Abstract
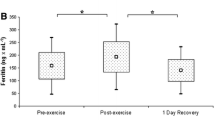
To determine the influence of exercise on serum levels of myoglobin, serum levels of this protein were determined by RIA in 90 healthy men, divided as follows: (1) Basal control (no exercise) 25 cases; (2) Moderate exercise (after subject had been working for 12 h in Medicine Emergency Service) 19 cases, and (3) Intensive exercise: (a) football professional (45-min match) 10 cases; (b) football amateur (45-min match) 10 cases; (c) basketball professional (45-min match) 10 cases, and (d) basketball professional (90-min training) 16 cases. Our results led us to the following conclusions. (1) Moderate exercise, such as the usual daily work, does not modify myoglobin levels; (2) Myoglobin serum levels after exercise increase in nearly all individuals. They are higher in untrained people; (3) There seems to be a correlation between exercise intensity and increase of myoglobin serum levels, and (4) The detection of serum myoglobin by RIA may have a wide field of application for sport medicine.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bywaters EGL (1945) Ischaemic muscle necrosis (“Crush Syndrome”). Br Med Bull 3:107–112
Haimovici A (1960) Arterial embolism with acute massive ischemic myopathy and myoglobinuria: Evaluation of hitherto unreported syndrome with report of two cases. Surgery 47:739–744
Howenstein JA (1960) Exertion—induced myoglobinuria and hemoglobinuria. JAMA 173:493–499
Kagen LJ (1971) Myoglobinemia and myoglobinuria in myositis syndromes. Arthritis Rheum 14:457–464
Kagen LJ (1973) Chemical Factors. In: Kagen LJ (ed) Myoglobin: Biochemical, Physiological and Clinical Aspects. Columbia University Press, New York London, p 9–39
Jackson RC (1970) Exercise induced renal failure and muscle damage. Proc Roy Soc Med 63:566–570
Nuttall FQ, Jones B (1968) Creatine kinase and glutamic oxalacetic transaminase activity in serum: kinetics of change with exercise and effect of physical conditioning. J Lab Clin Med 71:847–854
Ritter WS, Stone MJ, Willerson JT (1979) Reduction in exertional myoglobinemia after physical conditioning. Arch Int Med 139:644–647
Smith RF (1968) Exertional rhabdomyolysis in naval officer candidates. Arch Int Med 121:313–319
Stone MJ, Willerson JT, Gómez Sanchez CE, Waterman MR (1975) Radioimmunoassay of myoglobin in human serum. Results in patients with acute myocardial infarction. J Clin Invest 561:334–339
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sabriá, M., Ruibal, A., Rey, C. et al. Influence of exercise on serum levels of myoglobin measured by radioimmunoassay. Eur J Nucl Med 8, 159–161 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00252887
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00252887