Summary
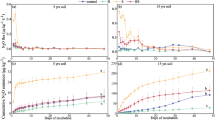
The behaviour of urease activity, ammoniacal N concentrations and pH in flood water and that of ammonia flux was investigated in a water-logged soil either in the presence or in the absence of rice and with three different treatments (control, urea and urea + phenyl phosphorodiamidate). In the presence of the phenyl phosphorodiamidate (PPD), that is a urease inhibitor, increases in ammoniacal N concentrations and in ammonia evolution were delayed but not eliminated. The degradation and/or the inactivation of PPD might have occurred, thus removing the inhibition of the enzyme activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beaton JD (1973) Urea: Its popularity grows as a dry source of nitrogen. Crops Soils 30:11–14
Bouldin DR, Alimagno BV (1976) Volatilization from IRRI. paddies following broadcast application of fertilizer nitrogen (Terminal Report). International Rice Research Institute, Los Baños, Philippines
Byrnes BH, Savant NK, Craswell ET (1983) Effect of a urease inhibitor phenyl phosphorodiamidate on the efficiency of urea applied to rice. Soil Sci See Am J 47:270–274
Cao ZH, De Datta SK, Fillery IRP (1984a) Effect of placement methods on flood water properties and recovery of applied nitrogen (15N-labeled urea) in wetland rice. Soil Sci Soc Am J 48:196–203
Cao ZH, De Datta SK, Fillery IRP (1984b) Nitrogen-15 balance and residual effects of urea -N in wetland rice fields as affected by deep placement techniques. Soil Sci Soc Am J 48:203–208
Craswell ET, Vlek PLG (1979) Fate of fertilizer nitrogen applied to wetland rice. In: International Rice Research Institute, Los Baños, Philippines (ed) Nitrogen and rice, pp 175–192
Craswell ET, De Datta SK, Obcemea WN, Hartantyo M (1981) Time and mode of nitrogen fertilizer application to tropical wetland rice. Fert Res 2:247–259
De Datta SK (1978) Fertilizer management for efficient use in wetland rice soils. In: International Rice Research Institute, Los Baños, The Philippines (ed) Soils and rice, pp 671–701
De Datta SK (1981) Principles and practices of rice production. Wiley, New York
De Laune RD, Patrick WH Jr (1970) Urea conversion to ammonia in waterlogged soils. Proc Soil Sci Soc Am 34:603–607
Faurie G, Bardin R (1979) Volatilization of ammonia. Influence of climatic factors and plant cover. Ann Agron 30:401–414
Fillery IRP, Simpson JR, De Datta SK (1984) Influence of field environment and fertilizer management on ammonia loss from flooded rice. Soil Sci Soc Am J 48:914–920
Held P, Land S, Tradler E, Klepel M, Drofine D, Hartbrich HJ, Rothe G, Scheler H, Grundmeier S, Trautmann A (1976) Agents for reducing the loss of plant-available nitrogen in cultivated soil. East German Patent No. 122, 177 (Chemical Abstract 87:67315w)
Hignett TP (1979) Fertilizer manual. Reference manual IFDO-R.I. International Fertilizer Development Center, MuscleShoals, AL
Kleczkowski K, Hiort V, Kating H (1966) Studies of the metabolism of urea in microorganisms. IV Adaptive urease formation in Micrococcus denitrificans Beij. Arch Mikrobiol 52:177–183
Magana-Plaza I, Ruiz-Herrera J (1967) Mechanisms of regulation of urease biosynthesis in Proteus rettgeri. J Bacteriol 93:1294–1301
Martens DA, Bremner JM (1984) Urea hydrolysis in soils: factors influencing the effectiveness of phenyl phosphorodiamidate as a retardant. Soil Biol Biochem 16:515–519
Mikkelsen DS, De Datta SK, Obcemea WN (1978) Ammonia volatilization losses from flooded rice soils. Soil Sci Soc Am J 42:725–730
Pedrazzini FR, Tarsitano R (1986) Ammonia volatilization from flooded soil following urea-application. Plant and Soil 91:101–107
Ponnamperuma FN (1978) Electrochemical changes in submerged soils and the growth of rice. In: International Rice Research Institute, Los Banos, The Philippines (ed) Soils and rice, pp 421–441
Prasad R, De Datta SK (1979) Increasing fertilizer nitrogen efficiency in wetland rice. In: International Rice Research Institute, Los Banos, The Philippines (ed) Nitrogen and rice, pp 465–484
Sahrawat KL (1980) Urease activity in tropical rice soils and flood water. Soil Biol Biochem 12:195–196
Savant NK, De Datta SK (1982) Nitrogen transformations in wetland rice soil. Adv Agron 35:241–302
Simpson JR, Freney JR, Wetselaar R, Murhead WA, Leuning R, Denmead OT (1984) Transformations and losses of urea nitrogen after application to flooded rice. Aust J Agric Res 35:189–200
Vlek PLG, Craswell ET (1979) Effect of nitrogen source and management on ammonia volatilization losses from flooded rice-soil systems. Soil Sci Soc Am J 43:352–358
Vlek PLG, Craswell ET (1982) Ammonia volatilization from flooded soils. Fert Res 2:227–245
Zantua MI, Bremner JM (1976) Production and persistence of urease activity in soils. Soil Biol Biochem 8:369–374
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pedrazzini, F., Tarsitano, R. & Nannipieri, P. The effect of phenyl phosphorodiamidate on urease activity and ammonia volatilization in flooded rice. Biol Fert Soils 3, 183–188 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00255781
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00255781