Summary
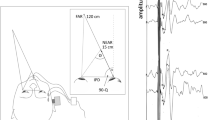
The vertical vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR) was recorded in cats using electro-oculography during sinusoidal angular pitch. Peak stimulus velocity was 50°/s over a frequency range from 0.01 to 4.0 Hz. To test the effect of gravity on the vertical VOR, the animal was pitched while sitting upright or lying on its side. Upright pitch changed the cat's orientation relative to gravity, while on-side pitch did not. The cumulative slow component position of the eye during on-side pitch was less symmetric than during upright pitch. Over the mid-frequency range (0.1 to 1.0 Hz), the average gain of the vertical VOR was 14.5% higher during upright pitch than during on-side pitch. At low frequencies (<0.05 Hz) changing head position relative to gravity raised the vertical VOR gain and kept the reflex in phase with stimulus velocity. These results indicate that gravity-sensitive mechanisms make the vertical VOR more compensatory.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson JH (1981) Behavior of the vertical canal VOR in normal and INC-lesioned cats. In: Fuchs AF, Becker W (eds) Progress in oculomotor research. Elsevier/North Holland, New York, pp 395–401
Anderson JH, Liston SL (1983) Asymmetry in the human vertical vestibuloocular reflex. Abstr Assn Res Otolaryngol 6: 82
Baloh RW, Richman L, Yee RD, Honrubia V (1983) The dynamics of vertical eye movements in normal human subjects. Aviat Space Environm Med 54: 32–38
Barmack NH (1981) A comparison of the horizontal and vertical vestibulo-ocular reflexes of the rabbit. J Physiol (Lond) 314: 547–564
Benson AJ, Guedry FE (1971) Comparison of tracking-task performance and nystagmus during sinusoidal oscillation in yaw and pitch. Aerospace Med 42: 593–601
Blakemore C, Donaghy M (1980) Co-ordination of head and eyes in the gaze changing behavior of cats. J Physiol (Lond) 300: 317–335
Boehmer A, Henn V (1983) Horizontal and vertical vestibuloocular and cervico-ocular reflexes in the monkey during high frequency rotation. Brain Res 277: 241–248
Cohen B, Matsuo V, Raphan Th (1977) Quantitative analysis of the velocity characteristics of optokinetic nystagmus and optokinetic after-nystagmus. J Physiol (Lond) 270: 321–344
Collewijn H, Van der Steen J, Ferman L, Jansen TC (1985) Human ocular counterroll: assessment of static and dynamic properties from electromagnetic scleral coil recordings. Exp Brain Res 59: 185–196
Correia MJ, Perachio AA, Eden AR (1985) The monkey vertical vestibulo-ocular response (VVOR): a frequency domain study. J Neurophysiol 54: 532–548
Darlot C, Lopez-Barneo J, Tracey D (1981) Asymmetries of vertical vestibular nystagmus in the cat. Exp Brain Res 41: 420–426
Fernandez C, Goldberg JM (1976) Physiology of peripheral neurons innervating otolith organs of the squirrel monkey. III. Response dynamics. J Neurophysiol 39: 996–1008
Gauthier GM, Martin BJ, Stark LW (1986) Adapted head- and eye-movement responses to added-head inertia. Aviat Space Environm Med 57: 336–42
Goldberg JM, Fernandez C (1971) Physiology of peripheral neurons innervating semicircular canals of the squirrel monkey. I. Resting discharge and response to constant angular accelerations. J Neurophysiol 34: 635–660
Goldberg JM, Fernandez C (1982) Eye movements and vestibular-nerve responses produced in the squirrel monkey by rotations around an earth-horizontal axis. Exp Brain Res 46: 393–402
Honrubia V, Scott BJ, Ward PH (1967) Experimental studies on optokinetic nystagmus. I. Normal cats. Acta Otolaryngol 64: 388–402
Igarashi M, Takahashi M, Kubo T, Levy JK, Homick JL (1978) Effect of macular ablation on vertical optokinetic nystagmus in the squirrel monkey. ORL 40: 312–318
Lackner JR, Graybiel A (1984) Elicitation of motion sickness by head movements in the microgravity phase of parabolic flight maneuvers. Aviat Space Environm Med 55: 513–520
Matsuo V, Cohen B (1984) Vertical optokinetic nystagmus and vestibular nystagmus in the monkey: up-down asymmetry and effects of gravity. Exp Brain Res 53: 197–216
Matsuo V, Cohen B, Raphan T, De Jong V, Henn V (1979) Asymmetric velocity storage for upward and downward nystagmus. Brain Res 176: 159–164
Schor RH, Miller AD, Tomko DL (1984) Responses to head tilt in cat central vestibular neurons. I. Direction of maximum sensitivity. J Neurophysiol 53: 1444–1452
Suzuki J-I, Tokumasu K, Goto K (1969) Eye movements from single utricular nerve stimulation in the cat. Acta Otolaryngol 68: 350–362
Tomko DL, Wall C III, Robinson FR (1984) Vertical eye movement and vertical semicircular canal responses in cat during normal pitch and during pitch with the animal positioned on its side. Neurosci Abstr 10(2): 539
Wall C III, Black FO (1981) An algorithm for the clinical analysis of nystagmus eye movements. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 28: 638–646
Wall C III, Black FO (1984) The modulation component of nystagmus during earth-horizontal rotation: relationship with gaze angle. Acta Otolaryngol (Stockh) 97: 193–201
Wilson VJ, Melvill Jones G (1979) Mammalian vestibular physiology. Plenum Press, New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tomko, D.L., Wall, C., Robinson, F.R. et al. Influence of gravity on cat vertical vestibulo-ocular reflex. Exp Brain Res 69, 307–314 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00247576
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00247576