Abstract
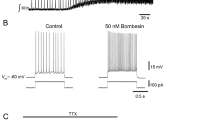
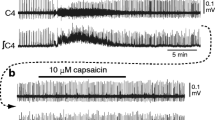
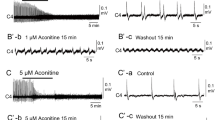
In brainstem-spinal cord preparations isolated from newborn rats, intrinsic burst-generating properties of preinspiratory (Pre-I) neurons in the rostral ventrolateral medulla, which have been suggested to be primary respiratory rhythm-generating neurons, were studied by “perforated” whole-cell recordings using the antibiotic nystatin. Nystatin causes small pores to be formed in the cells, through which pass small monovalent ions. For blockade of chemical synaptic transmission, perfusate Ca2+ concentration was lowered to 0.2 mM and the Mg2+ concentration was increased to 5 mM. In Iow-Ca2+, high-Mg2+ solution (referred to here as “low Ca”), 10 of 55 Pre-I neurons generated rhythmic bursts (burst type), 14 fired tonically (tonic type), and 31 were silent (silent type). Burst-type neurons showed periodic depolarization of 5–12 mV in low Ca, at a rate of 12±6.5/min. Hyperpolarization of the membrane caused decrease in or disappearance of the periodic depolarization and prolongation of the cycle period. Thus, the burst generations were voltage dependent. The firing frequency of tonictype neurons was 2.3±1.6 Hz and was decreased by hyperpolarization. In 6 of these neurons, the firing patterns changed to burst patterns during continuous hyperpolarization. Membrane depolarization by continuous outward current injection into some silent-type neurons (3 of 11 tested) induced bursting activity. Activity of C4 and Pre-I neurons was completely silent with 0.1–1 μM tetrodotoxin (TTX) added to the standard perfusate. In low Ca, burst-type neurons (n=3) were also silent with 1 μM TTX perfusion. Inspiratory neurons either became silent (n=4) or fired tonically (n=1) in low Ca. The present study by “perforated” whole-cell recordings confirmed that some Pre-I neurons possess intrinsic burst-generating properties, which were not attributable to phasic synaptic inputs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akaike N, Harata N (1994) Nystatin perforated patch recording and its applications to analyses of intracellular mechanisms. Jpn J Physiol 44:433–473
Alonso A, Llinas RR (1992) Electrophysiology of the mammillary complex in vitro. II. Medial mammillary neurons. J Neurophysiol 68:1321–1331
Arata A, Onimaru H, Homma I (1990) Respiration-related neurons in the ventral medulla of newborn rats in vitro. Brain Res Bull 24:599–604
Arata A, Onimaru H, Homma I (1992) Electrophysiology and morphology of respiratory neurons in brainstem-spinal cord preparations from newborn rats (abstract). Neurosci Res 17:S221
Augustine GJ, Charlton MP (1986) Calcium dependence of presynaptic calcium current and post-synaptic response at the squid giant synapse. J Physiol (Lond) 381:619–640
Bennett MVL, Spira ME, Spray DC (1978) Permeability of gap junctions between embryonic cells of Fundulus: a reevaluation. Dev Biol 65:114–125
Blanton MG, Lo Turco JJ, Kriegstein AR (1989) Whole cell recording from neurons in slices of reptilian and mammalian cerebral cortex. J Neurosci Methods 30:203–210
Feldman JL, Smith JC (1989) Cellular mechanisms underlying modulation of breathing pattern in mammals. Ann NY Acad Sci 563:114–130
Fitzgerald M (1985) The post-natal development of cutaneous afferent fibre input and receptive field organization in the rat dorsal horn. J Physiol (Lond) 364:1–18
French CR, Sah P, Buckett KJ, Gage PW (1990) A voltage-dependent persistent sodium current in mammalian hippocampal neurons. J Gen Physiol 95:1139–1157
Horn R, Marty A (1988) Muscarinic activation of ionic currents measured by a new whole-cell recording method. J Gen Physiol 92:145–159
Hu B, Bourque CW (1992) NMDA receptor-mediated rhythmic bursting activity in rat supraoptic nucleus neurones in vitro. J Physiol (Lond) 458:667–687
Inenaga K, Akamatsu N, Nagatomo T, Ueta Y, Yamashita H (1992) Intracellular EGTA alters phasic firing of neurons in the rat supraoptic nucleus in vitro. Neurosci Lett 147:189–192
Johnson SM, Smith JC, Funk GD, Feldman JL (1994) Pacemaker behavior of respiratory neurons in medullary slices from neo natal rat. J Neurophysiol 72:2598–2608
Kashiwagi M, Onimaru H, Homma I (1993a) Correlation analysis of respiratory neuron activity in ventrolateral medulla of brainstem-spinal cord preparation isolated from newborn rat. Exp Brain Res 95:277–290
Kashiwagi M, Onimaru H, Homma I (1993b) Effects of NMDA on respiratory neurons in newborn rat medulla in vitro. Brain Res Bull 32:65–69
