Summary
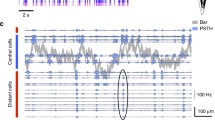
Evidence is presented that simple cells in the cat striate cortex (area 17) fail to respond to two dimensional random patterns but respond vigorously to one dimensional patterns with identical power at the preferred orientation of the cell. Further observations suggest that complex cells inhibit simple cells so as to permit them to respond selectively to one-dimensional stimuli. Implications for the role of this inhibition in visual analysis are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benevento LA, Creutzfeldt OD, Kuhnt U (1972) Significance of intracortical inhibition in the visual cortex. Nature New Biol 238: 124–126
Bishop PO, Coombs JS, Henry GH (1976) Receptive fields of simple cells in the cat striate cortex. J Physiol (Lond) 231: 31–60
Blakemore C, Tobin EA, (1972) Lateral inhibition between orientation detectors in the cat's visual cortex. Exp Brain Res 15: 439–440
Creutzfeldt OD, Kuhnt U, Benevento LA (1974) An intracellular analysis of cortical neurons to moving stimuli. Responses in a cooperative neuronal network. Exp Brain Res 21: 251–274
Creutzfeldt O, Innocenti GM, Brooks D (1975) Neurophysiological experiments on afferent and intrinsic connections in the visual cortex. In: Santini M (ed) Golgi centennial symposium. Perspectives in neurobiology. Raven Press, New York, pp 319–338
De Valois RL, De Valois KK (1980) Spatial vision. Ann Rev Psychol 31: 309–341
Ginsburg A (1977) Ph. D. Thesis, University of Cambridge.
Hammond P, MacKay DM (1975) Differential responses of cat visual cortical cells to textured stimuli. Exp Brain Res 22: 427–430
Hammond P, MacKay DM (1977) Differential responsiveness of simple and complex cells in cat striate cortex of visual texture. Exp Brain Res 306: 275–296
Hammond P, MacKay DM (1978) Modulation of simple cell activity in cat by moving textured backgrounds. J Physiol (Lond) 284: 117P
Henry GH, Bishop PO, Dreher B (1974) Orientation axis and direction as stimulus parameters for striate cortex. Vision Res 14: 767–777
Hoffmann KP, Seelen W von (1978) Analysis of neuronal networks in the visual system of the cat using statistical signal. Simple and complex cells. Biol Cybern 31: 175–185
Hubel DH, Wiesel TN (1962) Receptive fields binocular interaction and functional architecture in the cat's visual cortex. J Physiol (Lond) 160: 106–154
Lennie P (1980) Parallel visual pathways. A review. Vision Res 20: 561–594
Maffei L, Fiorentini A (1973) The visual cortex as a spatial frequency analyser. Vision Res 13: 1255–1267
Maffei L, Morrone C, Pirchio M, Sandini G (1979) Responses of visual cortical cells to periodic and non periodic stimuli. J Physiol (Lond) 296: 27–47
Movshon JA, Thompson ID, Tolhurst DJ (1978) Receptive field organization of complex cells in the cat's striate cortex. J Physiol (Lond) 283: 79–99
Orban GA (1975) Movement-sensitive neurones in the peripheral projections of area 18 of the cat. Brain Res 85: 181–182
Pettigrew JD, Nikara T, Bishop PO (1968) Responses to moving slits by single units in cat striate cortex. Exp Brain Res 6: 373–390
Robson JC (1975) Receptive fields neural representation of the spatial and intensive attributes of the visual image. In: Carterette E, Friedman MP (eds) Handbook of perception, vol V. pp 81–116
Sillito, AM (1975) The contribution of inhibitory mechanisms to the receptive field properties of neurones in the striate cortex of the cat. J Physiol (Lond) 250: 305–329
Sillito AM, Kemp A, Milson JA, Berardi N (1980) A reevaluation of the mechanisms underlying simple cefl orientation selectivity. Brain Res 194: 517–520
Singer W, Tretter F, Cynader M (1975) Organization of cat striate cortex. A correlation of receptive field properties with afferent and efferent connections. J Neurophysiol 38: 1080–1098
Tsumoto T, Eckart W, Creutzfeldt OD (1979) Modification of orientation sensitivity of cat visual cortex neurons by removal of GABA-mediated inhibition. Exp Brain Res 34: 351–363
Watkins DW, Berkley MA (1974) The orientation selectivity of single neurones in cat striate cortex. Exp Brain Res 19: 433–446
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by a European Exchange Fellowship from the Royal Society, London
Supported by a Fellowship from Scuola Normal Superiore, Pisa
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Burr, D., Morrone, C. & Maffei, L. Intra-cortical inhibition prevents simple cells from responding to textured visual patterns. Exp Brain Res 43, 455–458 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00238391
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00238391