Abstract
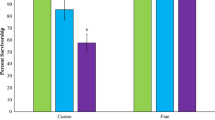
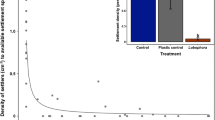
Planulae collected from the reef coral Pocillopora damicornis were exposed to four different levels of sediment (0, 10, 100, 1000 mg l-1) for 14 days under two contrasting water agitation levels (aerated vs. non-aerated). There was no significant difference in larval settlement among the varius sediment treatments and between agitation levels used in this study. However, a significant number of settled planulae underwent reversed metamorphosis (“polyp bail-out”) in the 100 and 1000 mg l-1 treatments of both water aeration regimes indicating conditions were not appropriate for continued development and growth. Data suggested that successful recruitment may be limited in areas with greater than normal sediment loads.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babcock R, Davies P (1991) Effect of sedimentation on settlement of Acropora millepora. Coral Reefs 9:205–208
Birkeland C, Rowley D, Randall R (1981). Coral recruitment patterns at Guam. Proc 4th Int Coral Reef Symp 2:339–344
Chansang H, (1988) Coastal tin mining and marine pollution in Thailand. Ambio 17:223–228
Chansang H, Boonyanate P, Charuchinda M (1981) Effect of sedimentation from coastal mining on corals on the northwestern coast of Phuket Island, Thailand. Proc 4th Int Coral Reef Symp 1:129–136
Craik W, Kenchington R, Kelleher G (1990) Coral reef management. In: Dubinsky Z (ed) Coral reefs. Elsevier, Amsterdam (Ecosystem of the world, vol 25, pp 453–468)
Gomez ED (1988) Overview of the environmental problems in the East Asian Seas Region. Ambio 17:166–169
Harrigan JF (1972) The planula larva of Pocillopora damicornis: lunar periodicity of swarming and substratum selection behavior. PhD dissertation, Department of Zoology, University of Hawaii, Honolulu
Hodgson G (1989) The effects of sedimentation on Indo-Pacific reef corals. Ph D dissertation, Department of Zoology, University of Hawaii, Honolulu
Hodgson G (1990) Sediment and the settlement of larvae of the reef coral Pocillopora damicornis. Coral Reefs 9:41–43
Hodgson G, Dixon JA (1988) Logging versus fisheries and tourism in Palawan: An environmental and economic analysis. East-West Environment and Policy Institute Occassional Paper 7
Hubbard DK (1986) Sedimentation as a control of reef development: St. Croix, U.S.V.I. Coral Reefs 5:117–125
Lewis JB (1974) The settlement behavior of planulae larvae of the hermatypic coral Favia fragum (Esper). J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 15:165–172
Richmond RH, Jokiel PL (1984) Lunar periodicity in larval release in the reef Pocillopora damicornis at Enewetak and Hawaii. Bull Mar Sci 34:280–287
Richmond RH (1985) Reversible metamorphosis in coral planula larvae. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 22:181–185
Richmond RH (1987) Energetic relationships and biogeographical differences among frecundity, growth, and reproduction in the reef coral Pocillopora damicornis. Bull Mar Sci 41:594–604
Richmond RH (1988) Competency and dispersal potential of planulae larvae of a spawning versus a brooding coral. Proc 6th Int Coral Reef Symp 2:827–831
Rogers CS (1990) Responses of coral reefs and reef organisms to sedimentation. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 62:185–202
Rogers CS, Fitz HC, Gilnack M, Beets J, Hardin J (1984) Scleractinian coral recruitment patterns at Salt River submarine canyon, St. Croix, U.S.V.I. Coral Reefs 3:69–76
Te FT (1991) The effects of two petroleum products on Pocillopora damicornis planulae. Pac Sci 45:290–298
Veron JEN (1986) Corals of Australia and the Indo-Pacific. Australian Institute of Marine Science. Angus and Robertson, Sydney, pp 1–644
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Te, F.T. Response to higher sediment loads by Pocillopora damicornis planulae. Coral Reefs 11, 131–134 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00255466
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00255466