Summary
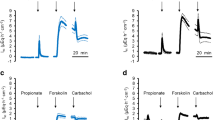
Unidirectional 22Na+ and 36Cl− fluxes were determined in short-circuited, stripped rumen mucosa from sheep by using the Ussing chamber technique. In both CO2/HCO 3− -containing and CO2/HCO 3− -free solutions, replacement of gluconate by short-chain fatty acids (SCFA, 39 mM) significantly enhanced mucosal-toserosal Na+ absorption without affecting the Cl− transport in the same direction. Short-chain fatty acid stimulation of Na+ transport was at least partly independent of Cl− and could almost completely be abolished by 1 mM mucosal amiloride, while stimulation of Na+ transport was enhanced by lowering the mucosal pH from 7.3 to 6.5. Similar to the SCFA action, raising the PCO2 in the mucosal bathing solution led to an increase in the amiloride-sensitive mucosal-to-serosal Na+ flux. Along with its effect on sodium transport, raising the PCO2 also stimulated chloride transport. The results are best explained by a model in which undissociated SCFA and/or CO2 permeate the cell membrane and produce a raise in intracellular H+ concentration. This stimulates an apical Na+/H+ exchange, leading to increased Na+ transport. The stimulatory effect of CO2 on Cl− transport is probably mediated by a Cl−/HCO 3− exchange mechanism in the apical membrane. Binding of SCFA anions to that exchange as described for the rat distal colon (Binder and Mehta 1989) probably does not play a major role in the rumen.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DIDS :
-
4,4'-diisothiocyanatostilbene-2,2'-disulfonic acid
- G t :
-
transepithelial conductance (mS·cm-2)
- HSCFA :
-
undissociated short-chain fatty acids
- J ms :
-
mucosal-to-serosal flux (μEq · cm-2 · h-1)
- J net :
-
net flux (μEq · cm-2 · h-1)
- J sm :
-
serosal-to-mucosal flux (μEq · cm-2 · h-1)
- PD :
-
transepithelial potential difference (mV)
- SCFA :
-
dissociated short-chain fatty acids
- SCFA :
-
short-chain fatty acids
References
Argenzio RA, Miller N, v Engelhardt W (1975) Effect of volatile fatty acids on water and ion absorption from the goat colon. Am J Physiol 229:997–1002
Argenzio RA, Southworth M, Lowe JE, Stevens CE (1977) Interrelationship of Na, HCO 3− and volatile fatty acid transport by equine large intestine. Am J Physiol 233:E469-E478
Aronson PS (1985) Kinetic properties of the plasma membrane Na+-H+-exchanger. Ann Rev Physiol 47:545–560
Aronson PJ, Nee J, Sahm MA (1982) Modifier role of internal H+ in activating the Na+/H+ exchanger in renal microvillus membrane vesicles. Nature 299:161–163
Ash RW, Dobson A (1963) The effect of absorption on the acidity of rumen contents. J Physiol 169:39–61
Bergman EN (1990) Energy contributions of volatile fatty acids from the gastrointestinal tract in various species. Physiol Rev 70:567–590
Binder HJ, Mehta P (1989) Short-chain fatty acids stimulate active sodium and chloride absorption in vitro in the rat distal colon. Gastroenterology 96:989–996
Bugaut M (1987) Occurrence, absorption, and metabolism of short chain fatty acids in the digestive tract of mammals. Comp Biochem Physiol 86B:439–472
Charney AN, Egnor RW (1989) Membrane site of action of CO2 on colonic sodium absorption. Am J Physiol 256:C584-C590
Chien W-J, Stevens CE (1972) Coupled active transport of Na and Cl across forestomach epithelium. Am J Physiol 223:997–1003
Christofferson GRJ, Skibsted LH (1975) Calcium ion activity in physiological salt solutions: influence of anions substituted for chloride. Comp Biochem Physiol 52:317–322
Counotte GM (1981) Regulation of lactate metabolism in the rumen. PhD thesis, University of Utrecht, Netherlands
Crump MH, Argenzio RA, Whipp SC (1980) Effects of acetate on absorption of solute and water from the colon. Am J Vet Res 41:1565–1568
Dirksen G (1970) Acidosis. In: Phillipson AT (ed) Physiology of digestion and metabolism in the ruminant. Oriel Press, Newcastle upon Tyne, pp 612–625
