Summary
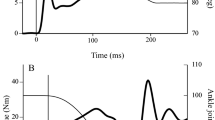
The resistance to stretch provided by short latency (SL) reflexes in human triceps surae muscles was investigated under three experimental conditions: control, ischaemia, and with 100 Hz vibration applied to the Achilles tendon. Incremental changes in plantar flexion force always showed a strong initial resistance followed by yielding in response to rapid dorsiflexion of the foot about the ankle joint. These changes were attributed to inherent stiffness of the triceps surae muscles. The force curves for each experimental condition diverged during the yield phase some 20 ms after the onset of SL EMG reflexes. During ischaemia, SL EMG reflexes were reduced to 8% of control values and yielding continued until the onset of medium latency EMG activity whereas the yielding was interrupted by SL action in the control situation. The difference between the ischaemia and control force curves was attributed to force recruited by SL reflexes under normal stretch conditions. Vibration reduced the SL EMG reflex amplitude to 20% of control values and produced with it a reduced force response.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allum JHJ, Mauritz K-H, Vögele H (1982) Stiffness regulation provided by short-latency reflexes in human triceps surae muscles. Brain Res 234: 159–164
Brown MC, Engberg I, Matthews PBC (1967) The relative sensitivity to vibration of muscle receptors of the cat. J Physiol (Lond) 192: 773–800
Burke D, Hagbarth K-E, Löfstedt L, Wallin BG (1976) The responses of human muscle spindle endings to vibration during isometric contraction. J Physiol (Lond) 261: 695–711
Burke RE, Rudomin P, Zajac FE (1970) Catch property in single mammalian motor units. Science 168: 122–124
Dietz V, Mauritz K-H, Dichgans J (1980) Body oscillations in balancing due to segmental stretch reflex activity. Exp Brain Res 40: 89–95
Goodwin GM, Hoffmann D, Luschei ES (1978) The strength of the reflex response to sinusoidal stretch of monkey jaw closing muscles during voluntary contraction. J Physiol (Lond) 279: 81–111
Hendrie A, Lee RG (1978) Selective effects of vibration on human spinal and long-loop reflexes. Brain Res 157: 369–375
Joyce GC, Rack PMH, Westbury DR (1969) The mechanical properties of cat soleus muscle during controlled lengthening and shortening movements. J Physiol (Lond) 204: 461–474
Magladery JW, McDougal DB, Stoll J (1950) Electrophysiological studies of nerve and reflex activity in normal man. II. The effects of peripheral ischaemia. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp 86: 291–312
Matthews PBC (1959) The dependence of tension upon extension in the stretch reflex of the soleus muscle of the decerebrate cat. J Physiol (Lond) 147: 521–546
Nichols TR, Houk JC (1976) Improvement in linearity and regulation of stiffness that results from actions of the stretch reflex. J Neurophysiol 39: 119–142
Schenck E, Bayer H (1951) Die Wirkung künstlicher Zirkulationsunterbrechung in der Peripherie auf Eigenreflexe beim Menschen. Dtsch Z Nervenheilkd 165: 90–108
Stein RB, Bawa P (1976) Reflex responses of human soleus muscle to small perturbations. J Neurophysiol 39: 1105–1116
Rhymer WZ, Hasan Z (1981) Prolonged time course for vibratory suppression of stretch reflex in the decerebrate cat. Exp Brain Res 44: 101–112
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by the Swiss National Science Foundation grants no. 3.585.79 and 3.505.79, the Dr. Erik Slack-Gyr Foundation, the Sandoz Foundation, and Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft grant SFB 70
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Allum, J.H.J., Mauritz, K.H. & Vögele, H. The mechanical effectiveness of short latency reflexes in human triceps surae muscles revealed by ischaemia and vibration. Exp Brain Res 48, 153–156 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00239584
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00239584