Summary
The use of mixed cultures in the food industry is hindered by the lack of rapid and specific measurement techniques. The coculture of Streptococcus thermophilus and Lactobacillus bulgaricus, used for producing starters for yoghurt production, is a simple model of a mixed culture.
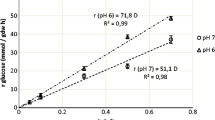
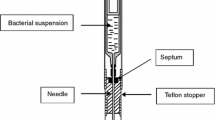
After verifying that Streptococcus thermophilus specifically degraded urea, we attempted to correlate the cell concentration of the species first with urease activity and then with the rate of CO2 production from urea in the medium. The measurement was performed in real time with a specific electrode for dissolved CO2. The results obtained with the method have the same uncertainy as those obtained by cell counts. The estimation is valid between 107 and 109 cells/ml.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Accolas JP, Bloquel R, Didienne R, Régnier J (1977) Propriétés acidifiantes des bactéries lactiques thermophiles en relation avec la fabrication du yoghourt. Le Lait 57:1–23
Bautista ES, Dahiya RS, Speck ML (1966) Identification of compounds causing symbiotic growth of Streptococcus thermophilus and Lactobacillus bulgaricus in milk. J Dairy Res 33:299–307
Barrère C, Ducasse M, Vigne C, Vidal M, Tallec A (1976) Dosage du CO2 dans les vins. Vignes et vins 273:31–38
Bracquart P, Lorient D (1977) Effet des acides aminés sur la croissance de Streptococcus thermophilus. Milchwissen-schaft 32:221–224
Breed RS (1911) The determination of the number of bacteria in milk by direct microscopic examination. Zentralblatt für Bakt Part II 30:227
Cantéri G (1984) Utilization of a specific probe for determination of carbon dioxide produced by lactic acid bacteria. Bio-Science 14:7–10
Desmazeaud MJ, Hermier J (1972) Isolement et détermination de la composition qualitative des peptides issus de la caséine, stimulant la croissance de Streptococcus thermophilus. Eur J Biochem 28:190–198
Driessen FM, Kingma F, Stadhouders J (1982) Evidence that Lactobacillus bulgaricus in yogurt is stimulated by carbon dioxide produced by Streptococcus thermophilus. Neth Milk Dairy J 36:135–144
Farrow JAE, Collins MD (1984) DNA base composition, DNA-DNA homology and long chain fatty acid studies on Streptococcus thermophilus and Streptococcus salivarius. J Gen Microbiol 130:357–362
Galesloot TE, Hassing F, Veringa HA (1968) Symbiosis in yoghurt (I) Stimulation of Lactobacillus bulgaricus by a factor produced by Streptococcus thermophilus. Neth Milk Dairy J 22:50–62
Hugenholtz J, Velkamp H (1985) Competition between strains of Streptococcus cremoris. TEMS Microbiology Letters ecology 31:57–62
Lonvaud-Funel A, Matsumoto N (1979) Le coefficient de solubilité du gaz carbonique dans les vins. Vitis 18:137–147
Lopez ME (1984) Selectivity of the potentiometric carbon dioxide gas-sensing electrode. Anal Chem 56:2360–2366
Miozzari GF, Niederberger P, Hütter R (1978) Permeabilisation of microorganisms by triton X-100. Analytical Biochem 90:220–233
Moon NJ, Reinbold GW (1976) Commensalism and competition in mixed cultures of Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptoccus thermophilus. J Milk Food Technol 39:337–341
Nelson GEM, Peterson RE, Cigler A (1973) Serine deshydratase from bacteria. J Appl Bacteriol 36:245–247
Pette JW, Lolkema H (1950) Yoghurt (I) Symbiosis and antisymbiosis in mixed culture of Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus. Neth Milk Dairy J 6:209–224
Plaquet R, Leflon F (1975) Automatisation du, dosage de l'ammoniaque per la réaction de Nessler. Bulletin de la Societé de Pharmacie de Lille 1:45–51
Shoda M, Ishikawa Y (1981) Carbon dioxide sensor for fermentation systems. Biotechnol Bioeng 23:461–466
Tayeb J, Bouillanne C, Desmazeaud MJ (1984) Computerized control of growth with temperature in a mixed culture of lactic acid bacteria. J Ferment Technol 62:461–470
Tinson W, Broome MC, Hillier AJ, Jago GR (1982) Metabolism of Streptococcus thermophilus production of CO2 and NH3 from urea. Aust J Dairy Technol 37:14–16
Veringa HA, Galesloot TE, Davelaar H (1968) Symbiosis in yoghurt (II) Isolation and identification of a growth factor for Lactobacillus bulgaricus produced by Streptococcus thermophilus. Neth Milk Dairy J 22:114–120
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Spinnler, H.E., Bouillanne, C., Desmazeaud, M.J. et al. Measurement of the partial pressure of dissolved CO2 for estimating the concentration of Streptococcus thermophilus in coculture with Lactobacillus bulgaricus . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 25, 464–470 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00253320
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00253320