Dobson A (1959) Active transport through the epithelium of the reticulo-rumen sac. J Physiol 146:235–251
Engelhardt Wv, Rechkemmer G (1983) Absorption of inorganic ions and short-chain fatty acids inthe colon of mammals. In: Gilles-Baillien M, Gilles R (eds): Intestinal transport. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 26–45
Gäbel G, Bell M, Martens H (1989) The effect of low mucosal pH on sodium and chloride movement across the isolated rumen mucosa of sheep. Q J Exp Physiol 74:35–44
Gäbel G, Smith E, Martens H (1988) Stimulation of rumen Na absorption by short chain fatty acids. Pflügers Arch (Suppl. 1) 411: R107
Gäbel G, Smith E, Reale E, Martens H (1987) The effect of short chain fatty acids (SCFA) and mucosal pH on Na and Cl movement across isolated rumen epithelium of sheep. Z Gastroenterol 25:627
Goldfarb DS, Egnor RW, Charney AN (1988) Effects of acid-base variables on ion transport in rat colon. J Clin Invest 81:1903–1910
Haiger H (1982) Biometrische Methoden in der Tierproduktion. Verlagsunion Agrar, Wien
Hatch M (1987) Short-chain fatty acid transport and their effects on ion transport by rabbit caecum. Am J Physiol 253:G171-G178
Holtenius K, Dahlborn K (1990) Water and sodium movements across the ruminal epithelium in fed and food-deprived sheep. Exp Physiol 75:57–67
Holtug K (1989) Mechanisms of absorption of short chain fatty acids-coupling to intracellular pH regulation. Acta Vet Scand (Suppl.) 86:126–133
Krapf R, Berry CA, Alpern RJ, Rector Jr FC (1988) Regulation of cell pH by ambient bicarbonate, carbon dioxide tension and pH in the rabbit proximal convoluted tubule. J Clin Invest 81:381–389
Martens H, Gäbel G (1988) Transport of Na and Cl across the epithelium of ruminant forestomachs: Rumen and omasum. A review. Comp Biochem Physiol 90A:569–575
Martens H, Gäbel G, Strozyk B (1991) Mechanism of electrically silent Na and Cl transport across the rumen epithelium. Exp Physiol 76:103–114
Matsuzaki K, Stokes JB, Schuster VL (1989) Stimulation of Cl− self-exchange by intracellular HCO 3− in rabbit cortical collecting duct. Am J Physiol 257:C94-C101
Petersen KU, Wood JR, Schulze G, Heintze K (1981) Stimulation of gallbladder fluid and electrolyte absorption by butyrate. J Membr Biol 62:183–193
Rajendran VM, Binder HJ (1990) Characterization of Na−H exchange in apical membrane vesicles of rat colon. J Biol Chem 265:8408–8414
Soergel KH, Harig JM, Loo FD, Ramaswamy K, Wood CM (1989) Colonic fermentation and absorption of SCFA in man. Acta Vet Scand (Suppl.) 86:107–115
Stevens CE (1964) Transport of sodium and chloride by the isolated rumen epithelium. Am J Physiol 206:1099–1105
Stevens CE (1970) Fatty acid transport through the rumen epithelium. In: Phillipson AT (ed) Physiology of digestion and metabolism in the ruminant. Oriel Press, Newcastle upon Tyne, pp 101–112
Thorlacius SO, Lodge GA (1973) Absorption of steam-volatile fatty acids from the rumen of the cow as influenced by diet, buffers, and pH. Can J Anim Sci 53:279–288
Vernay M (1986) Colonic absorption of inorganic ions and volatile fatty acids in the rabbit. Comp Biochem Physiol 83A:775–784
Wagner JD, Kurtin P, Charney AN (1986) Effect of systemic acid-base disorders on ileal intracellular pH and ion transport. Am J Physiol 250:G588-G593
Weigand E, Young JW, McGilliard AD (1975) Volatile fatty acid metabolism by rumen mucosa from cattle fed hay or grain. J Dairy Sci 58:1294–1300
Yoshitomi K, Frömter E (1984) Cell pH of rat proximal tubule in vivo and the conductive nature of peritubular HCO 3− (OH−) exit. Pflügers Arch 402:300–305
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gäbel, G., Vogler, S. & Martens, H. Short-chain fatty acids and CO2 as regulators of Na+ and Cl− absorption in isolated sheep rumen mucosa. J Comp Physiol B 161, 419–426 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00260803
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00260803