Summary
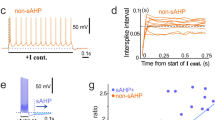
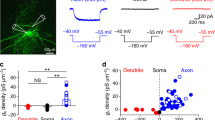
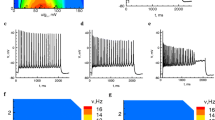
An in vitro slice preparation was used to obtain intracellular recordings of neostriatal neurons. Indirect evidence for the presence of an early outward conductance in neostriatal neurons is presented. With near threshold stimulation neostriatal neurons fired very late during the pulse. The long firing latency was associated with a slow (ramp-like) depolarization. In the presence of TTX the slow depolarization was lost and outward-going rectification dominated the subthreshold response. This finding demonstrated that both, outward and inwardgoing conductances play a role during the ramp-like depolarization. Outward-going rectification during depolarizing responses could be further augmented if the depolarizing stimulus was preceded by a conditioning hyperpolarization. A conditioning hyperpolarization prolonged the firing latency and slowed the firing frequency. A conditioning depolarization had opposite effects. After TTX treatment, the response showed a hyperpolarizing “sag” when depolarizing stimulation was preceded by conditioning hyperpolarization. 4-AP (0.5–2.5 mM) blocked the effects of the conditioning hyperpolarization on the firing latency and on the voltage trajectory. 4-AP also disclosed a slow depolarization which could produce neuronal firing very early during the pulse. This depolarization was TTX-sensitive and Co++-insensitive. In contrast to 4-AP, TEA (20 mM) did not produce a reduction in the firing latency but disclosed a membrane oscillatory behavior most probably produced by the interplay of these opposing conductances: the slow inward (probably Na+) and the transient outward (probably K+). Repetitive firing during 4-AP treatment was of the “phasictonic” type with an initial burst riding on the initial Co++-insensitive slow depolarization and a somehow irregular train of spikes during the remainder of the stimulation. Action potentials during 4-AP treatment were followed by an afterdepolarization which dominated the initial part of the interspike interval.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aghajanian GK (1985) Modulation of a transient outward current in serotonergic neurones by α1-adrenoceptors. Nature (Lond) 315: 501–503
Bargas J, Galarraga E, Aceves J (1988) Electrotonic properties of neostriatal neurons are modulated by extracellular potassium. Exp Brain Res 72: 390–398
Barrett EF, Barrett JN (1976) Separation of two voltage-sensitive potassium currents and demonstration of a tetrodotoxinresistant calcium current in frog motoneurons. J Physiol (Lond) 255: 737–774
Belluzzi O, Sacchi O (1988) The interactions between potassium and sodium currents in generating action potentials in the rat sympathetic neurone. J Physiol (Lond) 397: 127–147
Belluzzi O, Sacchi O, Wanke E (1985) A fast transient outward current in the rat sympathetic neurone studied under voltageclamp conditions. J Physiol (Lond) 358: 91–108
Byrne JH (1980a) Analysis of ionic conductance mechanisms in motor cells mediating inking behavior in Aplysia californica. J Neurophysiol 43: 630–650
Byrne JH (1980b) Quantitative aspects of ionic conductance mechanisms contributing to firing pattern of motor cells mediating inking behavior in Aplysia californica. J Neurophysiol 43: 651–668
Calabresi P, Mercuri N, Stanzione P, Stefani A, Bernardi G (1987a) Intracellular studies on the dopamaine-induced firing inhibition of neostriatal neurons in vitro: evidence for D1 receptor involvement. Neuroscience 20: 757–771
Calabresi P, Misgeld U, Dodt HU (1987b) Intrinsic membrane properties of neostriatal neurons can account for their low level of spontaneous activity. Neuroscience 20: 293–303
Cherubini E, Lanfumey L (1987) An inward calcium current underlying regenerative calcium spikes in rat striatal neurons in vitro enhanced by BAY K 8644. Neuroscience 24: 997–1005
Connor JA (1975) Neural repetitive firing: a comparative study of membrane properties of crustacean walking leg axons. J Neurophysiol 38: 922–932
Connor JA (1982) Mechanisms of pacemaker discharge in invertebrate neurons. In: Carpenter DO (ed) Cellular pacemakers. J Wiley and Sons, New York
Connor JA (1985) Neural pacemakers and rhythmicity. Ann Rev Physiol 47: 17–28
Connor JA, Stevens CF (1971) Prediction of repetitive firing behaviour from voltage clamp data on an isolated neurone soma. J Physiol (Lond) 213: 31–53
Dekin MS, Getting PA (1984) Firing pattern of neurons in the nucleus tractus solitarius: modulation by membrane hyperpolarization. Brain Res 324: 180–184
