Summary
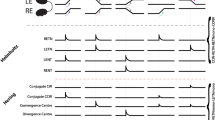
Saccadic omnipause neurons (OPNs) were intracellularly labelled with horseradish peroxidase (HRP) in alert cats and squirrel monkeys. The somas of OPNs were located on or near the midline in the caudal pons and their axons projected to regions of the pontomedullary reticular formation that contain the excitatory and inhibitory burst neurons.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Curthoys IS, Markham CH, Furuya N (1984) Direct projection of pause neurons to nystagmus-related excitatory burst neurons in the cat pontine reticular formation. Exp Neurol 83: 414–422
Evinger C, Kaneko CRS, Fuchs AF (1982) The activity of omnipause neurons in alert cats during saccadic eye movements and visual stimuli. J Neurophysiol 47: 827–844
Furuya N, Markham CH (1982) Direct inhibitory synaptic linkage of pause neurons with burst inhibitory neurons. Brain Res 245: 139–143
Hikosaka O, Igusa Y, Nakao S, Shimazu H (1978) Direct inhibitory synaptic linkage of pontomedullary reticular burst neurons with abducens motoneurons in the cat. Exp Brain Res 33: 337–352
Igusa Y, Sasaki S, Shimazu H (1980) Excitatory premotor burst neurons in the cat pontine reticular formation related to the quick phase of vestibular nystagmus. Brain Res 182: 451–456
Keller EL (1977) Control of saccadic eye movements by midline brainstem neurons. In: Baker R, Berthoz A (eds) Control of gaze by brain stem neurons. Developments in neuroscience, Vol 1. Elsevier, New York, pp 327–336
King WM, Precht W, Dieringer N (1980) Afferent and efferent connections of cat omnipause neurons. Exp Brain Res 38: 395–403
Langer TP, Kaneko CRS (1983) Efferent projections of the cat oculomotor reticular omnipause neurons region: an autoradiographic study. J Comp Neurol 217: 288–306
McCrea RA, Yoshida K, Berthoz A, Baker R (1980) Eye movement related activity and morphology of second order vestibular neurons terminating in the cat abducens nucleus. Exp Brain Res 40: 468–473
Nakao S, Curthoys IS, Markham CH (1980) Direct inhibitory projection of pause neurons to nystagmus-related pontomedullary reticular burst neurons in the cat. Exp Brain Res 40: 283–293
Ohgaki T, Curthoys IS, Markham CH (1986) Intracellular injection of HRP in eye movement-related pause neurons in cat. Soc Neurosci Abstr 12: 457
Strassman A, Highstein SM, McCrea RA (1986a) Anatomy and physiology of saccadic burst neurons in the alert squirrel monkey. I. Excitatory burst neurons. J Comp Neurol 249: 358–380
Strassman A, Highstein SM, McCrea RA (1986b) Anatomy and physiology of saccadic burst neurons in the alert squirrel monkey. II. Inhibitory burst neurons. J Comp Neurol 249: 337–357
Yoshida K, McCrea RA, Berthoz A,Vidal PP (1982) Morphological and physiological characteristics of inhibitory burst neurons controlling horizontal rapid eye movements in the alert cat. J Neurophysiol 48: 761–784
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Strassman, A., Evinger, C., McCrea, R.A. et al. Anatomy and physiology of intracellularly labelled omnipause neurons in the cat and squirrel monkey. Exp Brain Res 67, 436–440 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00248565
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00248565