbrecht D, El Nawawy MA, Schlegel HG (1978) Excretion of metabolites by hydrogen bacteria. I. Autotrophic and heterotrophic fermentations. Eur J Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 6:145–155
Vollbrecht D, Schlegel HG, Stoschek G, Janczikowski A (1979) Excretion of metabolites by hydrogen bacteria. IV. Respiration rate-dependent formation of primary metabolites and of poly-3-hydroxybutanoate. Eur J Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 7:267–276
Ward AC, Rowley BI, Dawes EA (1977) Effect of oxygen and nitrogen limitation on poly-β-hydroxybutyrate biosynthesis in ammonium grown Azotobacter beijerinckii. J Gen Microbiol 102:61–68
Whittenburg R (1978) Biochemical characteristics of Streptococcus species. In: Skinner FA, Quesnel LB (eds.) Streptococci. Academic Press, London, pp 51–69
Williamson JR, Mellanby J (1974) d(−)-3-Hydroxybutyrat. In: Bergmeyer HU (ed) Methoden der enzymatischen Analyse, 3rd edn, Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, pp 1883–1886
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Steinbüchel, A., Schlegel, H.G. Excretion of pyruvate by mutants of Alcaligenes eutrophus, which are impaired in the accumulation of poly(β-hydroxybutyric acid) (PHB), under conditions permitting synthesis of PHB. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 31, 168–175 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00262457
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00262457