Dolly JO (1988) Potassium channels — what can the protein chemistry contribute? TINS 11: 186–188
Frankenhaeuser B, Vallbo AB (1965) Accomodation in myelinated nerve fibers of Xenopus laevis as computed on the basis of voltage clamp data. Acta Physiol Scand 63: 1–20
Galarraga E, Bargas J, Aceves J (1985) Slow sodium and IA currents in neostriatal neurons. Soc Neurosci Abstr 11: 202
Galarraga E, Bargas J, Sierra A, Aceves J (1989) The role of calcium in the repetitive firing of neostriatal neurons. Exp Brain Res 75: 157–168
Galvan M (1982) A transient outward current in rat sympathetic neurones. Neurosci Lett 31: 295–300
Galvan M, Sedlmeir C (1984) Outward currents in voltageclamped rat sympathetic neurones. J Physiol (Lond) 356: 115–133
Gustafsson B, Galvan M, Grafe P, Wigström H (1982) A transient outward current in a mammalian central neuron blocked by 4-aminopyridine. Nature (Lond) 299: 252–254
Jahnsen H, Llinás R (1984) Ionic basis for the electroresponsiveness and oscillatory properties of guinea-pig thalamic neurons in vitro. J Physiol (Lond) 349: 227–247
Josephson IR, Sanchez-Chapula J, Brown AM (1984) Early outward current in rat single ventricular cells. Circ Res 54: 157–162
Kenyon JL, Gibbons WR (1979) 4-Aminopyridine and the early outward current of sheep cardiac purkinje fibers. J Gen Physiol 73: 139–157
Kita H, Kita T, Kitai ST (1985a) Active membrane properties of rat neostriatal neurons in an in vitro slice preparation. Exp Brain Res 60: 54–62
Kita H, Kita T, Kitai ST (1985b) Regenerative potentials in rat neostriatal neurons in an in vitro slice preparation. Exp Brain Res 60: 63–70
Kita T, Kita H, Kitai ST (1985c) Effects of 4-Aminopyridine (4-AP) on rat neostriatal neurons in an in vitro slice preparations. Brain Res 361: 10–18
Kitai ST, Kita H (1984) Electrophysiological study of the neostriatum in brain slice preparation. In: Dingledine R (ed) Brain slices, Plenum Press, New York, pp 285–296
Misgeld U, Okada Y, Hassler R (1979) Locally evoked potentials in slices of rat neostriatum: a tool for the investigation of intrinsic excitatory processes. Exp Brain Res 34: 575–590
Nakajima Y, Nakajima S, Leonard RJ, Yamaguchi K (1986) Acetylcholine raises excitability by inhibiting the fast transient potassium current in cultured hippocampal neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83: 3022–3026
Numann RE, Wadman WJ, Wong RKS (1987) Outward currents of single hippocampal cells obtained from the adult guineapig. J Physiol (Lond) 393: 331–353
Rogawski MA (1985) The A-current: how ubiquitous a feature os excitable cells is it? TINS 8: 214–219
Rudy B (1988) Diversity and ubiquity of K channels. Neuroscience 25: 729–749
Salkoff L (1985) Development of ion channels in the flight muscles of Drosophila. J Physiol (Paris) 80: 275–282
Segal M, Barker JL (1984) Rat hippocampal neurons in culture: potassium conductances. J Neurophysiol 51: 1409–1433
Segal M, Rogawski MA, Barker JL (1984) A transient potassium conductance regulates the excitability of cultured hippocampal and spinal neurons. J Neurosci 4: 604–609
Storm JF (1987) Action potential repolarization and a fast afterhyperpolarization in rat hippocampal pyramidal cells. J Physiol (Lond) 385: 733–759
Strong JA (1984) Modulation of potassium current kinetics in bag cell neurons of Aplysia by an activator of adenylate cyclase. J Neurosci 4: 2772–2783
Strong JA, Kaczmareck LK (1987) Potassium currents that regulate action potentials and repetitive firing. In: Kaczmarek LK, Levitan IB (eds) Neuromodulation. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 119–137
Sugimori M, Preston RJ, Kitai ST (1978) Response properties and electrical constants of caudate nucleus neurons in the cat. J Neurophysiol 41: 1662–1675
Surmeier DJ, Bargas J, Kitai ST (1988) Voltage-clamp analysis of a transient potassium current in rat neostriatal neurons. Brain Res 473: 187–192
Thompson S (1982) Aminopyridine block of transient potassium current. J Gen Physiol 80: 1–18
Yarom Y, Sugimori M, Llinás R (1985) Ionic currents and firing patterns of mammalian vagal motoneurons in vitro. Neuroscience 16: 719–737
Zbicz KL, Weight FF (1985) Transient voltage and calcium-dependent outward currents in hippocampal CA3 pyramidal neurons. J Neurophysiol 53: 1038–1058
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bargas, J., Galarraga, E. & Aceves, J. An early outward conductance modulates the firing latency and frequency of neostriatal neurons of the rat brain. Exp Brain Res 75, 146–156 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00248538
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00248538