Abstract
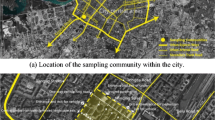
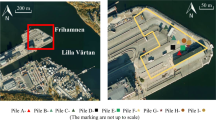
Snow disposal creates problems each year in Montreal. Snow dumping in water courses is favored due to both esthetic and economic considerations. Used snow must be considered as a potential pollutant. Its impact on the aquatic receiving environment is not well known. With river dumping in progress, snow samples were collected at 3 sites: Concorde Bridge, and at piers 30 and 52 in Montreal Harbor. Analysis of 28 routine parameters demonstrated that the quality of snow ultimately dumped in the river varies considerably according to its sources and the time it remains in the streets. Used-snow from residential areas was shown to be less polluted than the snow from commercial areas. Furthermore, from the total number of sampled districts, used-snow dumped at pier 30 appears to be relatively more polluted as it originated from downtown areas where vehicle circulation is more dense. Heavy metals in particles sizes between 0.45 and 63 μm represented more than 70% of the measured suspended solids which reflects the risk of bioaccumulation via benthic organisms. Principal component analysis of present data suggests that with analysis of chlorides, suspended solids and Pb alone, it is possible to approximately determine the quality of used-snow.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, F. S.: 1973, Farm Economics, Pennsylvania State University.
Anonymous: 1971, Environment Impact of Highway De-icing, Env. Prot. Agency Water Quality Research.
Anonymous: 1974, A Review of Literature on the Environmental Impact of the De-icing Compounds and Snow Disposal, Ontario Ministry of Environment, 66 p.
Anonymous: 1981, BMDP Statistical Software, Univ. of California Press, U.S.A., 926 p.
Anonymous: 1982a, SAS User's Guide: Basics, SAS Institute Inc., U.S.A., 921 p.
Anonymous: 1982b, Tail and Landscape Ottawa Field Naturalist Club 16, 252.
Anonymous: 1983, Rapports d'analyses, Montreal City Control and Research Laboratory.
APHA (American Public Health Association): 1980, Standard Methods, for the Examination of Water and Waste-Water, 1134 p.
Delisle, C. E., Zinger, L, Harvey, C., Delmas, D., and Morin, P.: 1985, Répercussions écologiques des déversements des neiges usées dans le fleuve St-Laurent du niveau du Port de Montreal, City of Montreal Confidential Report, 225 p.
Freick, G., Horne, R. A., and Yeale, D.: 1972, Science 175, 1142.
Goodnight, C. J.: 1973, Trans. Amer. Microscopy Soc. 92, 1.
Johnston, T.: 1984, Environmental Concerns from Snow Dumping in Metropolitan Toronto, Montreal, A.P.W.A. Snow Disposal Workshop.
Jonasson, I. R.: 1973, Nature 241, 447.
Lachambre, G.: 1981, The Need for a Comprehensive Plan and How to Gain Support for It, Baltimore A.P.W.A. Snow Conference, 24 p.
Landsberger, S.: 1984, Sulphur and Heavy Metal Pollution of Urban Snow and Environmental Impact, Montreal A.P.W.A. Snow Disposal Workshop, 8 p.
Landsberger, S. and Servis, R. E.: 1983, Int. J. of Env. Anal. Chem. 16, 95.
Lewis, J. E., Moore, T. R., and Enright, N. J.: 1983, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 20, 7.
Malmqvist, P. A.: 1984, Environmental Effects on Snow Disposal in Sweden, Montreal A.P.W.A. Snow Disposal Workshop.
Milne, J. B. and Dickman, M.: 1977, J. Env. Sc. Health 12, 173.
Niblett, P.: 1984, Understanding Pollution from Snow Melt, Environmental Profiling, Montreal A.P.W.A. Snow Disposal Workshop.
O'Brien, P.: 1974, Chemical Impact of Snow Dumping Practices, Env. Prot. Agency Res. Center, 27 p.
Olivier, B. G., Mine, J. B., and Labarre, N.: 1974, J. WPCF 46, 766.
OME (Ontario Ministry of Environment): 1975, Guidelines for Snow Disposal and De-icing Operations in Ontario, 8 p.
Percherkin, N. A. and Burmatova, E. A.: 1965, Chemical Composition of Snow on the Water Surface of the Kama and Votkinst Reservoirs, U.S. Army Cold Regions Research and Engineering Laboratory.
QME (Quebec Ministry of Environment): 1983, Lignes directrices pour l'elimination des neiges usées, 22 p.
Richards, J. L. et Ass. Lmt., Labrèche and Vezina et Ass.: 1973, Étude sur l'émination de la neige pour le territoire de la capitale nationale, 163 p.
Riverin, J. M.: 1982, Límination de la neige et la protection de l'environnement, Chicoutimi Env. Comity, 10 p.
Scott, W.: 1980, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 13, 187.
Viateur, A.: 1978, La disposition des neiges usées en milieu urbain et la qua/W de l'environnement, Quebec Env. Prot. Services, 17 p.
Zinger, 1.: 1985, ‘Qualité des neiges usées et impacts de leurs déversements dans la égion du Port du Montreal’, MSc. Dissertation, École Polytechnique of Montreal, 103 p.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zinger, I., Delisle, C.E. Quality of used-snow discharged in the ST-Lawrence river, in the region of the Montreal Harbor. Water Air Soil Pollut 39, 47–57 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00250947
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00250947