Summary
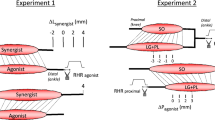
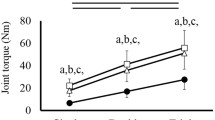
The static force sensitivity of soleus tendon organ (Ib) afferents has been studied by noting their responses to graded force development produced by isometric contractions of either the whole muscle or single motor units. Data included responses of 23 Ib afferents to contraction of 8 whole muscles (8 experiments) and 16 Ib afferents to contraction of 30 motor units (5 experiments). Tendon organ responses of varying magnitude to contraction of the whole muscle or several of its individual motor units could be explained by differences in the number of muscle fibers that insert into each receptor's capsule and by differences in the contraction strength of these fibers. This finding suggests that soleus tendon organs have similar absolute sensitivities to static force development. An estimate was made of this absolute sensitivity and the value obtained (314 pps/g of force actually coupled to the receptor) is 2 orders of magnitude greater than those previously reported indices that simply relate Ib firing rate to force as measured at the tendon. The relationship between force exerted on a tendon organ's capsule and Ib firing rate is shown to be curvilinear and in keeping with a possible saturation effect that reduces the receptor's responsiveness to active contractions at relatively long muscle lengths.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barker, D.: Morphology of muscle receptors. In: Handbook of Sensory Physiology, (Ed. C.C. Hunt), Vol. III/2. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1974
Burke, R.E., Tsairis, P.: Anatomy and innervation ratios in motor units of cat gastrocnemius. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 234, 749–765 (1973)
Burke, R.E., Levine, D.N., Salcman, M., Tsairis, P.: Motor units in cat soleus muscle: Physio logical, histochemical and morphological characteristics. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 238, 503–514 (1974)
Gans, C., Bock, W.J.: The functional significance of muscle architecture — a theoretical analysis. Ergebn. Anat. Entwickl.-Gesch. 38, 115–142 (1965)
Henneman, E., Olson, C.B.: Relations between structure and function in the design of skeletal muscles. J. Neurophysiol. 28, 581–598 (1965)
Houk, J.C., Henneman, E.: Responses of Golgi tendon organs to active contractions of the soleus muscle of the cat. J. Neurophysiol. 30, 466–481 (1967)
Houk, J.C., Simon, W.: Responses of Golgi tendon organs to forces applied to muscle tendon. J. Neurophysiol. 30, 1466–1481 (1967)
Houk, J.C., Singer, J.J., Henneman, E.: The adequate stimulus for Golgi tendon organs with observations on the mechanics of the ankle joint. J. Neurophysiol. 34, 1051–1065 (1971)
Jansen, J.K.S., Rudjord, T.: On the silent period and Golgi tendon organs of the soleus muscle of the cat. Acta physiol. scand. 62, 364–379 (1964)
Rack, P.M., Westbury, D.R.: The effects of length and stimulus rate on tension in the iso metric cat soleus muscle. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 204, 443–460 (1969)
Reinking, R.M., Stephens, J.A., Stuart, D.G.: The tendon organs of cat medial gastro cnemius: Significance of motor unit type and size for the activation of Ib afferents. J. Physiol. (Lond.) (In press, 1975)
Stauffer, E.K.: Physiological analysis of motor unit-tendon organ anatomy. Anat. Rec. 181, 486 (1975)
Stauffer, E.K.: The tendon organs of cat soleus: Static and dynamic responsiveness during isometric and anisometric contractions. Ph.D. dissertation. Tucson, Arizona: University of Arizona 1974
Stauffer, E.K., Stephens, J.A.: Responses of tendon organs to ramp changes of active in-series motor unit force. Proc. 4th Meet. Soc. for Neuroscri., p. 435, St. Louis 1974
Stephens, J.A., Reinking, R.M., Stuart, D.G.: The tendon organs of cat medial gastrocnemius: Responses to active and passive forces as a function of muscle length. J. Neurophysiol. (In press, 1975)
Stuart, D., Goslow, G.E., Mosher, C.G., Reinking, R.M.: Stretch responsiveness of Golgi tendon organs. Exp. Brain Res. 10, 463–476 (1970)
Stuart, D., Mosher, C.G., Gerlach, R.L., Reinking, R.M.: Mechanical arrangement and trans ducing properties of Golgi tendon organs. Exp. Brain Res. 14, 274–292 (1972)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stauffer, E.K., Stephens, J.A. The tendon organs of cat soleus: Static sensitivity to active force. Exp Brain Res 23, 279–291 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00239740
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00239740