Summary
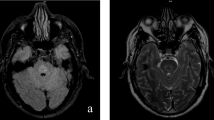
A 37-year-old chronic alcoholic suffered a brain contusion without skull fracture while involved in a traffic accident. Following gradual improvement of this condition for 15 days coma recurred and the patient died on the 18th day after the accident. On brain autopsy findings were: Cortico-subcortical contusions of the left fronto-polar area with extensive damage involving the lower right parietal and occipital lobe; hemorrhagic necrosis of the left thalamus; marked increase in brain volume due to edema with basal signs of increased intracranial pressure.
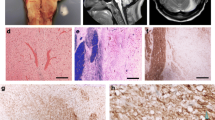
On histology a large fresh central pontine myelinolysis (cpml) was found typical in localization and shape, associated with an intensive plasma cell infiltration regional to the (marginal) area most recently affected by the lesion, a finding that was not known heretofore. The entire brain stem with particular preference of the pons displayed diffuse glial proliferation (difjuse pontine dystrophy), and all the other signs of hepatogenous encephalopathy could be demonstrated. In discussing the findings it is pointed out that the focal lesion in cpml is due to the alcoholism rather than to the trauma, the lesion not becoming manifest, however, until the posttraumatic period. In view of the present observations a new hypothesis on the pathogenesis of cpml is proposed invoking a bimodal toxic-autoimmunopathological process.
Zusammenfassung
Ein 37jähriger chronischer Alkoholiker erlitt bei einem Verkehrsunfall eine Gehirnkontusion ohne Schädelfraktur. Nach allmählicher Besserung des Zustandes fiel der Patient am 15. Tag wieder ins Koma und starb am 18. Tag nach dem Unfall. Die Gehirnsektion ergab cortico-subcorticale Kontusionen links fronto-polar sowie rechts ausgedehnt im unteren Parietal- und Occipitallappen, eine hämorrhagische Nekrose im linken Thalamus und starke ödematöse Volumenvermehrung mit basalen Druckzeichen.
Histologisch fand sich eine große, frische zentrale pontine Myelinolyse (zpMl) in typischer Lage und Form mit dem bisher unbekannten Befund einer intensiven Plasmazellinfiltration im Bereich der frischesten (Rand-) Bereiche der Läsion. Im gesamten Hirnstamm waren eine diffuse astrogliale Proliferation mit Betonung in der Brücke (difjuse pontine Dystrophie) und die übrigen Zeichen einer hepatogenen Encephalopathie nachweisbar. In der Diskussion wird ausgeführt, daß die zpMl-Herdläsion keine traumatisch bedingte Läsion, sondern alkoholbedingter Natur ist, jedoch erst während des posttraumatischen Verlaufs aufgetreten ist. Hinsichtlich der Pathogenese der zpMl wird auf Grund der mitgeteilten Befunde die neue Hypothese eines zweistufigen toxisch-autoimmunopathologischen Geschehens vorgebracht.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Adams, R. D., Victor, M., Mancall, E. L.: Central pontine myelinolysis. Arch. Neurol. Psychiat. (Chic.) 81, 154–172 (1959).
Jellinger, K.: Protrahierte Formen der posttraumatischen Encephalopathie. Beitr. gerichtl. Med. 23, 65–118 (1965).
Mifka, P.: Die Augensymptomatik bei der frischen Schädelhirnverletzung. Berlin: de Gruyter 1968.
Seitelberger, F., Gross, H.: Zur Neuropathologie des Alkoholismus. In: Arbeitstagung über Alkoholismus, Wien 1962, S. 12–30.
— Zur organischen Hirnschädigung des Alkoholkranken. Die Läsion der Brücke bei alkoholbedingten Encephalopathien (zentrale pontine Myelinolyse; diffuse pontine Dystrophie). In: Klinik und Therapie des Alkoholismus, Symposium über den Alkoholismus, S. 109–138. Wien: Verlag der Wiener Medizinischen Akademie 1968.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seitelberger, F., Jonasch, G. Zentrale pontine Myelinolyse nach Schädeltrauma. Deutsche Zeitschrift f. Nervenheilkunde 197, 28–41 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00242248
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00242248