Summary
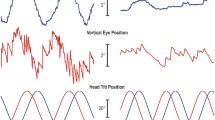
The horizontal vestibulo-ocular reflex was measured electrooculographically in four cats during sinusoidal rotations in the dark at frequencies from 0.01 Hz to 1.0 Hz in five body orientations. Vertical axis rotations in the prone and supine positions were used to stimulate horizontal canals only. Horizontal axis rotations, with the cat on the left or right side or nose down (pitched 90° from prone) were used to stimulate horizontal canal plus otolith organs. At frequencies below 0.05 Hz the horizontal vestibulo-ocular reflex produced by horizontal canal plus otolith stimulation showed a more accurately compensatory response than the horizontal vestibuloocular reflex produced by horizontal canal stimulation alone. Canal plus otolith horizontal vestibulo-ocular reflex gain and phase remained relatively constant across all frequencies, while the horizontal vestibulo-ocular reflex gain and phase from orientations involving canal stimulation alone changed dramatically as rotation frequency decreased. In addition, the reflex in the supine position showed gain decreases and phase advances at higher frequencies than in the prone position.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker J, Goldberg J, Peterson B, Schor R (1982) Oculomotor reflexes after semicircular canal plugging in cats. Brain Res 252: 151–155
Baker JF, Perlmutter SI, Peterson BW, Rude SA, Robinson FR (1987a) Simultaneous opposing adaptive changes in cat vestibulo-ocular reflex direction for two body orientations. Exp Brain Res 69: 220–224
Baker J, Wickland C, Goldberg J, Peterson B (1988) Motor output to lateral rectus in cats during the vestibulo-ocular reflex in three dimensional space. Neuroscience 25: 1–12
Baker J, Wickland C, Peterson B (1987b) Dependence of cat vestibulo-ocular reflex direction adaptation on animal orientation during adaptation and rotation in darkness. Brain Res 408: 339–343
Barmack NH (1981) A comparison of the horizontal and vertical vestibulo-ocular reflexes of the rabbit. J Physiol 314: 547–564
Benson AJ, Bodin MA (1966) Interaction of linear and angular accelerations on vestibular receptors in man. Aerospace Med 37: 144–154
Böhmer A, Henn V (1983) Horizontal and vertical vestibulo-ocular and cervico-ocular reflexes in the monkey during high frequency rotation. Brain Res 277: 241–248
Bond H, Ho P (1970) Solid miniature silver-silver chloride electrodes for chronic implantation. Electroenceph Clin Neurophysiol 28: 206–208
Cohen B, Suzuki JI, Raphan T (1983) Role of the otolith organs in generation of horizontal nystagmus: effects of selective labyrinthine lesions. Brain Res 276: 159–164
Correia MJ, Money KE (1970) The effect of all six semicircular canal ducts on nystagmus produced by linear acceleration in the cat. Acta Oto-laryng 69: 7–16
Correia MJ, Guedry FE (1966) Modification of vestibular responses as a function of rate of rotation about an earth-horizontal axis. Acta Oto-laryng 62: 297–308
Donaghy M (1980) The cat's vestibulo-ocular reflex. J Physiol 300: 337–351
Fluur E, Mellström A (1970) Utricular stimulation and oculomotor reactions. Laryngoscope 80: 1701–1712
Fluur E, Mellström A (1971) The otolith organs and their influence on oculomotor movements. Exp Neurol 30: 139–147
Goldberg J, Fernandez C (1975) Responses of peripheral vestibular neurons to angular and linear accelerations in the squirrel monkey. Acta Oto-laryng 80: 101–110
Guedry FE (1965) Orientation of the rotation-axis relative to gravity: its influence on nystagmus and the sensation of rotation. Acta Oto-laryng 60: 30–48
Henn V, Cohen B, Young L (1980) Visual — vestibular interaction in motion perception and the generation of nystagmus. Neurosci Res Prog Bull 18: 458–651
Keller EL (1978) Gain of the vestibulo-ocular reflex in monkey at high rotational frequencies. Vision Res 18: 311–315
Matsuo V, Cohen B (1984) Vertical optokinetic nystagmus and vestibular nystagmus in the monkey: up-down asymmetry and effects of gravity. Exp Brain Res 53: 197–216
Owada K, Shiizu S, Kimura K (1961) The influence of the utricle on nystagmus: Acta Oto-laryng 52: 216–220
Raphan T, Cohen B, Henn V (1981) Effects of gravity on rotatory nystagmus in monkeys. Ann NY Acad Sci 374: 44–55
Schwindt P, Richter A, Precht W (1973) Short latency utricular and canal input to ipsilateral abducens motoneurons. Brain Res 60: 259–262
Suzuki JI, Tokumasu K, Goto K (1969) Eye movements from single utricular nerve stimulation. Acta Oto-laryng 68: 350–362
Tomko DL, Wall C, Robinson FR, Staab JP (1988) Influence of gravity on cat vertical vestibulo-ocular reflex. Exp Brain Res 69: 307–314
Young L, Henn V (1975) Nystagmus produced by pitch and yaw rotation of monkeys. Fortschr Zool 23: 235–246
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rude, S.A., Baker, J.F. Dynamic otolith stimulation improves the low frequency horizontal vestibulo-ocular reflex. Exp Brain Res 73, 357–363 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00248228
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00248228