Abstract
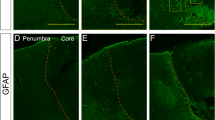
This study investigated astroglial responses after focal cerebral ischemia in the rat cortex induced by photothrombosis. Astrocyte activation was studied at various time points by immunocytochemistry for glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) and vimentin (VIM). We found a dual astrocytic response to focal ischemia: In the border zone of the infarct, GFAP-positive astrocytes were present within 2 days and persisted for 10 weeks. These astrocytes additionally expressed VIM. Remote from the ischemic lesion, cortical astrocytes of the entire ipsilateral hemisphere transiently expressed GFAP, but not VIM, beginning on day 3 after photothrombosis. This response had disappeared on day 14. By recording DC potentials, five to seven spreading depressions (SD) could be detected on the cortical surface during the first 2 h after photothrombosis. Treatment with MK801, a non-competitive NMDA-receptor antagonist, completely abolished SD and remote ipsilateral astrocytic activation, while the reaction in the border zone of the infarct remained unchanged. Functionally, persistent astrocytosis around the infarct might be induced by leukocyte-derived cytokines, while NMDA-receptor-mediated SD might cause remote responses.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bignami A, Dahl D (1976) Astroglial response to stabbing. Immunofluorescence studies with antibodies to astrocyte-specific protein (GFA) in mammalian and submammalian vertebrates. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 2:99–110
Dietrich WD, Feng ZC, Leistra H, Watson BD, Rosenthal M (1994) Photothrombotic infarction triggers multiple episodes of cortical spreading depression in distant brain regions. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 14:20–28
Domann R, Hagemann G, Kraemer M, Freund HJ, Witte OW (1993) Electrophysiological changes in the surrounding brain tissue of photochemically induced cortical infarcts in the rat. Neurosci Lett 155:69–72
Eng LF (1985) Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP): the major protein of glial intermediate filaments in differentiated astrocytes. J Neuroimmunol 8:203–214
Gass P, Spranger M, Herdegen T, Bravo R, Köck P, Hacke W, Kiessling M (1992) Induction of FOS and JUN proteins after focal ischemia in the rat: differential effect of the N-methyl-d-aspartate antagonist MK801. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 84:545–553
Gill R, Andine P, Hillered L, Persson L, Hagberg H (1992) The effect of MK801 on cortical spreading depression in the penumbral zone following ischemia in the rat. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 12:371–379
Guilian D, Woodward J, Young DG, Krebs JF, Lachman LB (1988) Interleukin-1 injected into mammalian brain stimulates astrogliosis and neovascularization. J Neurosci 8:2485–2490
Hansen AJ, Zeuthen T (1981) Extracellular ion concentrations during spreading depression and ischemia in the rat brain. Acta Physiol Scand 113:437–145
Herrera DG, Cuello AC (1992) MK801 affects the potassium-induced increase of glial fibrillary acidic protein immunoreactivity in rat brain. Brain Res 598:286–293
Hertz L (1979) Functional interactions between neurons and astrocytes. Prog Neurobiol 13:272–323
Jander S, Kraemer M, Schroeter M, Witte OW, Stoll G (1995) Lymphocytic infiltration and expression of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 in photochemically induced ischemia of the rat cortex. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 15:42–51
Kettenmann H, Schachner M (1985) Pharmacological properties of γ-aminobutyric acid, glutamate, aspartate induced depolarizations in cultured astrocytes. J. Neurosci 5:3295–3301
Kraig RP, Dong L, Thisted R, Jaeger CB (1991) Spreading depression increases immunohistochemical staining of glial fibrillary acidic protein. J Neurosci 11:2187–2198
Latov N, Nilaver G, Zimmerman EA, Johnson WG, Silverman AJ, Defendini R, Cote L (1979) Fibrillary astrocytes proliferate in response to injury. Dev Biol 72:381–384
Leao AAP (1944) Spreading depression of activity in the cerebral cortex. J Neurophysiol 7:359–390
Marrannes R, Willems R, De Prins E, Wauquier A (1988) Evidence for a role of the N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptor in cortical spreading depression in the rat. Brain Res 457:226–240
Miller RH, Raff MC (1984) Fibrous and protoplasmic astrocytes are biochemically and developmentally distinct. J Neurosci 4:585–592
Nathan CF (1987) Secretory products of macrophages. J Clin Invest 79:319–326
Petito CK, Morgello S, Felix JC, Lesser ML (1990) The two patterns of reactive astrocytosis in postischemic rat brain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metabol 10:850–859
Risau W, Wolburg H (1990) Development of the blood-brain barrier. Trends Neurosci 13:174–178
Schiffer D, Giordana MT, Migheli A, Giaccone G, Pezzotta S, Mauro A (1986) Glial fibrillary acidic protein and vimentin in experimental glial reaction of the rat brain. Brain Res 374:110–118
Schmidt-Kastner R, Wietesch K, Weigel H, Eysel UT (1993) Immunocytochemical staining for glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) after deafferentation in an ischemic infarction in the rat visual system: features of reactive and damaged astrocytes. Int J Dev Neurosci 11:157–174
Takamiya Y, Kohsaka S, Toya S, Otani M, Tsukada Y (1988) Immunocytochemical studies on the proliferation of reactive astrocytes and the expression of cytoskeletal proteins following brain injury in rats. Dev Brain Res 38:201–210
Walz W (1989) Role of glial cells in the regulation of the brain ion microenvironment. Prog Neurobiol 33:309–333
Watson BD, Dietrich WD, Busto P, Wachtel MS, Ginsberg MD (1985) Induction of reproducible brain infarction by photochemically initiated thrombosis. Ann Neurol 17:497–504
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schroeter, M., Schiene, K., Kraemer, M. et al. Astroglial responses in photochemically induced focal ischemia of the rat cortex. Exp Brain Res 106, 1–6 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00241351
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00241351