Korn SJ, Horn R (1989) Influence of sodium-calcium exchange on calcium current rundown and the duration of calcium-dependent chloride currents in pituitary cells, studied with whole cell and perforated patch recording. J Gen Physiol 94:789–812
Llinas RR (1988) The intrinsic electrophysiological properties of mammalian neurons: insights into central nervous system function. Science 242:1654–1664
Llinas RR, Alonso A (1992) Electrophysiology of the mammillary complex in vitro. I. Tuberomammillary and lateral mammillary neurons. J Neurophysiol 68:1307–1320
Llinas R, Sugimori M (1980a) Electrophysiological properties of in vitro Purkinje cell somata in mammalian cerebellar slices. J Physiol (Lond) 305:171–195
Llinas R, Sugimori M (1980b) Electrophysiological properties of in vitro Purkinje cell dendrites in mammalian cerebellar slices. J Physiol (Lond) 305:197–213
Murakoshi T, Suzue T, Tamai S (1985) A pharmacological study on respiratory rhythm in the isolated brainstem-spinal cord preparation of the newborn rat. Br J Pharmacol 86:95–104
Onimaru H, Homma I (1987) Respiratory rhythm generator neurons in medulla of brainstem-spinal cord preparation from newborn rat. Brain Res 403:380–384
Onimaru H, Homma I (1992) Whole cell recordings from respiratory neurons in the medulla of brainstem-spinal cord preparations isolated from newborn rats. Pflugers Arch 420:399–406
Onimaru H, Arata A, Homma I (1988) Primary respiratory rhythm generator in the medulla of brainstem-spinal cord preparation from newborn rat. Brain Res 445:314–324
Onimaru H, Arata A, Homma I (1989) Firing properties of respiratory rhythm generating neurons in the absence of synaptic transmission in rat medulla in vitro. Exp Brain Res 76:530–536
Onimaru H, Arata A, Homma I (1990) Inhibitory synaptic inputs to the respiratory rhythm generator in the medulla isolated from newborn rats. Pflugers Arch 417:425–432
Onimaru H, Arata A, Homma I (1992a) Analysis of pacemaker properties of respiratory neurons using “perforated” whole cell recordings (abstract). Neurosci Res 17:S212
Onimaru H, Homma I, Iwatsuki K (1992b) Excitation of inspiratory neurons by preinspiratory neurons in rat medulla in vitro. Brain Res Bull 29:879–882
Onimaru H, Kashiwagi M, Arata A, Homma I (1993) Possible mutual excitatory couplings between inspiratory neurons in caudal ventrolateral medulla of brainstem-spinal cord preparation isolated from newborn rat. Neurosci Lett 150:203–206
Richter DW, Ballanyi K, Schwarzacher S (1992) Mechanisms of respiratory rhythm generation. Curr Opin Neurobiol 2:788–793
Smith JC, Feldman JL (1987a) In vitro brainstem-spinal cord preparations for study of motor systems for mammalian respiration and locomotion. J Neurosci Methods 21:321–333
Smith JC, Feldman JL (1987b) Central respiratory pattern generation studied in an in vitro mammalian brain stem-spinal cord preparation. In: Sieck GC, Gandevia SG, Cameron WE (eds) Respiratory muscles and their neuromotor control. Liss, NewYork, pp 27–36
Smith JC, Greer JJ, Liu G, Feldman JL (1990) Neural mechanisms generating respiratory pattern in mammalian brain stem-spinal cord in vitro. I. Spatiotemporal patterns of motor and medullary neuron activity. J Neurophysiol 64:1149–1169
Smith JC, Ellenberger HH, Ballanyi K, Richter DW, Feldman JL (1991) Pre-Bötzinger complex: a brainstem region that may generate respiratory rhythm in mammals. Science 254:726–729
Smith JC, Ballanyi K, Richter DW (1992) Whole-cell patch-clamp recordings from respiratory neurons in neonatal rat brainstem in vitro. Neurosci Lett 314:153–156
Stewart WW (1978) Functional connections between cells as revealed by dye-coupling with a highly fluorescent naphthalimide tracer. Cell 14:741–759
Suzue T (1984) Respiratory rhythm generation in the in vitro brain stem-spinal cord preparation of the neonatal rat. J Physiol (Lond) 354:173–183
Takahashi T (1992) The minimal inhibitory synaptic currents evoked in neonatal rat motoneurones. J Physiol (Lond) 450:593–611
Zheng Y, Barillot JC, Bianchi AL (1992) Intracellular electrophysiological and morphological study of the medullary inspiratory neurons of the decerebrate rat. Brain Res 576:235–244
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Onimaru, H., Arata, A. & Homma, I. Intrinsic burst generation of preinspiratory neurons in the medulla of brainstem-spinal cord preparations isolated from newborn rats. Exp Brain Res 106, 57–68 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00241356
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00241356