Summary
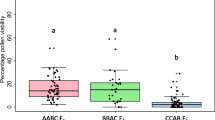
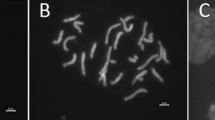
Based on meiotic chromosome behavior in intra- and interspecific hybrids, genome symbols were assigned to the following diploid (2n=40) Glycine species: G. canescens = AA; G. clandestina- Intermediate pod (Ip)=A 1 A 1; G. clandestina-Short pod (Sp)=BB; G. latifolia = B 1 B 1; G. tabacina = B 2 B 2; G. cyrtoloba = CC; and G. tomentella = DD. Genome symbol GG was reserved for the soybean, G. max. At metaphaseI, loose chromosome associations were observed in completely sterile interspecific hybrids whose parents differed in their genomes, suggesting some chromosome homologies among species. Although G. clandestina-Sp, G. latifolia and G. tabacina are morphologically distinct species, they differ only by a paracentric inversion. Similar observations were recorded for G. canescens and G. clandestina-Ip. Evidence is presented that demonstrates that G. tabacina (2n=80) and G. tomentella (2n=78, 80) are allotetraploid species complexes. Hybrid weakness, sterility, seedling lethality and seed inviability were found in intra- and interspecific hybrids.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernard RL, Weiss MG (1973) Qualitative Genetics. In: Caldwell BE (ed) Soybeans: improvement, production, and uses. Agronomy no 16. Agron Inc, Wisconsin, pp 117–154
Broué P, Douglass J, Grace JP, Marshal DR (1982) Interspecific hybridisation of soybeans and perennial Glycine species indigenous to Australia via embryo culture. Euphytica 31:715–724
Crane CF, Beversdorf WD, Bingham ET (1982) Chromosome pairing and associations at meiosis in haploid soybean (Glycine max). Can J Genet Cytol 24:293–300
Grant JE, Grace JP, Brown AHD, Putievsky E (1984a) Interspecific hybridization in Glycine Willd. Subgenus Glycine (Leguminosae). Aust J Bot 32:655–663
Grant JE, Brown AHD, Grace JP (1984b) Cytological and isozyme diversity in Glycine tomentella Hayata (Leguminosae). Aust J Bot 32:665–677
Gurley WB, Hepburn AG, Key JL (1979) Sequence organization of the Soybean genome. Biochim Biophys Acta 561: 167–183
Hadley HH, Hymowitz T (1973) Speciation and Cytogenetics. In: Caldwell BE (ed) Soybeans: improvement, production, and uses. Agronomy no 16. Agron Inc, Wisconsin, pp 97–116
Hermann FJ (1962) A revision of the genus Glycine and its immediate allies. USDA Tech Bull 1268:1–82
Hymowitz T, Newell CA (1981) Taxonomy of the genus Glycine, domestication and uses of soybeans. Econ Bot 35:272–288
Newell CA, Hymowitz T (1982) Successful wide hybridization between the soybean and a wild perennial relative, G. tomentella Hayata. Crop Sci 22:1062–1065
Newell CA, Hymowitz T (1983) Hybridization in the genus Glycine subgenus Glycine Willd. (Leguminosae, Papilionoideae). Am J Bot 70:334–348
Palmer RG (1974) Aneuploids in the soybean, Glycine max. Can J Genet Cytol 16:441–447
Palmer RG, Heer H (1976) Aneuploids from a desynaptic mutant in soybeans (Glycine max (L.) Merr.). Cytologia 41:417–427
Putievsky E, Broué P (1979) Cytogenetics of hybrids among perennial species of Glycine subgenus Glycine. Aust J Bot 27:713–723
Singh RJ, Hymowitz T (1985a) Intra- and interspecific hybridization in the genus Glycine subgenus Glycine Willd.: chromosome pairing and genome relationships. Z Pflanzenzücht (in press)
Singh RJ, Hymowitz T (1985b) An intersubgeneric hybrid between Glycine tomentella Hayata and the soybean, G. max (L.) Merr. Euphytica 34:187–192
Stebbins GL (1958) The inviability, weakness, and sterility of interspecific hybrids. Adv Genet 9:147–215
Tindale MD (1984) Two new eastern Australian species of Glycine Willd. (Fabaceae). Brunonia 7:207–213
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by G.S.Khush
This research was supported in part by the Illinois Agricultural Experiment Station and the U.S. Department of Agriculture (Special grant 82-CRSR-2-2007). Travel grants to collect Glycine germplasm were received from the Rockefeller Foundation, the Illinois Soybean Program Operating Board, the National Science Foundation (INT76-14753) and the International Board for Plant Genetic Resources
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, R.J., Hymowitz, T. The genomic relationships among six wild perennial species of the genus Glycine subgenus Glycine Willd.. Theoret. Appl. Genetics 71, 221–230 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00252059
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00252059